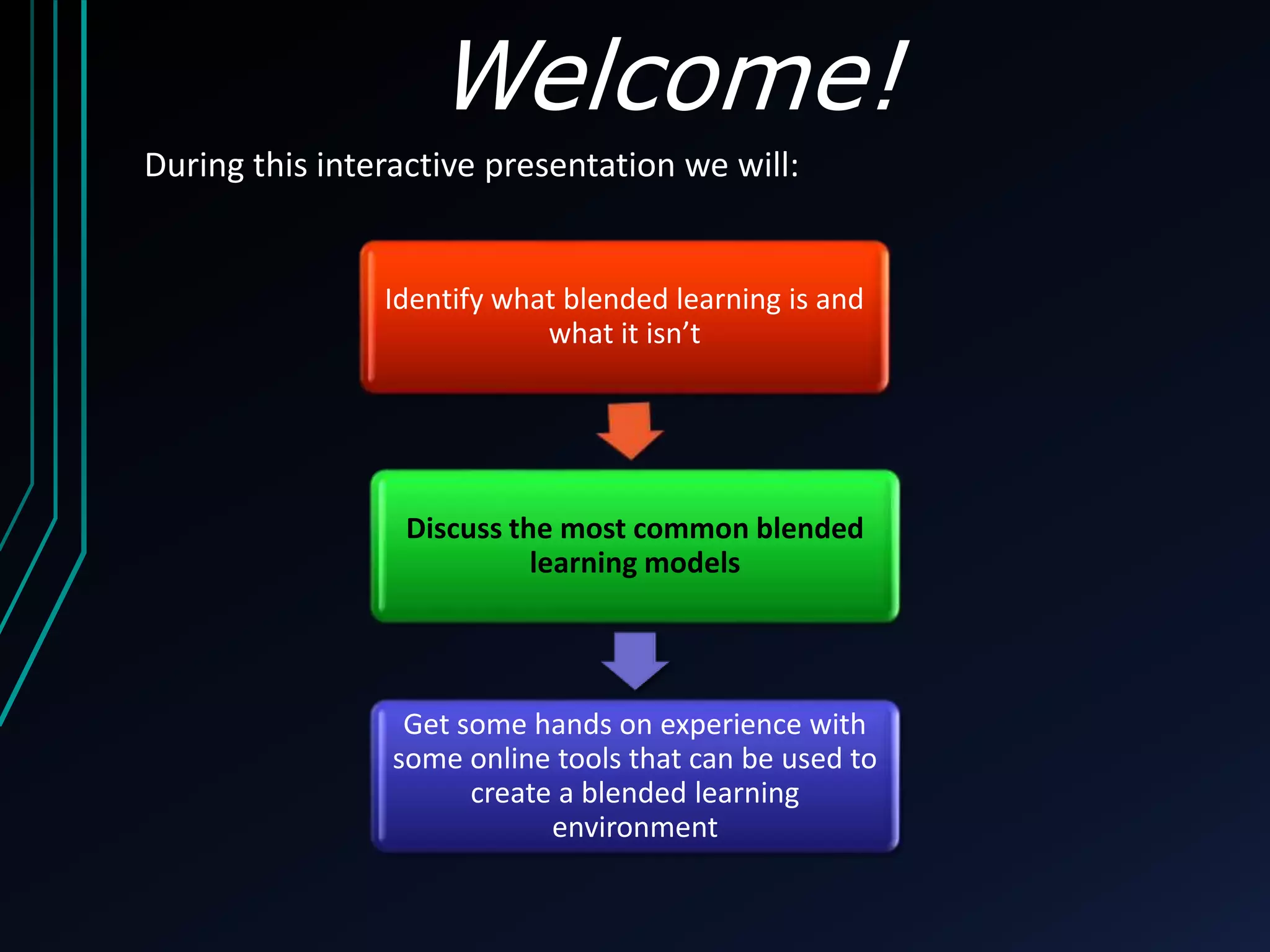
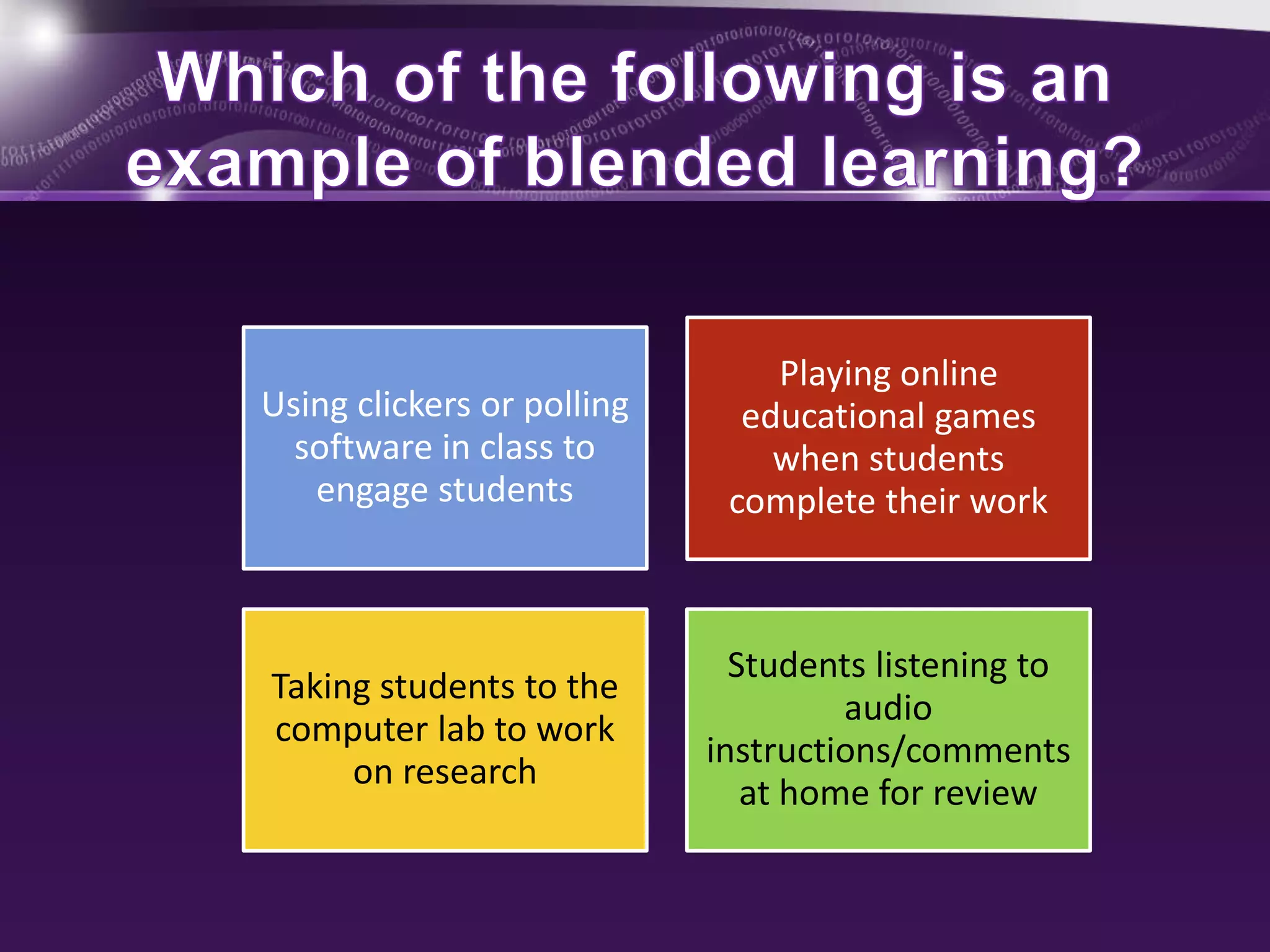
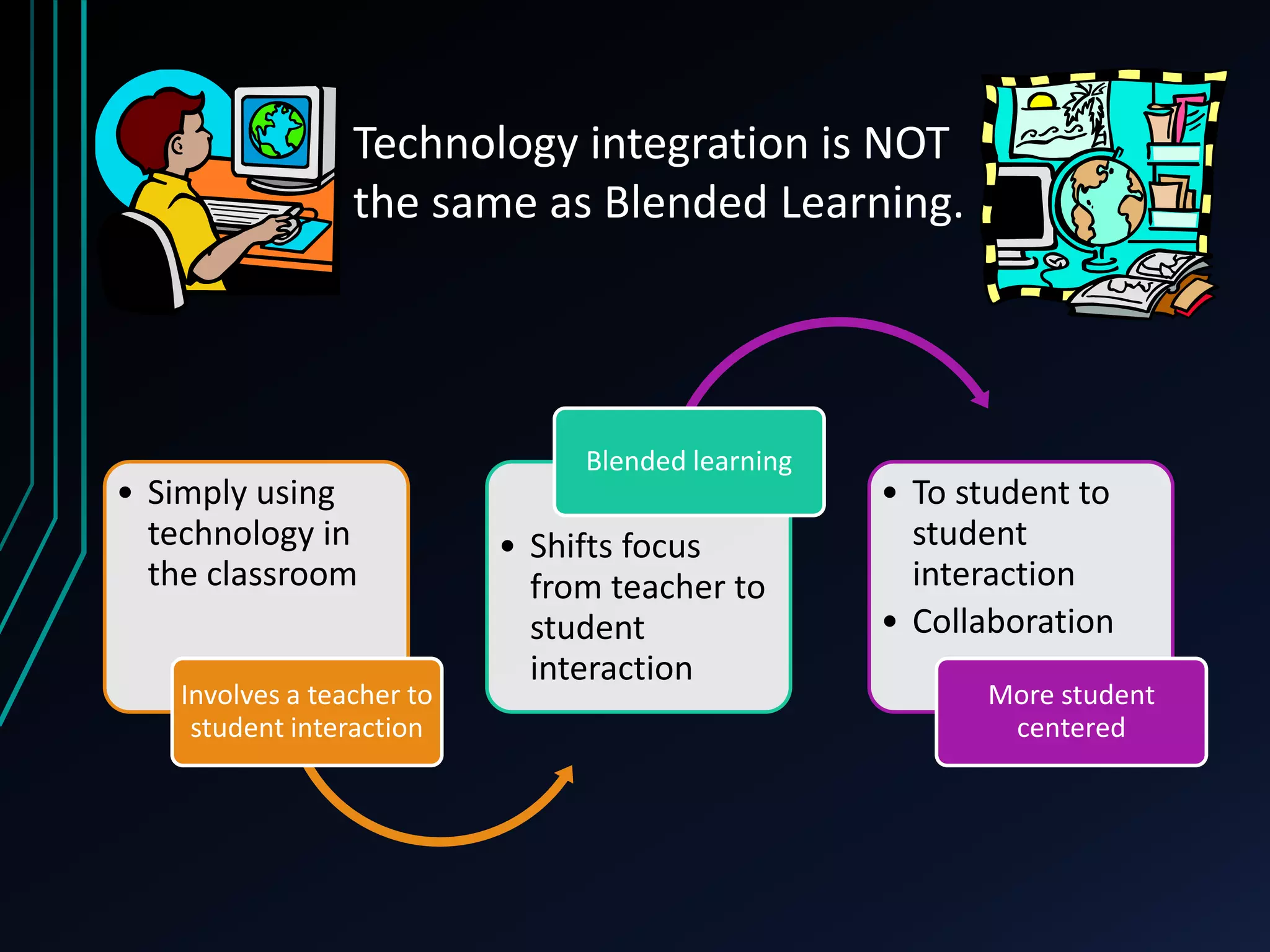
