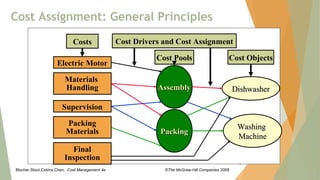
This document discusses cost drivers and their use in strategic cost management. It defines a cost driver as any factor that causes a change in total cost. Costs are grouped into cost pools and then assigned to cost objects using cost drivers. There are four types of cost drivers: volume-based, activity-based, structural, and executional. Volume-based drivers look at aggregate costs, while activity-based drivers examine costs at a more detailed operational level. Structural drivers influence long-term strategic decisions, while executional drivers affect short-term operational decisions. Understanding a company's value chain, strategic positioning, and relevant cost drivers provides insights into cost behavior.