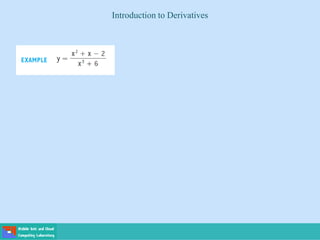
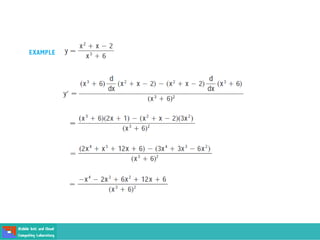
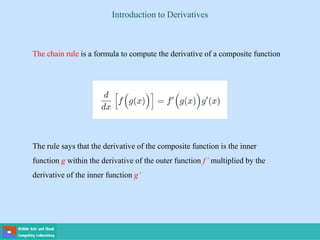
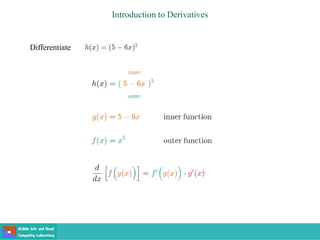
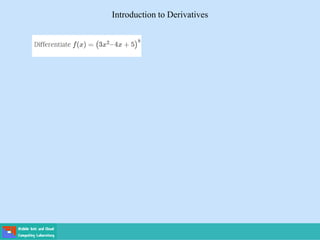
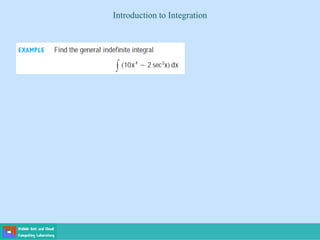
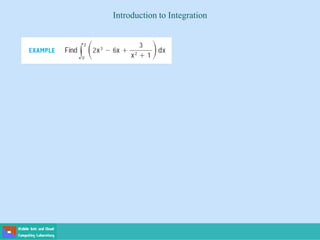
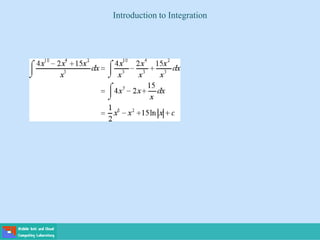
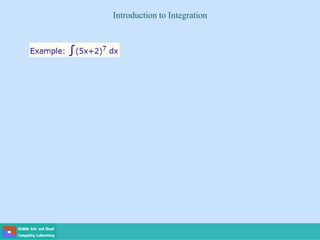
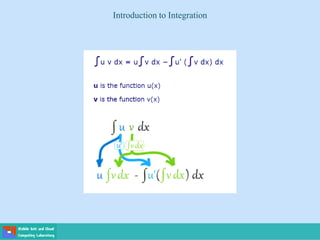
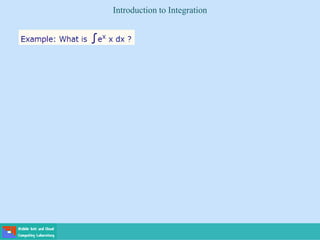
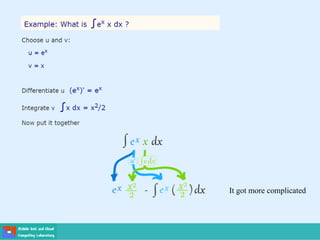
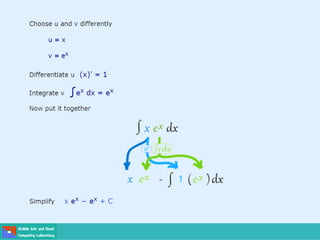
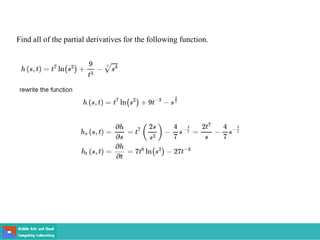
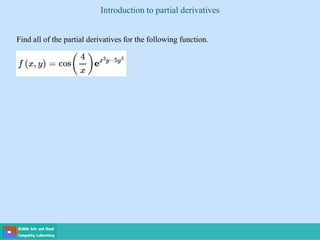
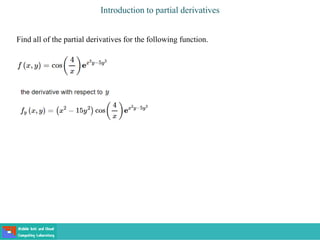
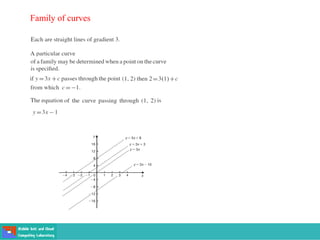
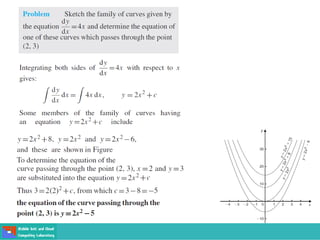
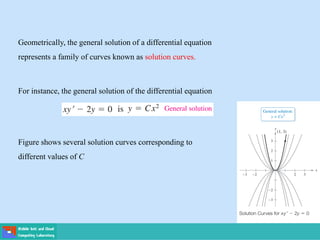
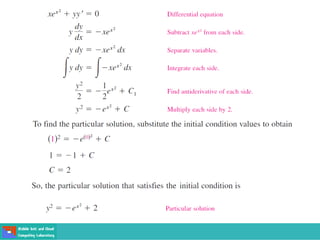
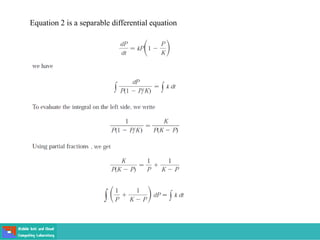
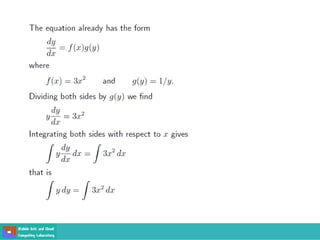
