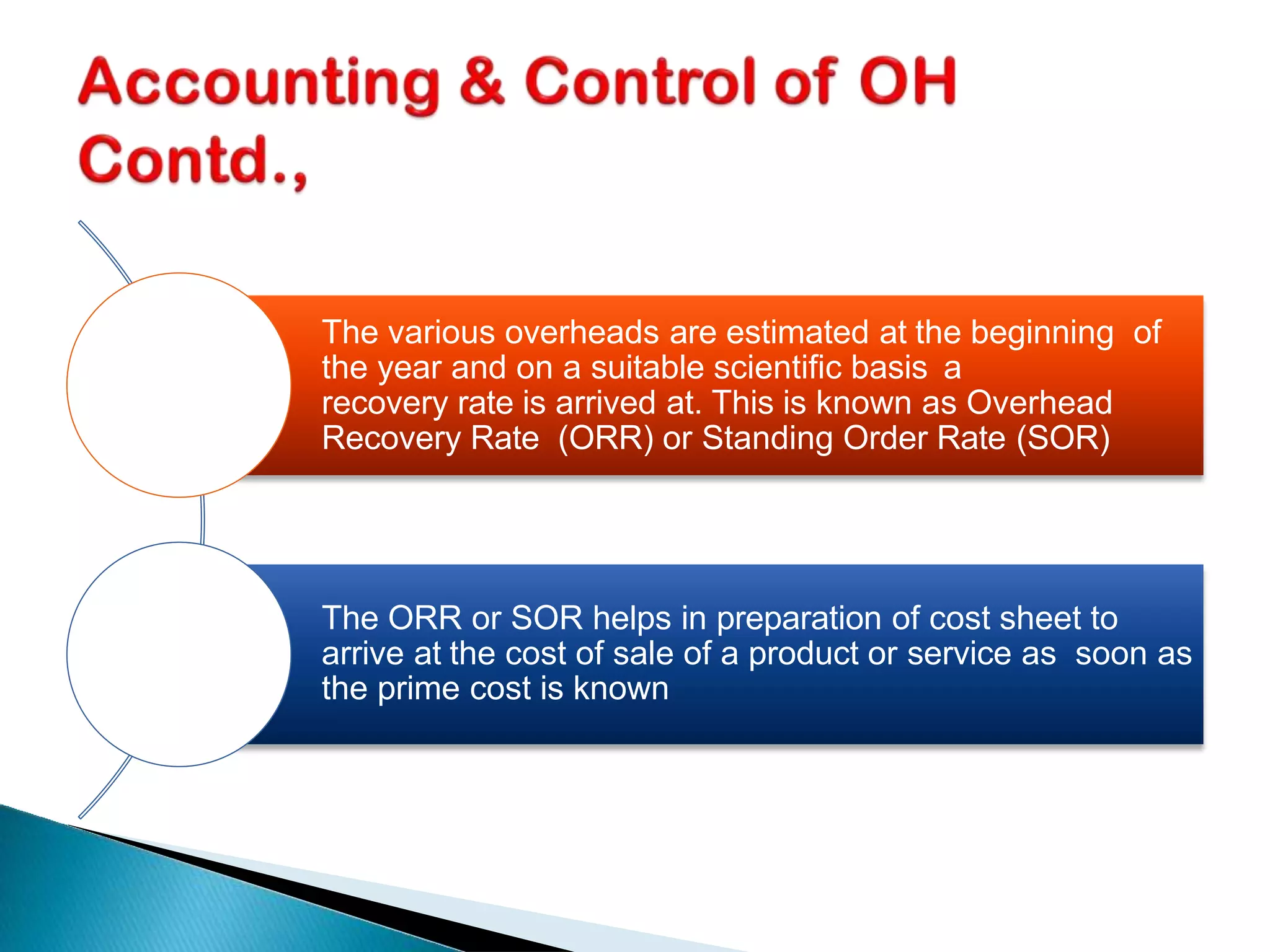
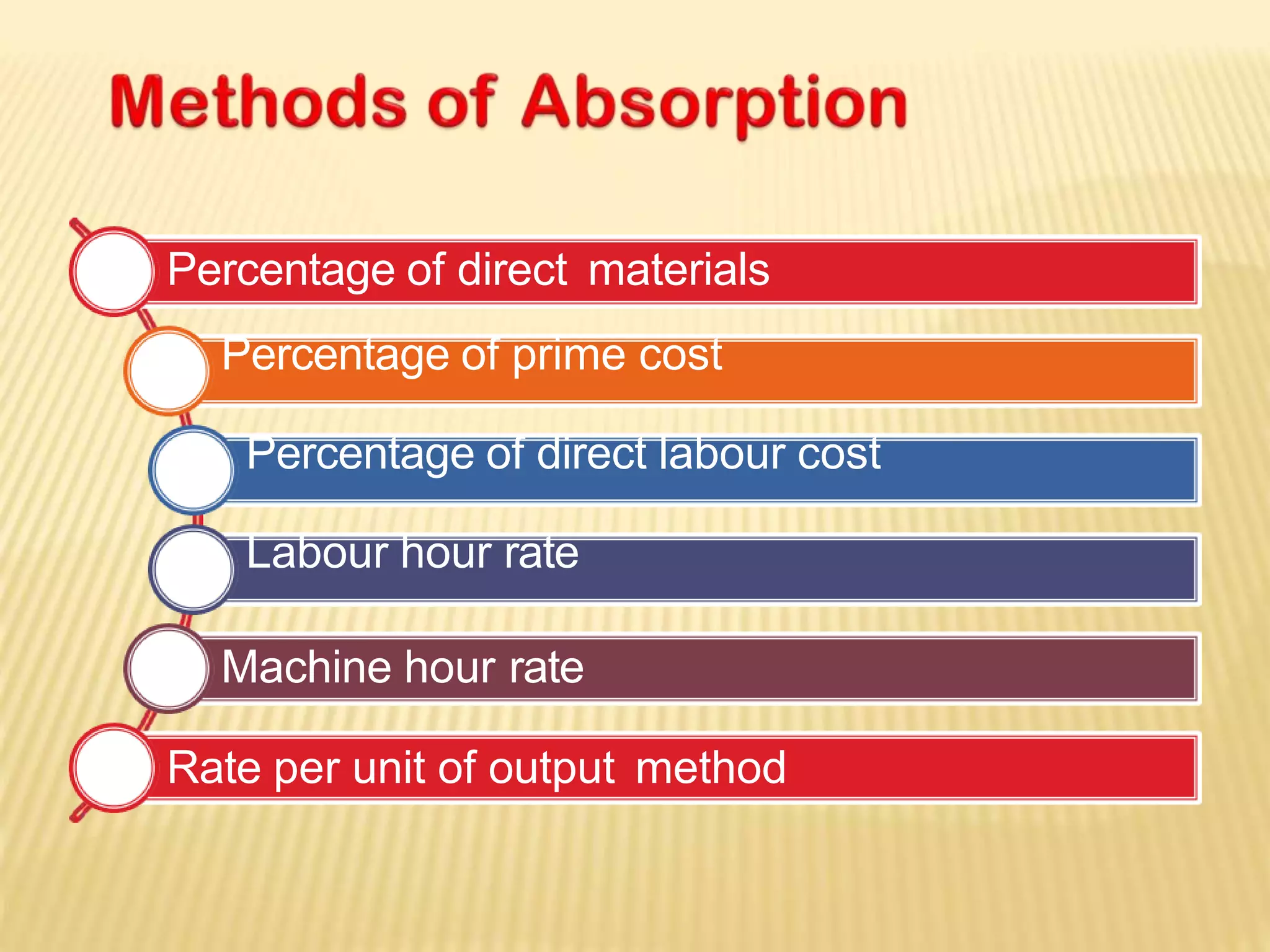
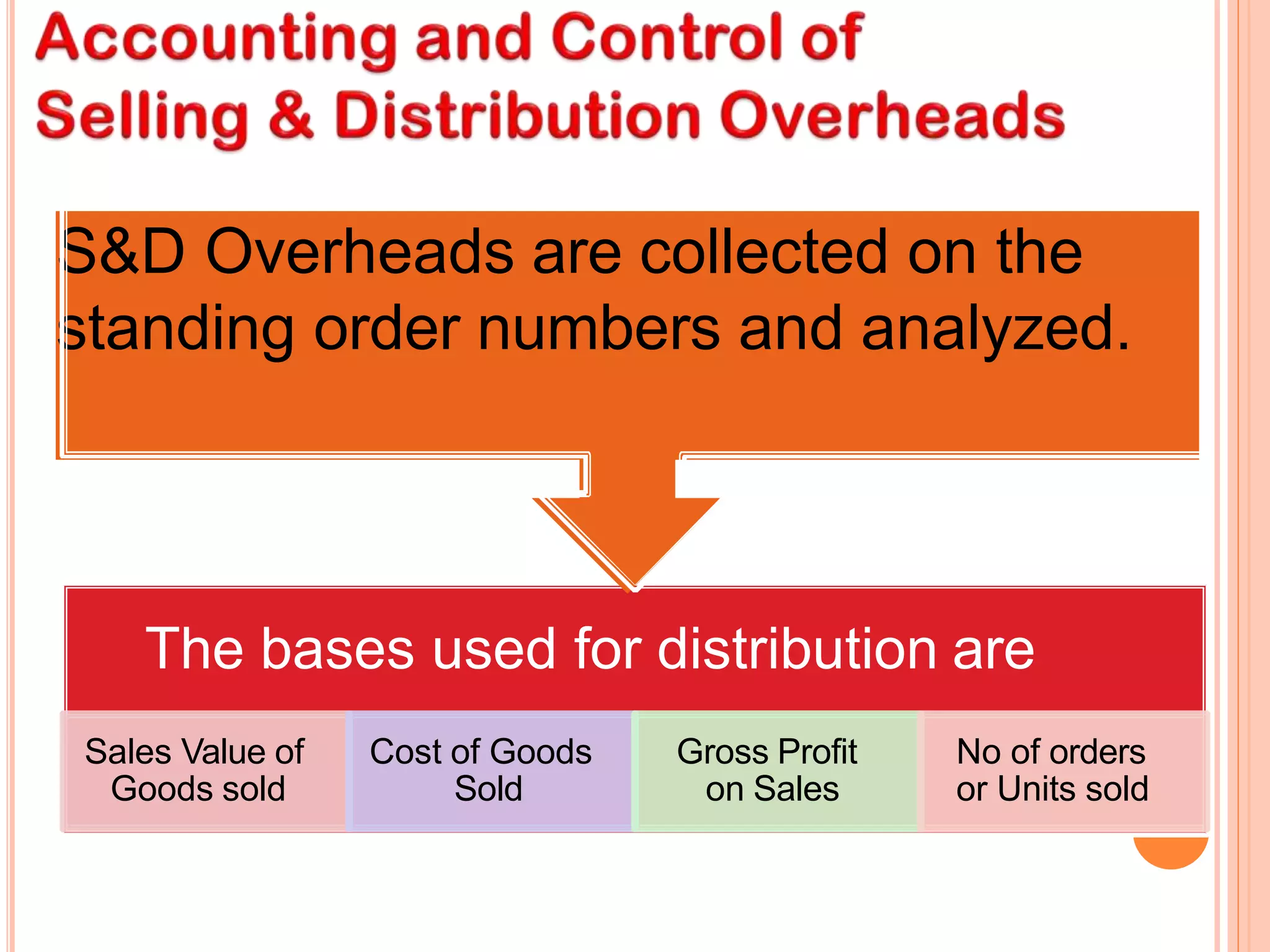
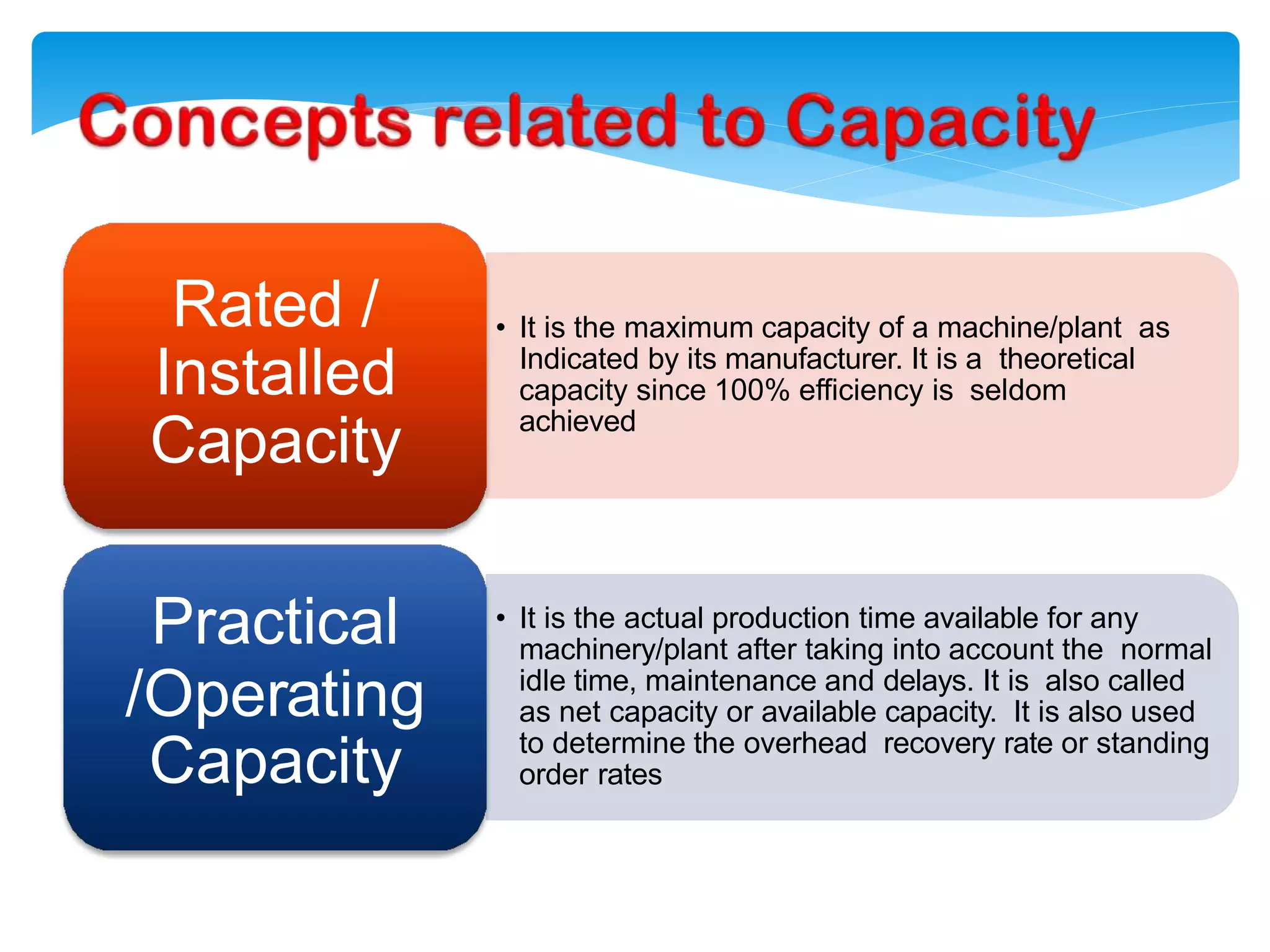
