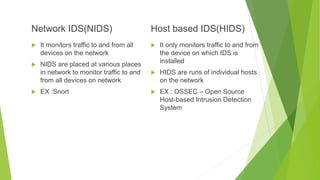
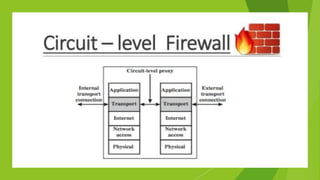
A firewall is a network security system that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and filters out unauthorized access based on a set of rules. It uses access control lists (ACLs) and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor traffic and identify potential threats. There are different types of firewalls including packet filtering, application-level gateways, circuit-level gateways, stateful multilayer inspection, and cloud-based firewalls that operate at different layers of the network and provide varying levels of security. Firewalls are a critical component of network security but must be properly configured to balance access needs with threat protection.