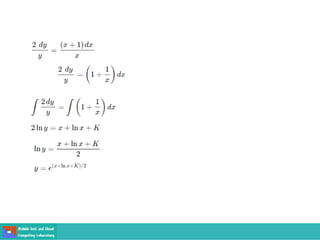
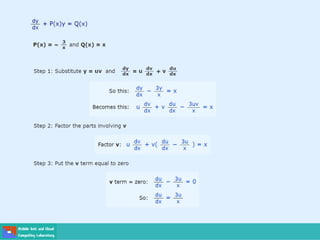
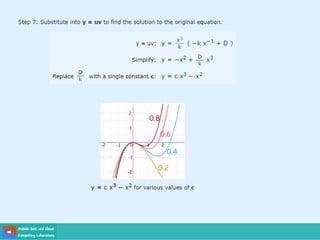
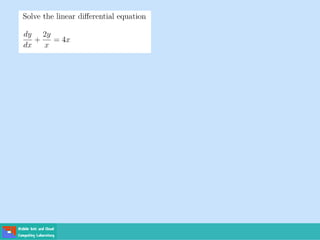
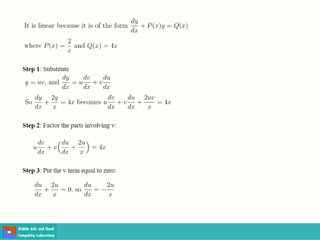
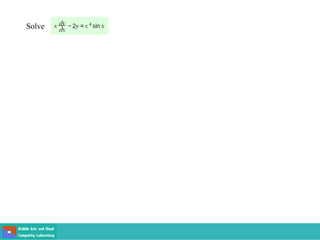
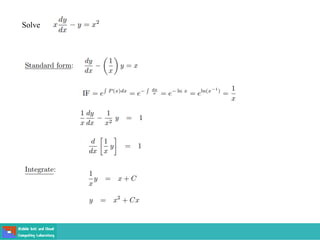
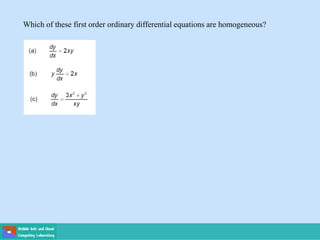
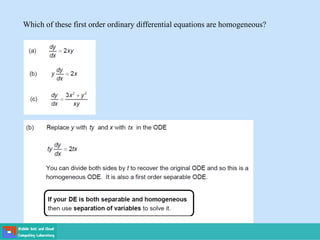
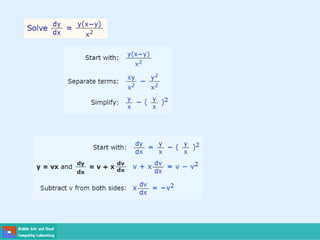
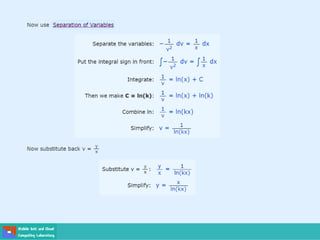
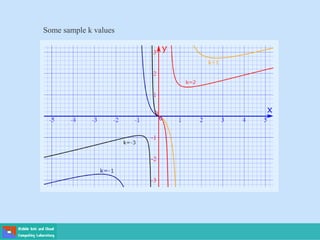
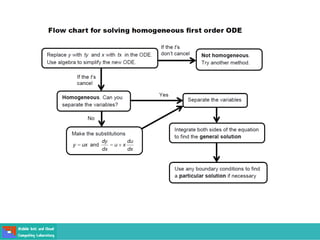
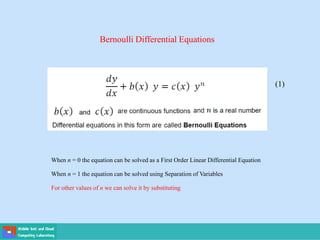
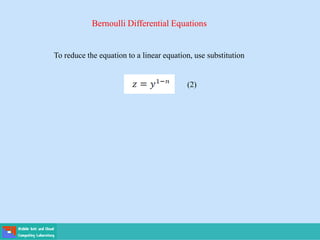
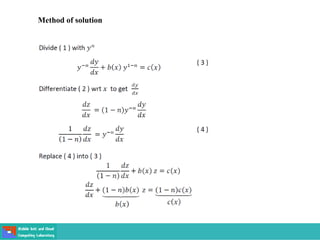
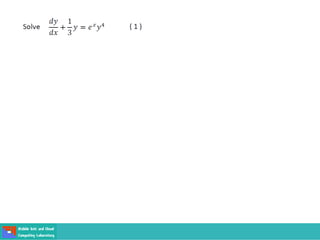
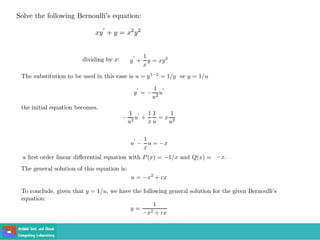
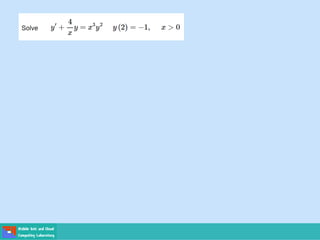
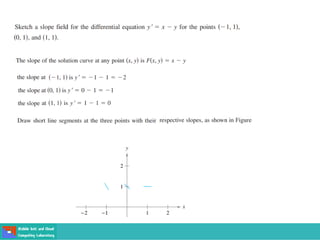
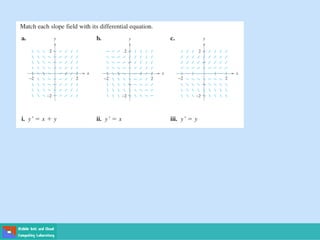
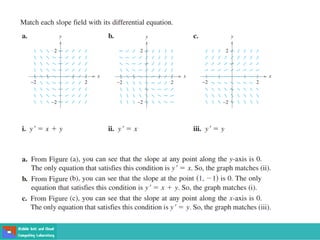