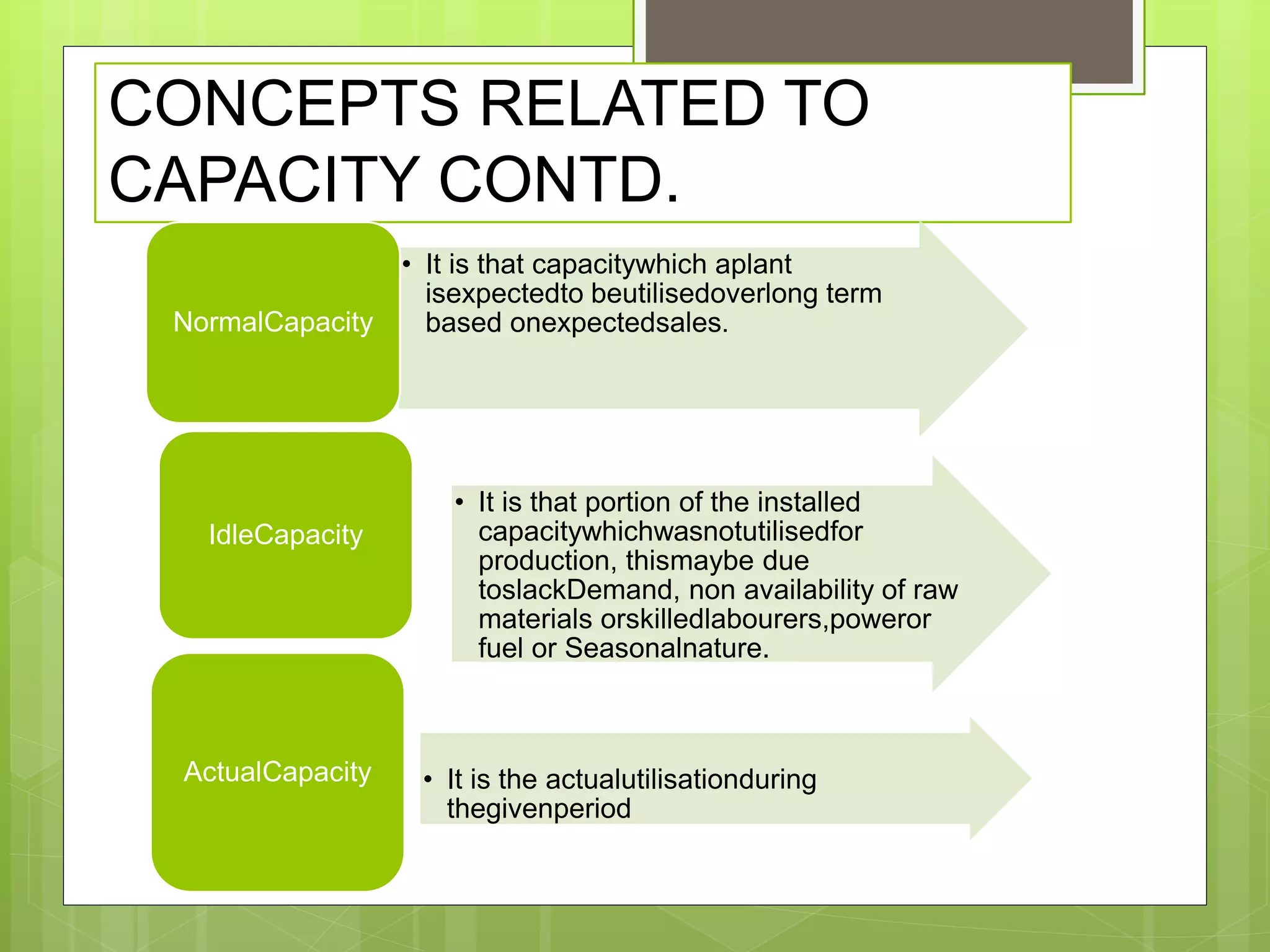
The document discusses the significance of overhead costs in a modern manufacturing unit, highlighting how these expenses, which cannot be directly traced to production, have grown with automation and now form a major part of production costs. It categorizes overheads into factory, administrative, sales, distribution, and research & development overheads, detailing their impact on cost accounting and management. The document also emphasizes methods for estimating, allocating, and controlling these overhead costs through various accounting principles and practices.