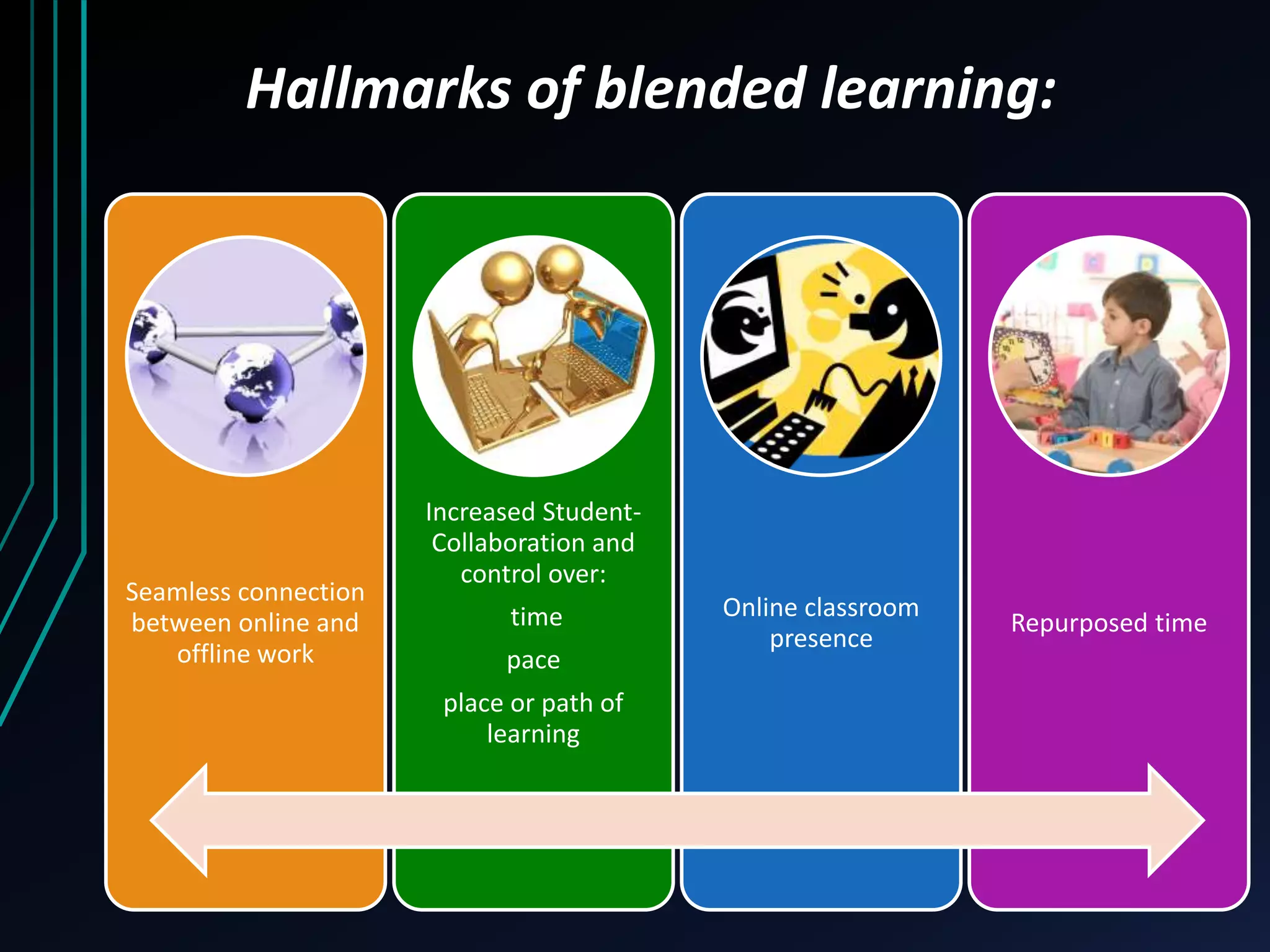
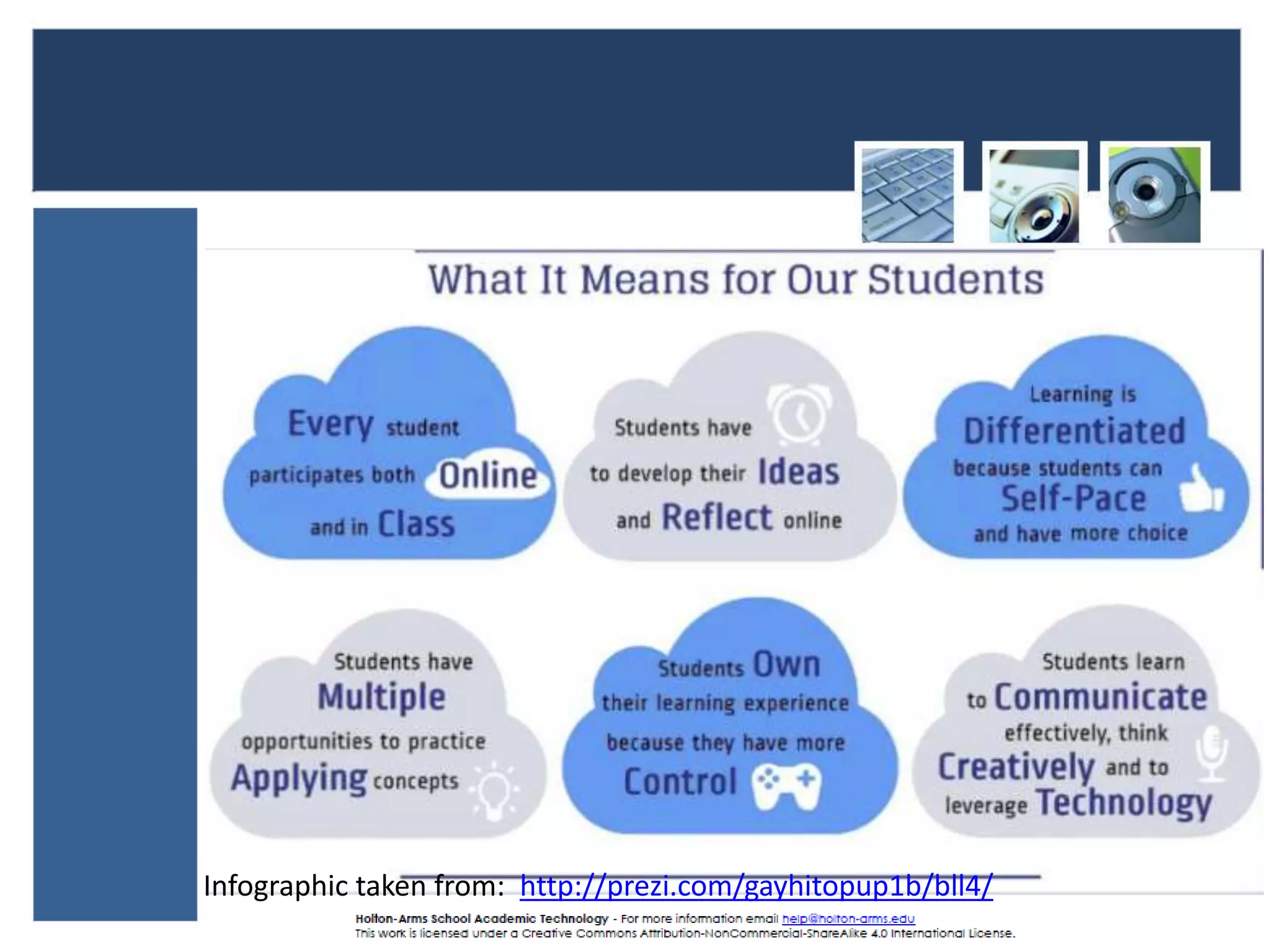
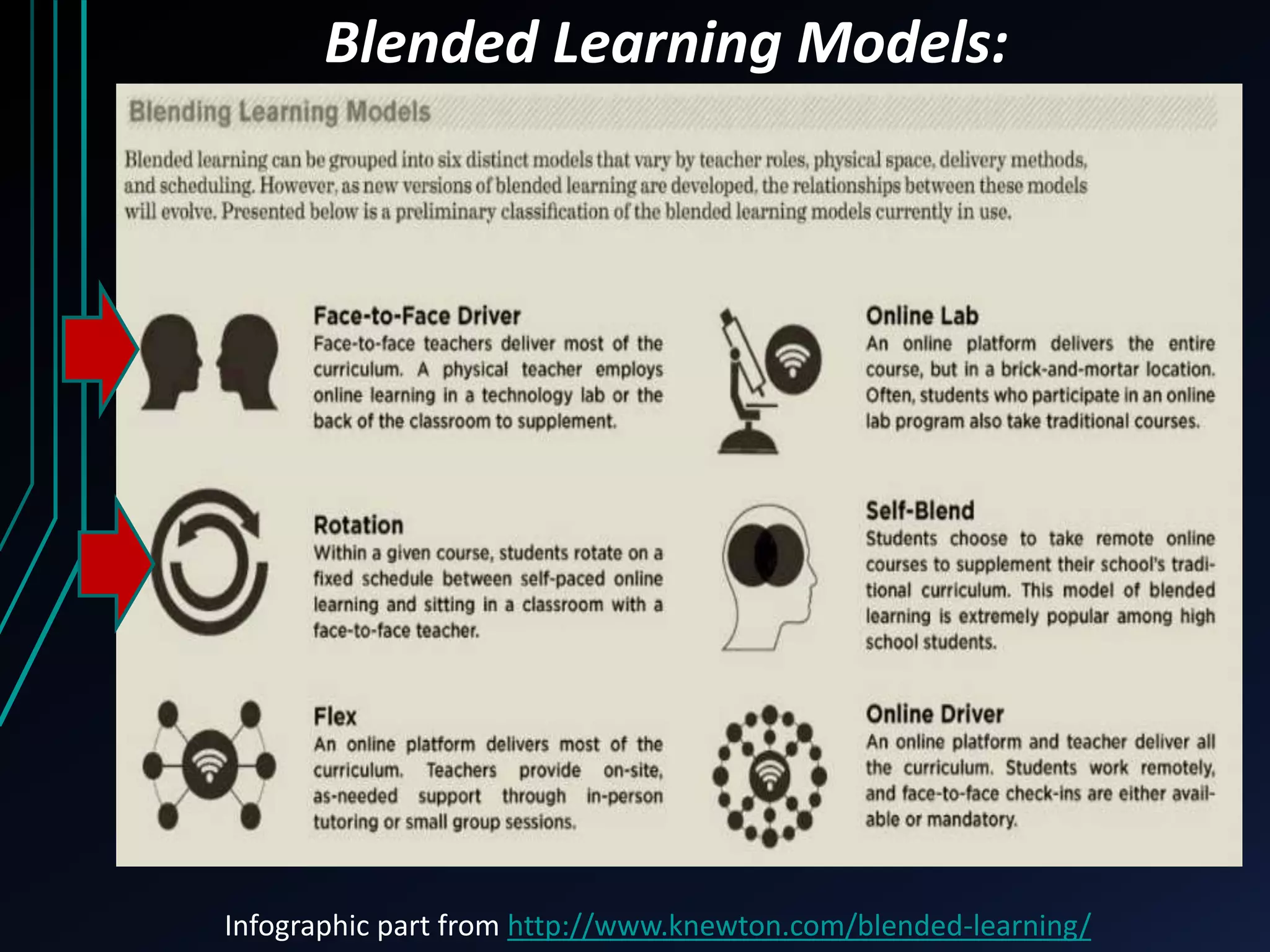