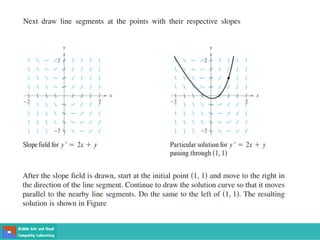
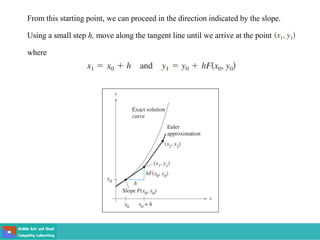
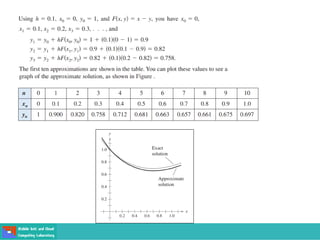
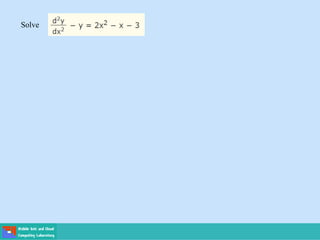
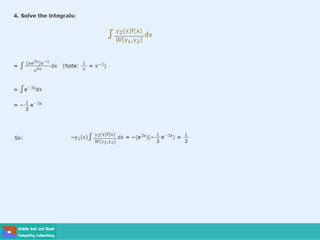
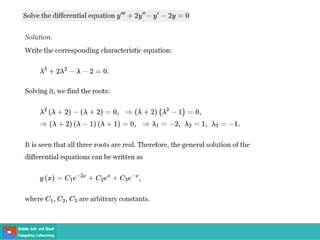
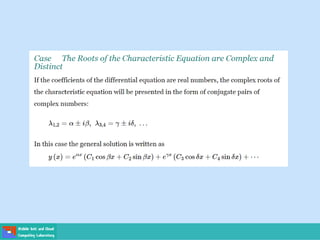
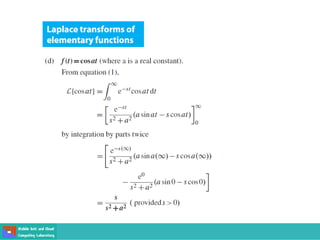
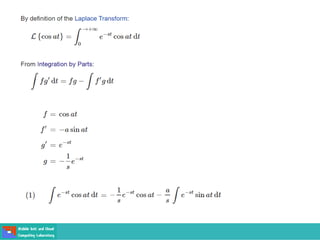
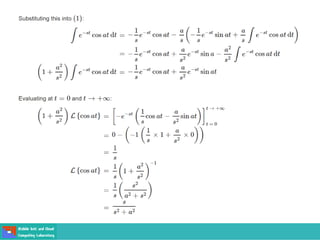
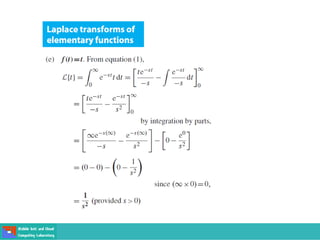
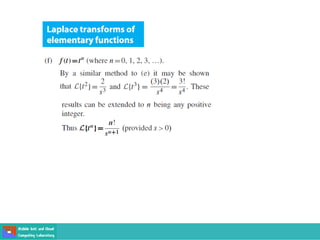
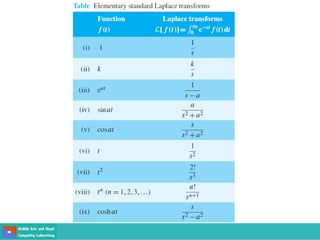
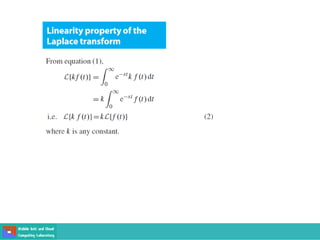
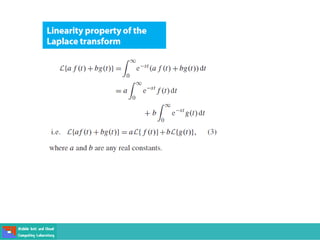
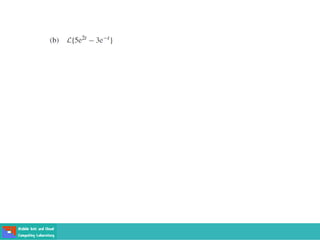
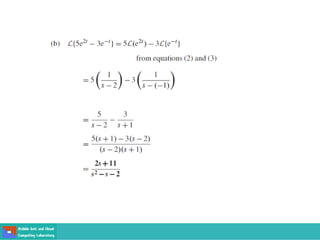
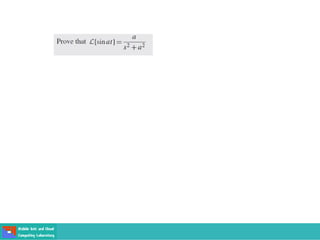
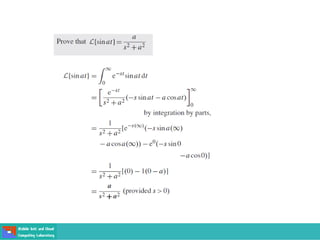
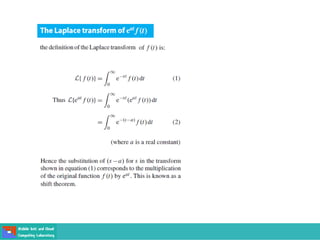
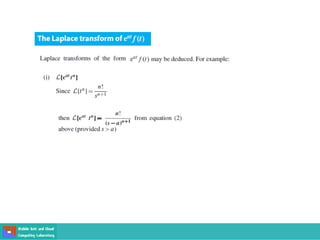
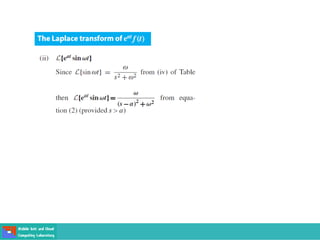
