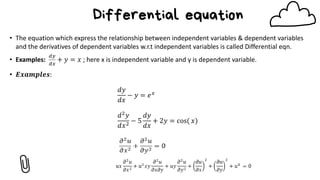
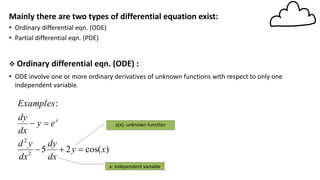
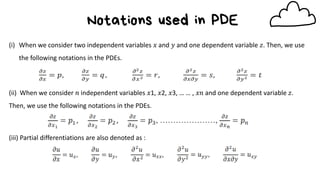
1) Partial differential equations (PDEs) contain partial derivatives of an unknown function of two or more independent variables.
2) The order of a PDE is defined as the order of the highest partial derivative. The degree is the highest order partial derivative after rationalization.
3) Notations used include subscripts for partial derivatives with respect to independent variables like ∂z/∂x.
4) First order PDEs are classified as linear if linear in derivatives, semi-linear if linear in derivatives and coefficients depend only on variables, and quasi-linear or nonlinear if not linear in derivatives.