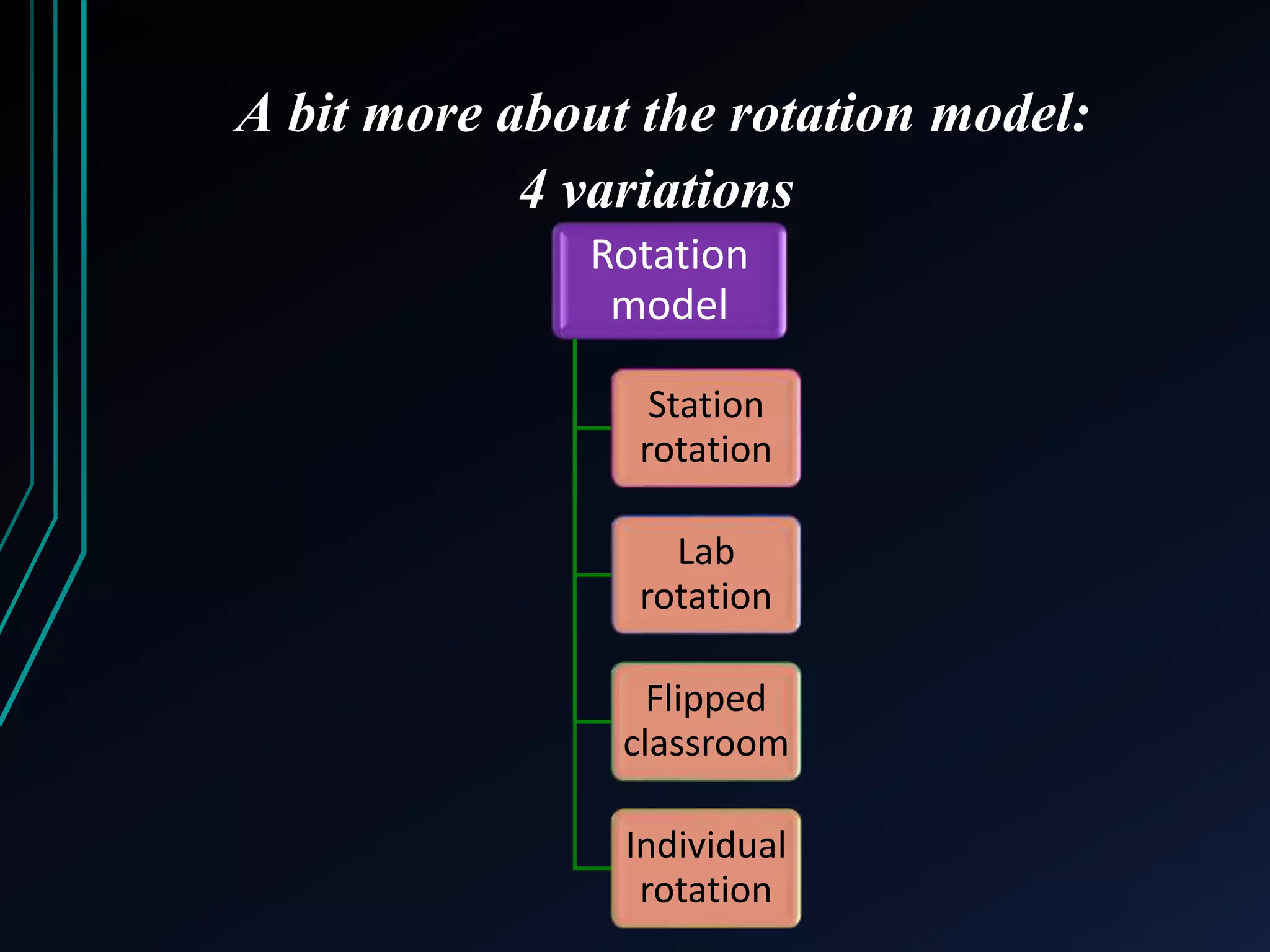
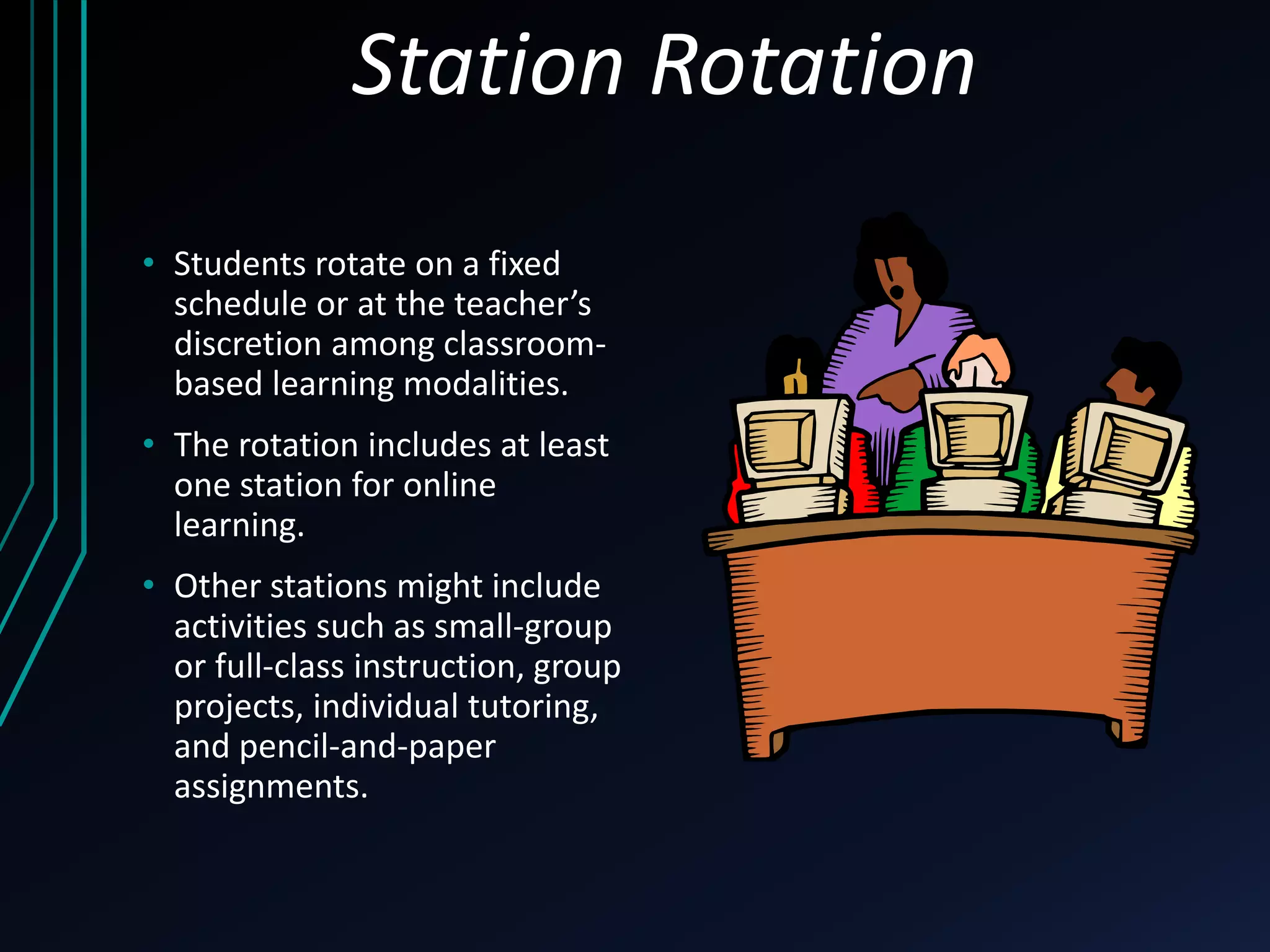
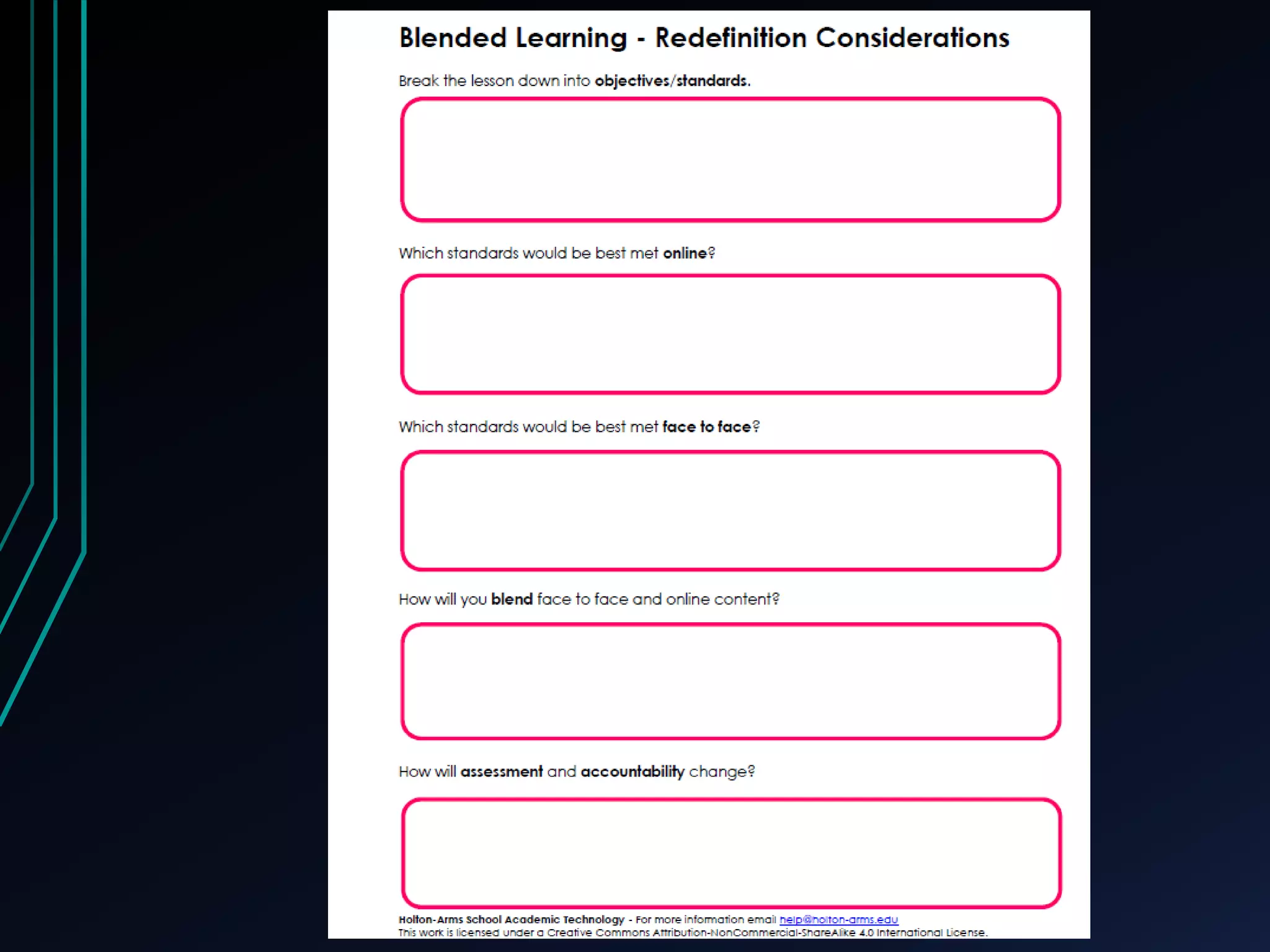
This document discusses blended learning models, strategies, and tools for lower school education. It defines blended learning as combining online digital media and tools with traditional classroom methods, requiring some element of online student control over time, place, pace or path of learning. The document reviews several common blended learning models including station rotation, lab rotation, flipped classroom, and individual rotation models. It emphasizes selecting the right blend of tools to meet learning objectives rather than just using technology for its own sake.