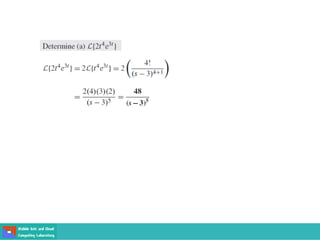
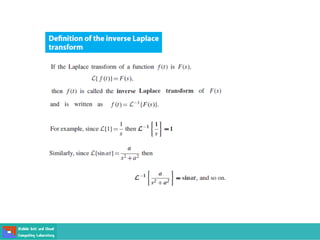
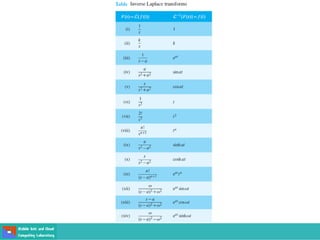
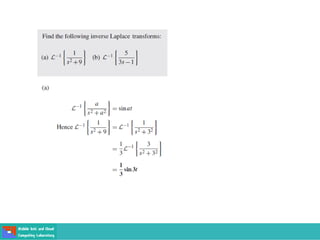
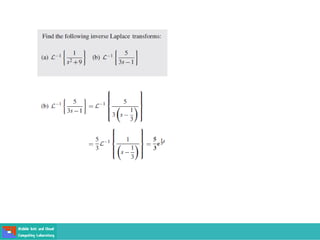
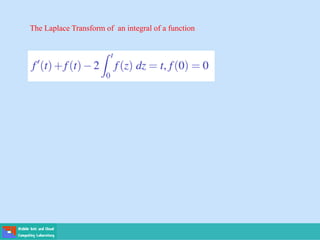
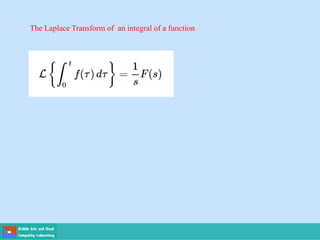
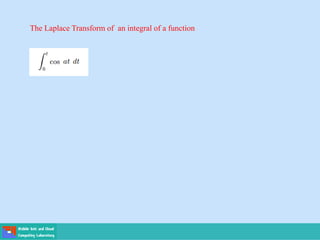
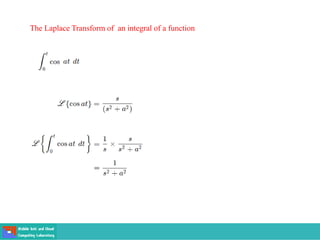
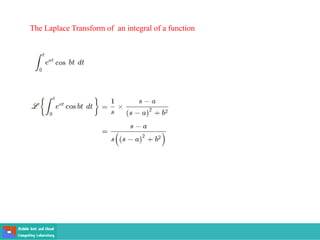
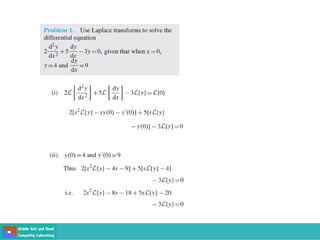
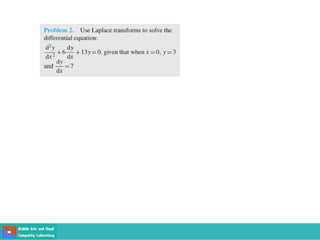
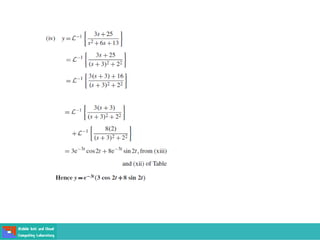
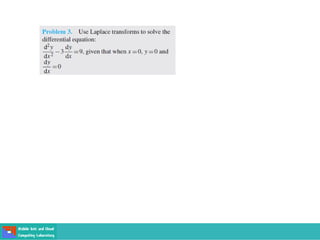
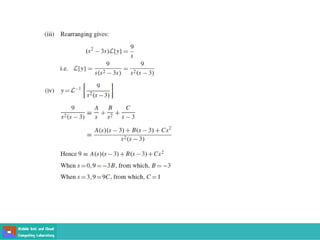
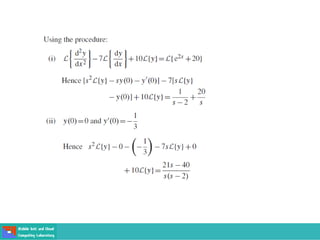
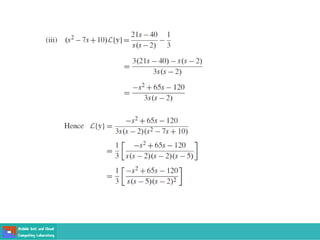
This document contains lecture slides on engineering mathematics from Sayed Chhattan Shah. It introduces differential equations and their applications. Some key points covered include:
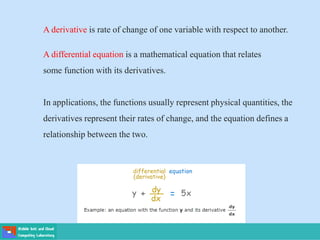
