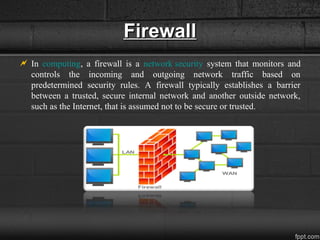
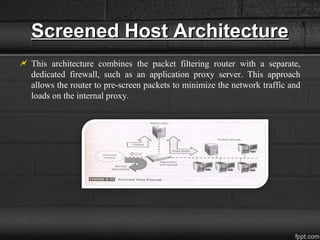
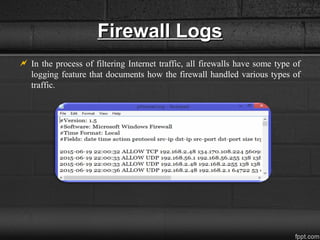
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules, acting as a barrier between a trusted internal network and an untrusted external network. Firewalls can be categorized into host-based and network firewalls, with various architectures like dual-homed host, screened host, and screened subnet providing different levels of protection and flexibility. Additionally, firewalls record logs that offer insights into traffic management, including IP addresses and protocols.