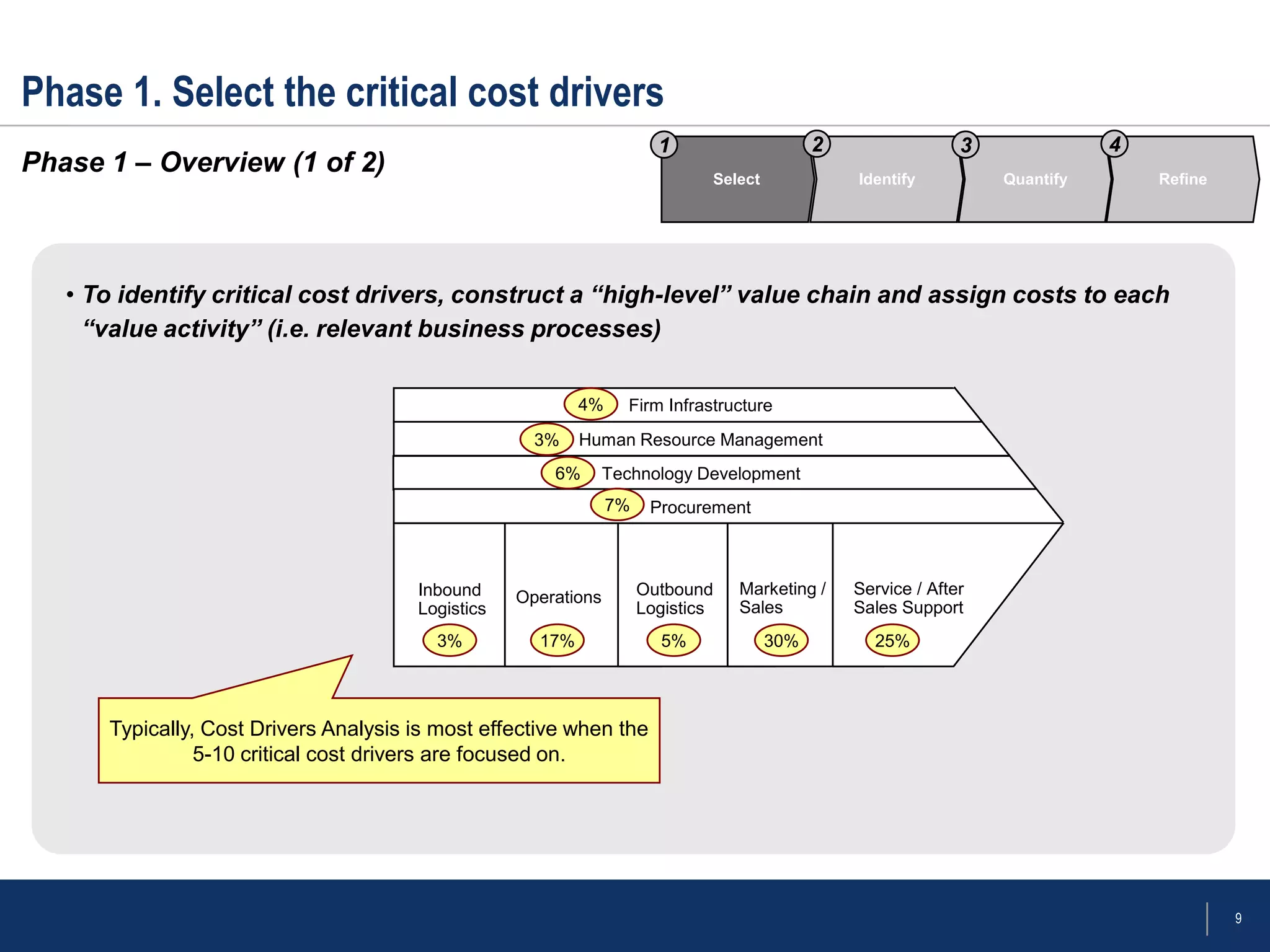
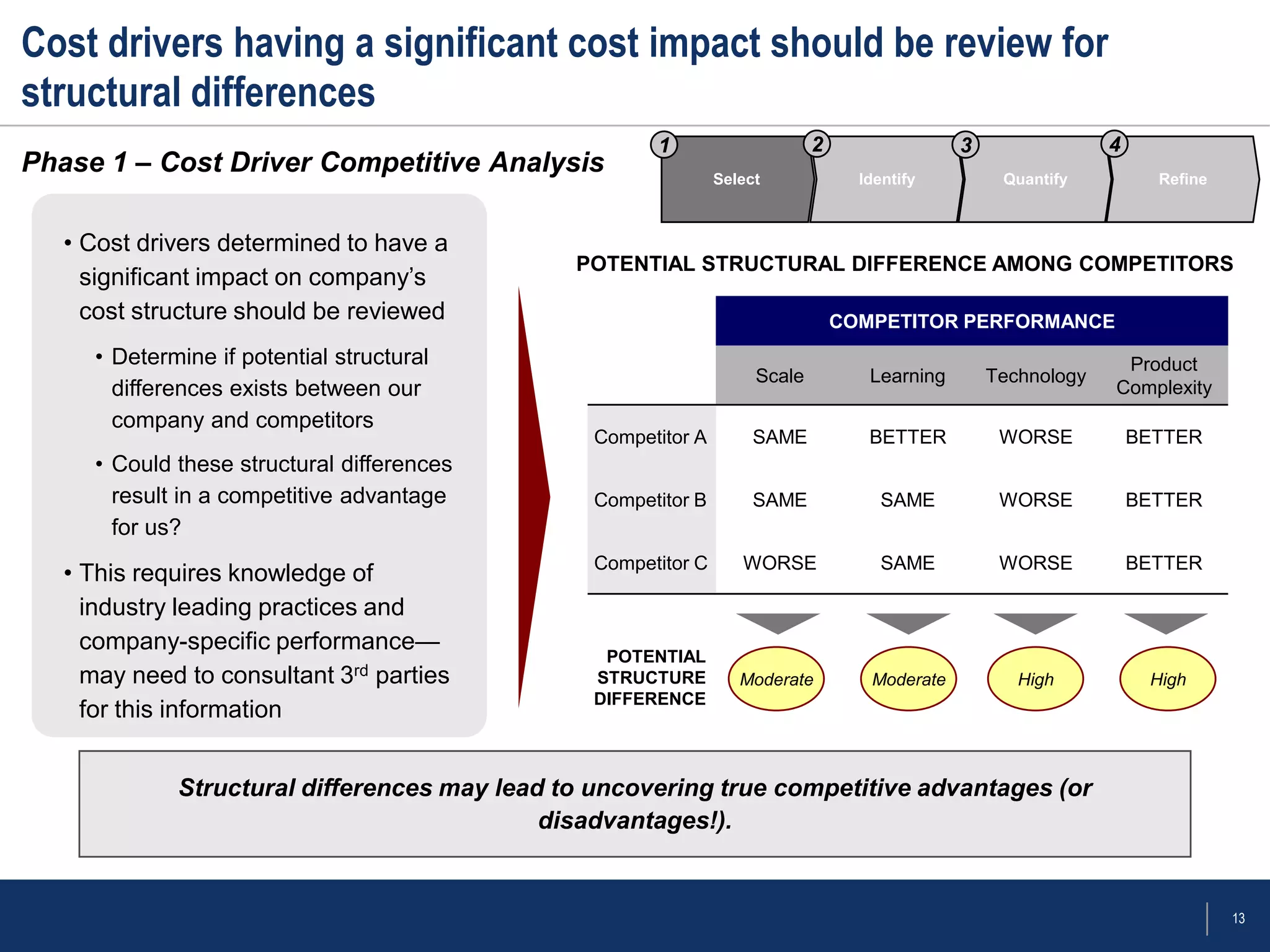
The document outlines a framework for conducting cost drivers analysis as part of competitive cost analysis, detailing techniques, phases of analysis, and benefits and limitations. It emphasizes identifying key cost drivers within a company's value chain, comparing them to competitors to uncover advantages, and quantifying these drivers for a clearer understanding of costs. The analysis involves selecting critical cost drivers, assessing structural differences among competitors, and validating hypotheses through detailed data examination.