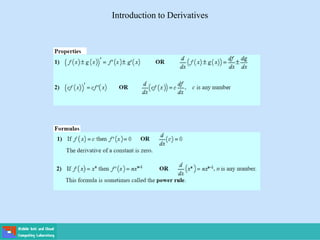
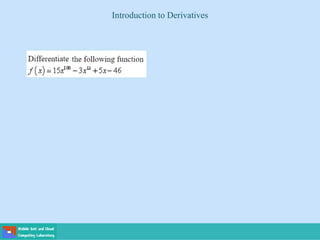
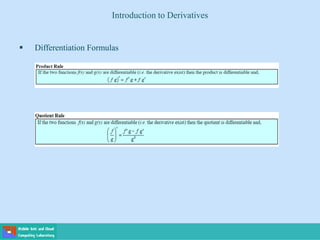
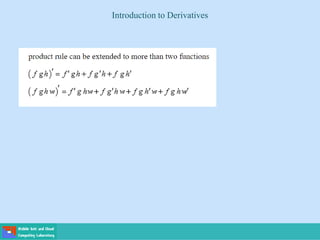
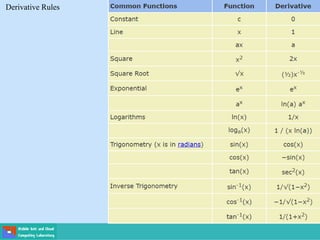
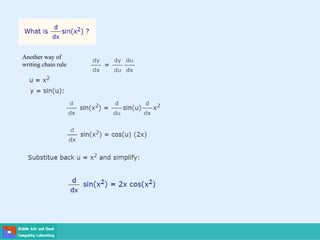
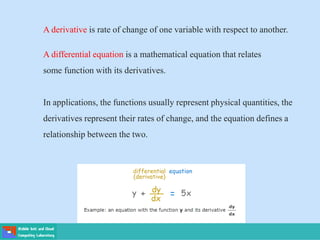
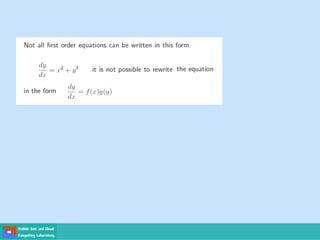
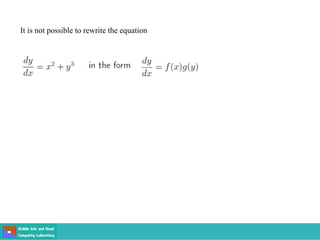
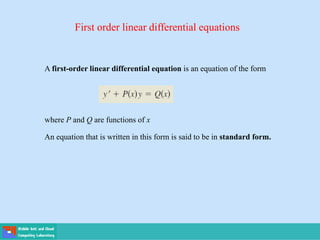
- A differential equation relates a function to its derivatives. The functions often represent physical quantities and the derivatives represent rates of change.
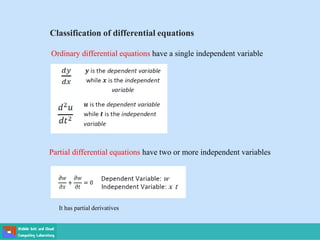
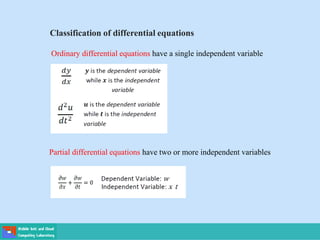
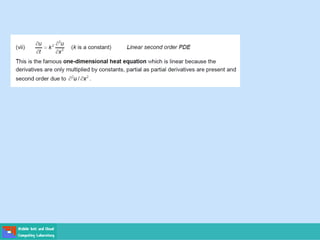
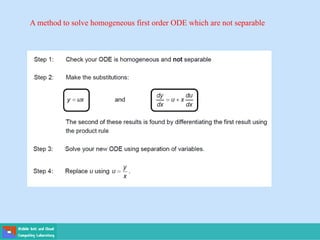
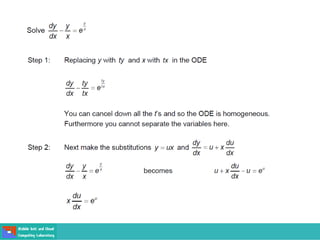
- Ordinary differential equations have one independent variable, while partial differential equations have two or more.
