The document discusses firewall fundamentals, including:
- Firewalls control network traffic flow between networks with different security levels. They authenticate access, manage traffic, and protect resources.
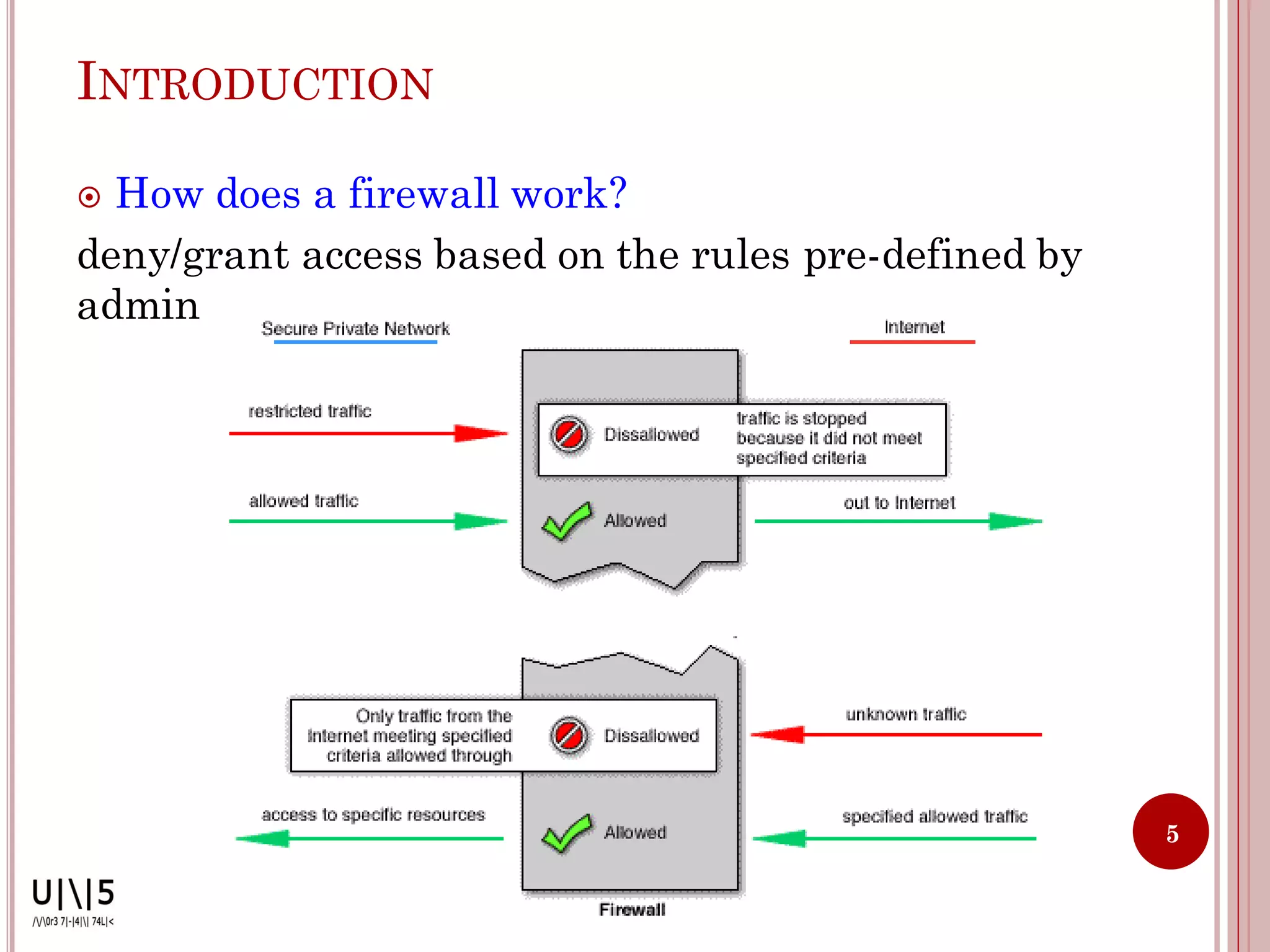
- Firewalls can be software, appliances, or integrated into devices. They operate at OSI layers 2-7 and deny or allow access based on predefined rules.
