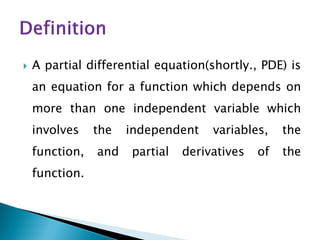
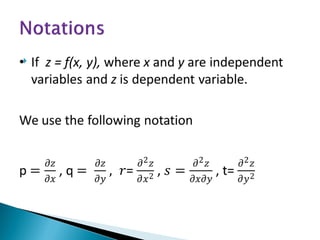
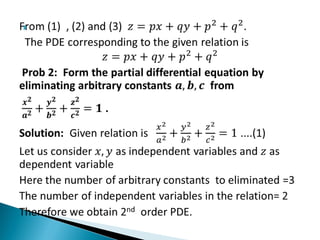
The document discusses first-order partial differential equations (PDEs), defining them as equations involving a function of multiple independent variables and their partial derivatives. It explains the concepts of order and degree of a PDE, as well as the conditions for forming a PDE through the elimination of arbitrary constants or functions. General rules are provided regarding the relationship between the number of arbitrary constants and the independent variables in determining the order of the resulting PDE.