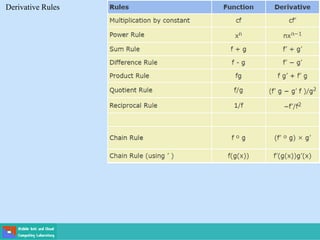
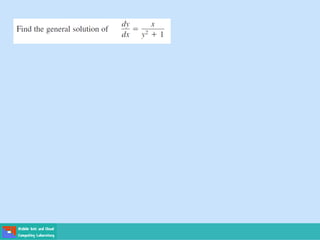
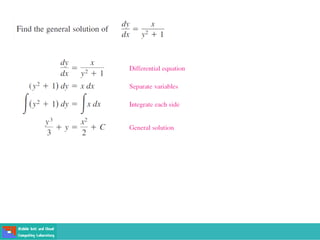
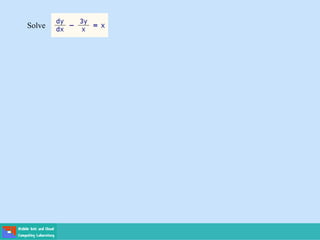
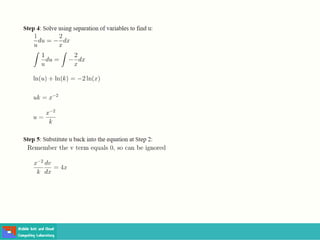
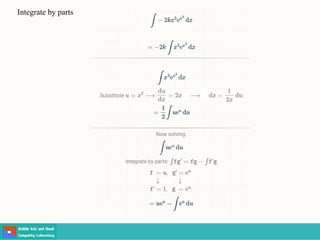
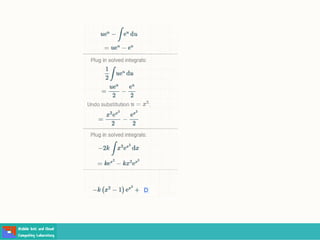
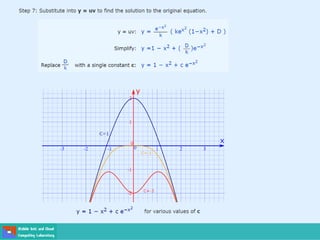
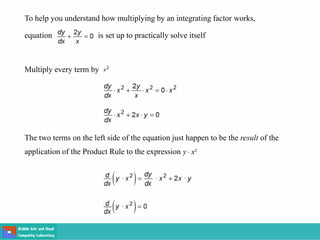
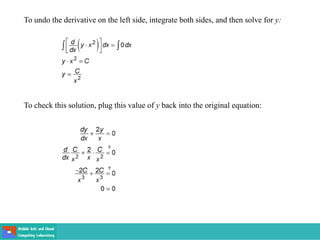
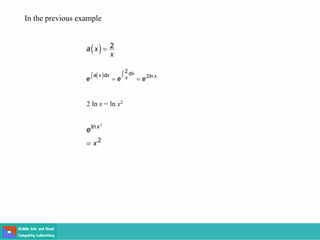
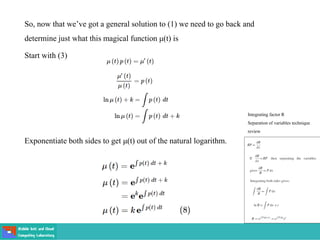
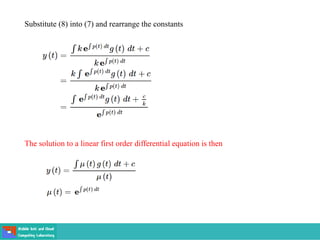
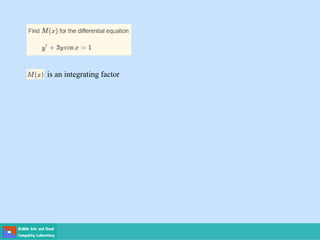
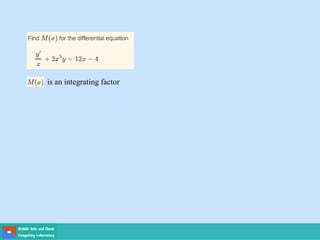
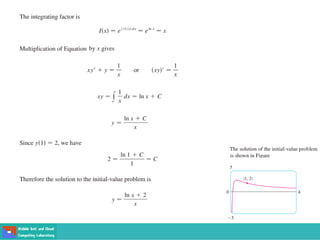
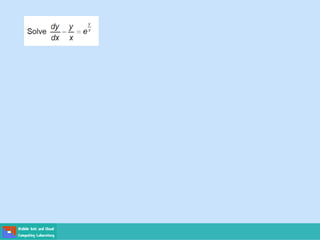
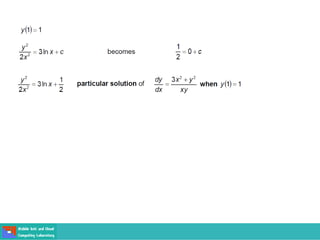
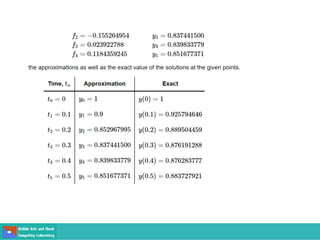
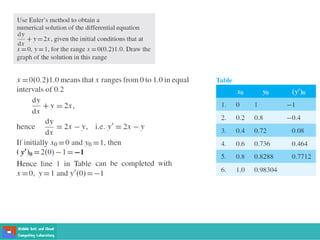
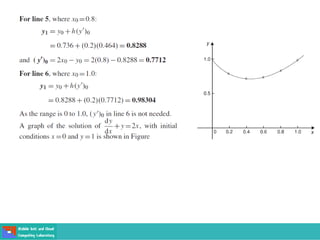
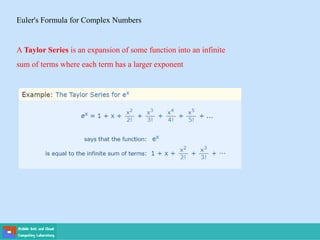
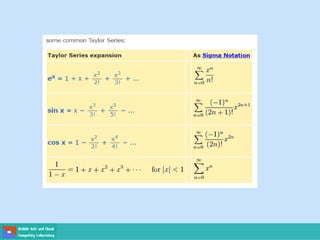
- Methods for solving differential equations include separation of variables, integrating factors, and numerical methods like Euler's method.