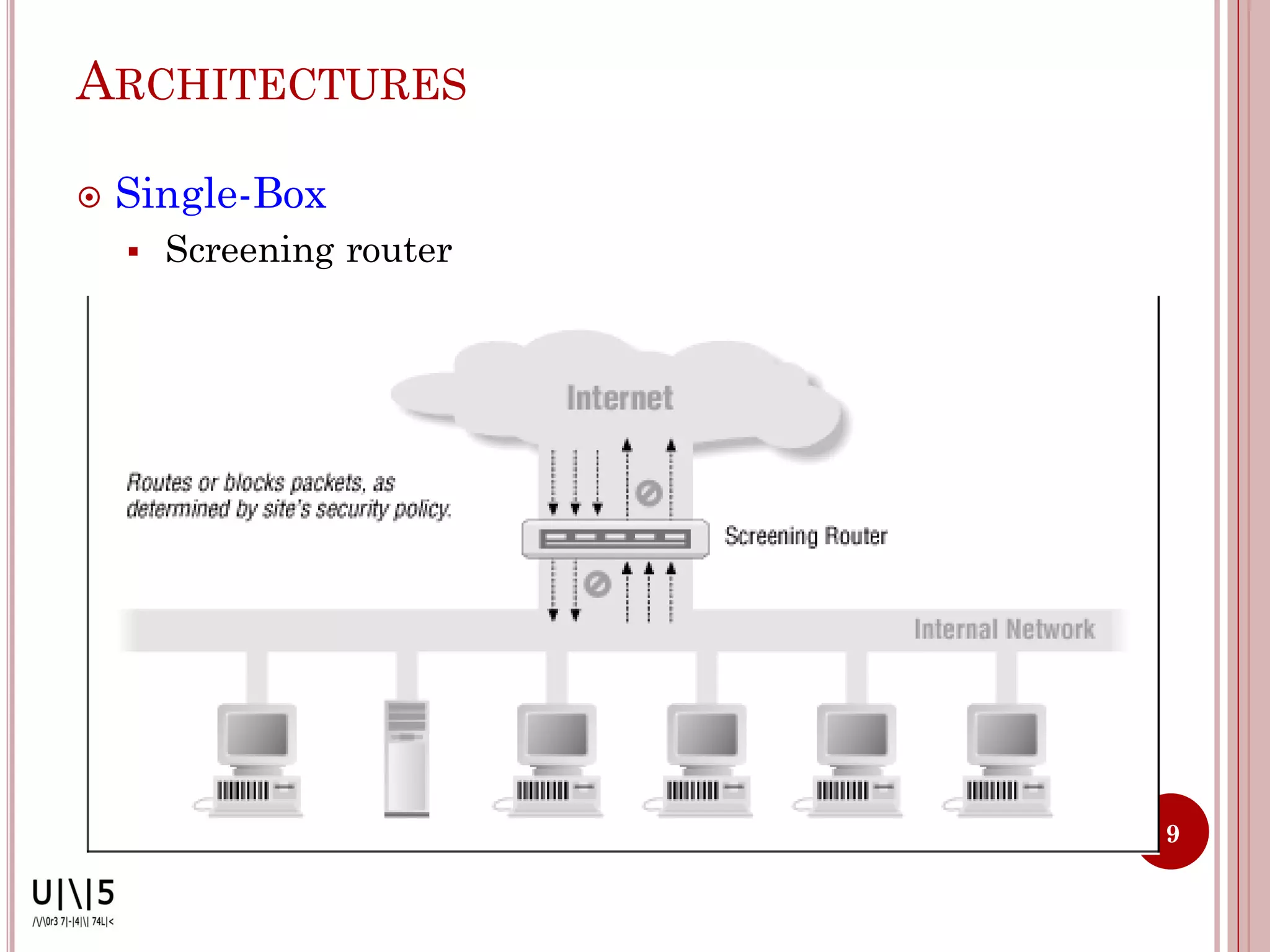
