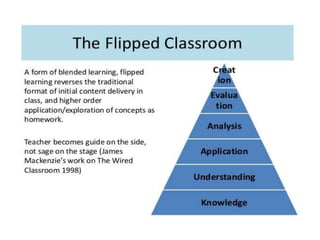
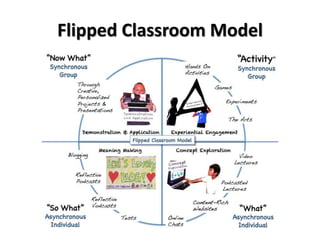
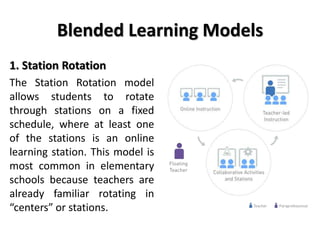
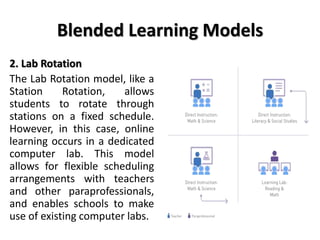
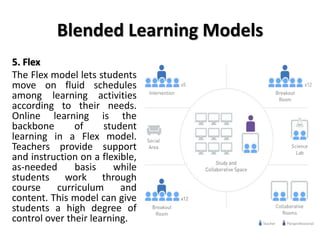
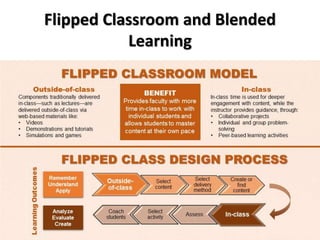
The document discusses flipped classroom and blended learning models. It defines flipped classroom as transferring work outside of class like watching lectures, and using class time for hands-on activities and practice. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, where students may learn content both online and in class. The document describes six blended learning models: Station Rotation, Lab Rotation, Individual Rotation, Flipped Classroom, Flex, and A La Carte. These models vary in how students access online content and receive support from teachers.