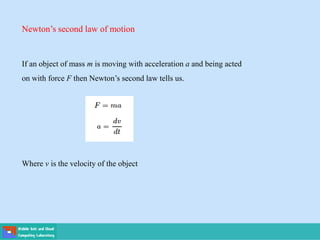
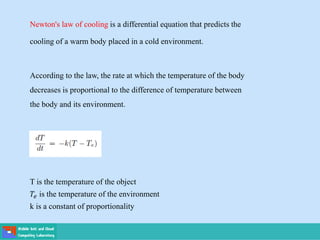
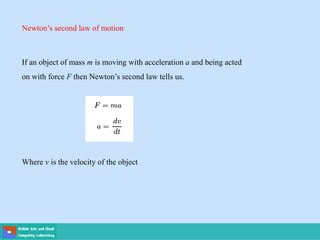
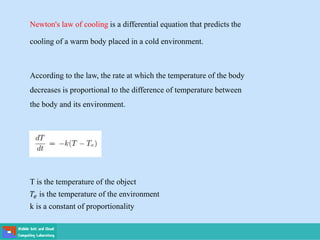
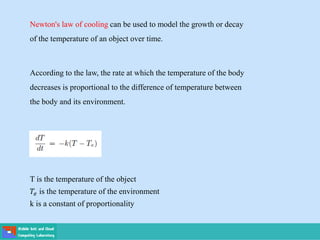
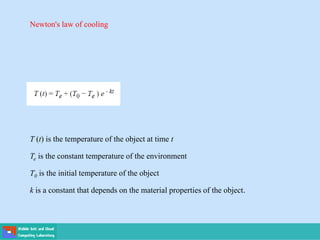
- Applications include Newton's laws of motion and cooling, and population growth models.
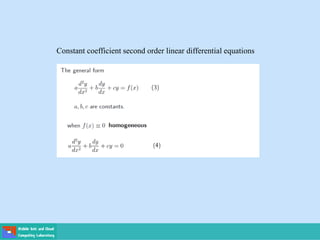
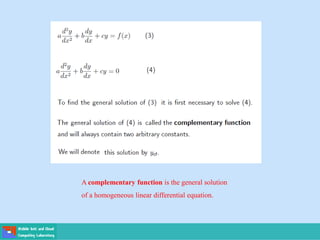
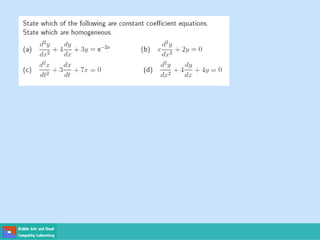
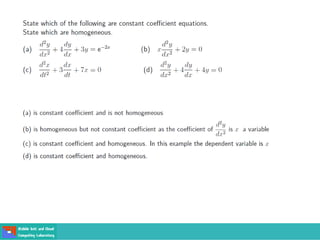
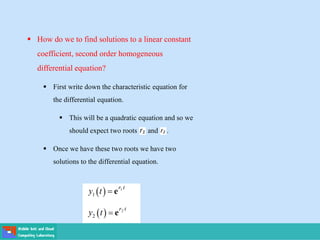
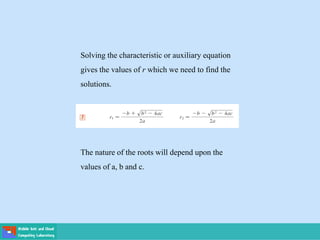
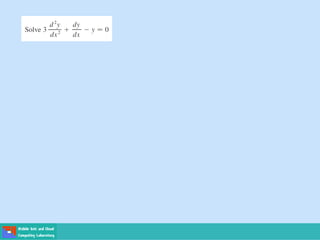
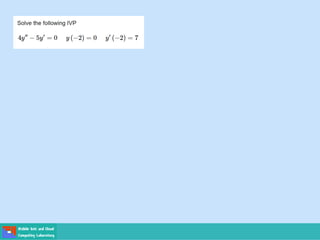
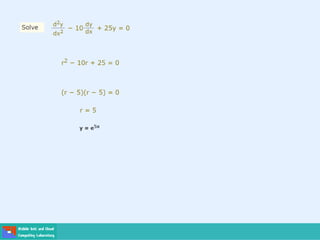
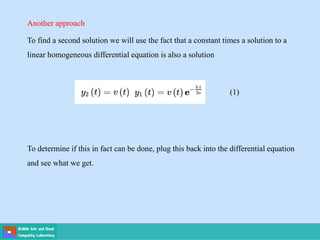
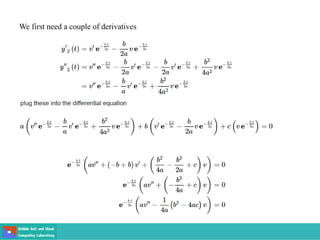
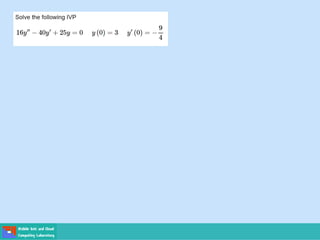
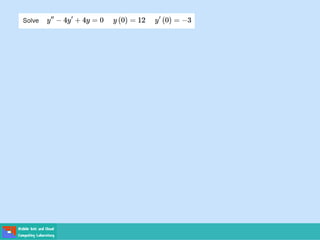
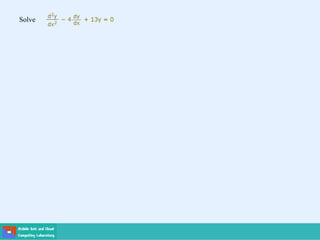
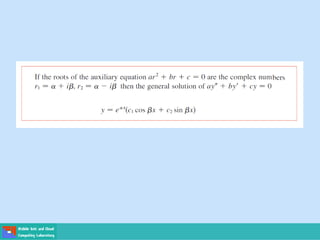
