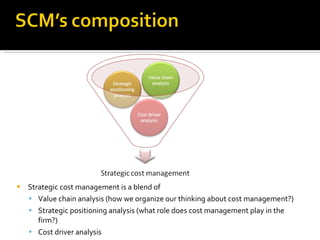
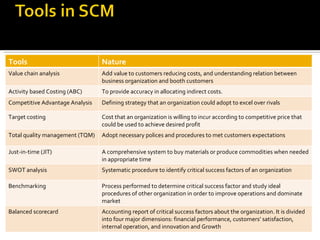
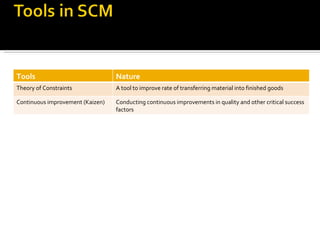
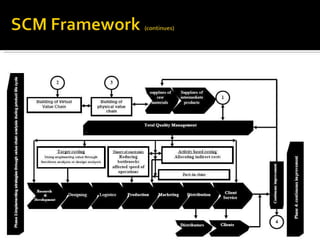
The document discusses strategic cost management (SCM) as an important tool for gaining competitive advantage. SCM analyzes costs in the broader context of a firm's overall value chain. It helps firms understand their cost structures to develop superior strategies. SCM uses tools like value chain analysis, activity-based costing, and analysis of cost drivers to examine how firms can configure activities to reduce costs or pursue different competitive strategies like cost leadership or differentiation.
![- By Sundarrajan M [email_address] Based on Shank and Govindarajan’s “Strategic Cost Management”: The New Tool for Competitive Advantage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategiccostmanagement-091225010512-phpapp01/85/Strategic-Cost-Management-1-320.jpg)
















![Send your feedbacks to: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategiccostmanagement-091225010512-phpapp01/85/Strategic-Cost-Management-22-320.jpg)