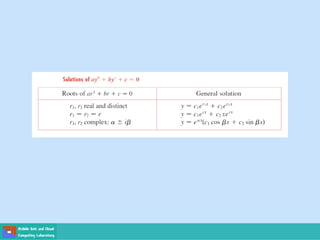
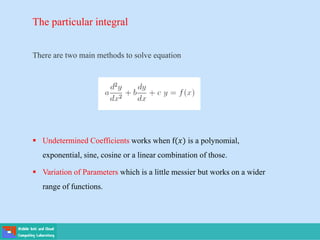
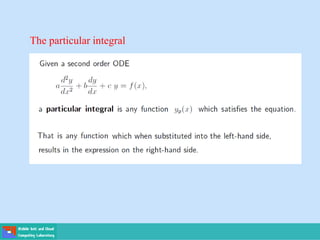
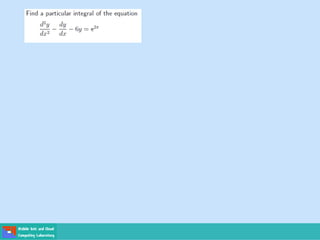
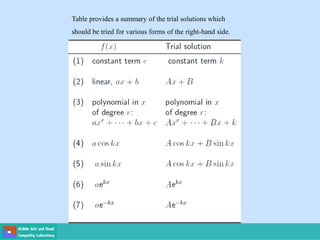
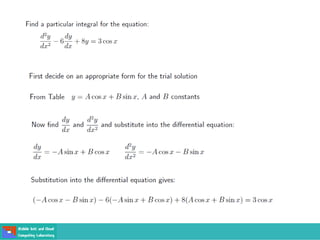
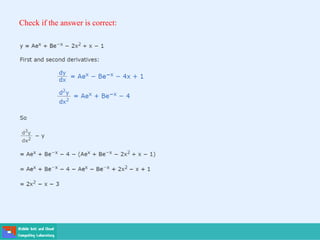
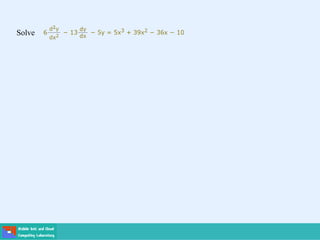
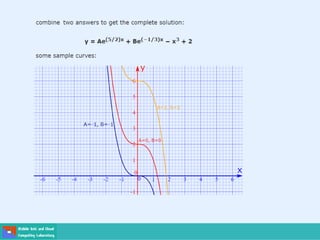
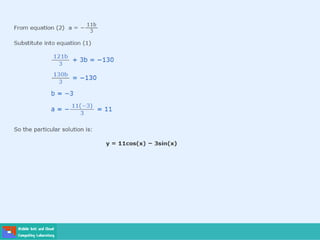
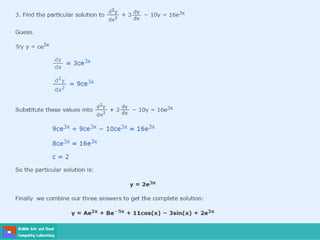
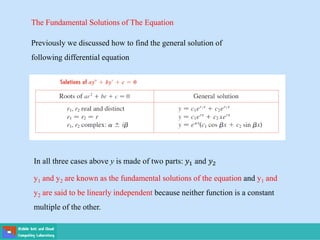
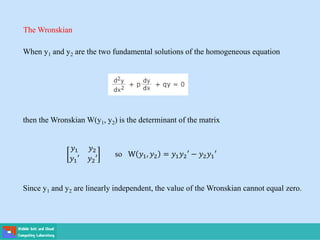
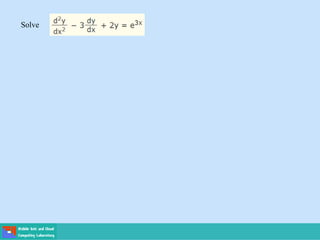
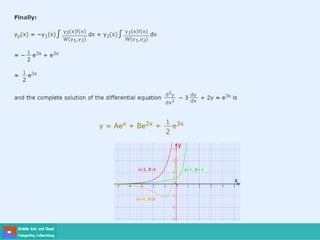
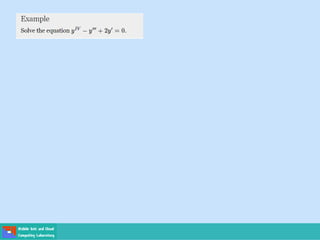
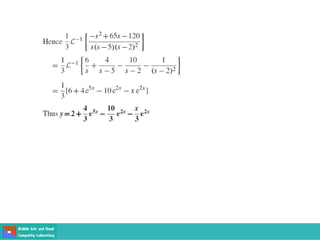
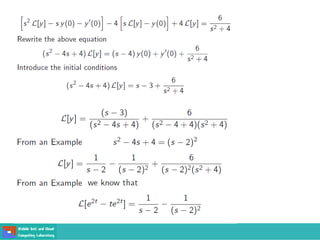
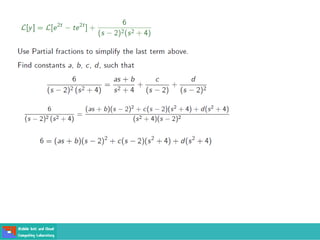
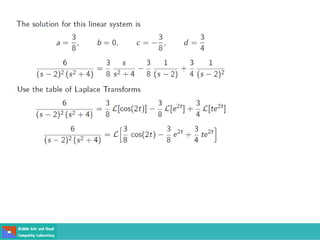
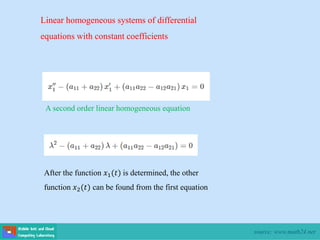
- Second order differential equations have solutions called complementary functions and particular integrals.