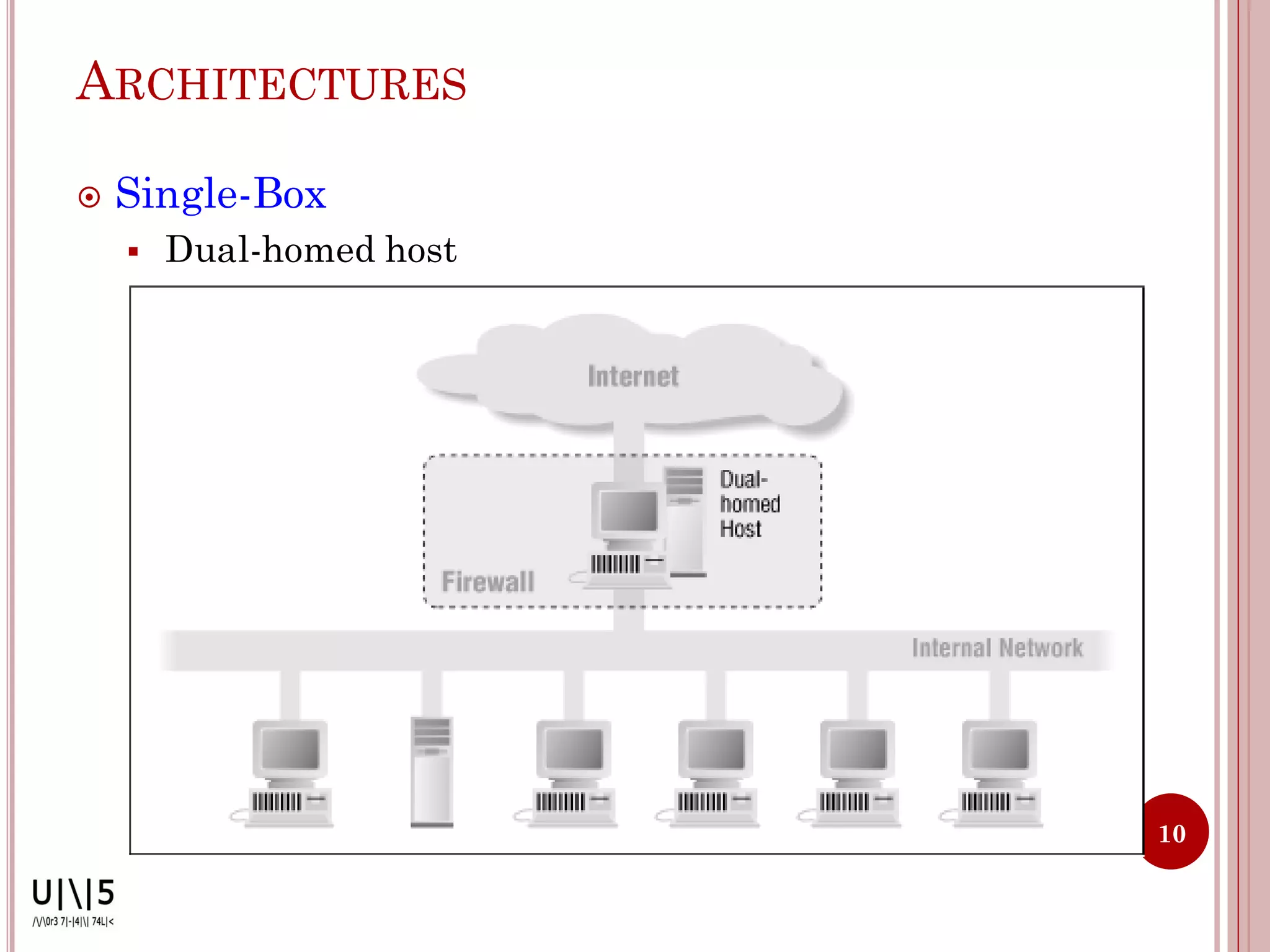
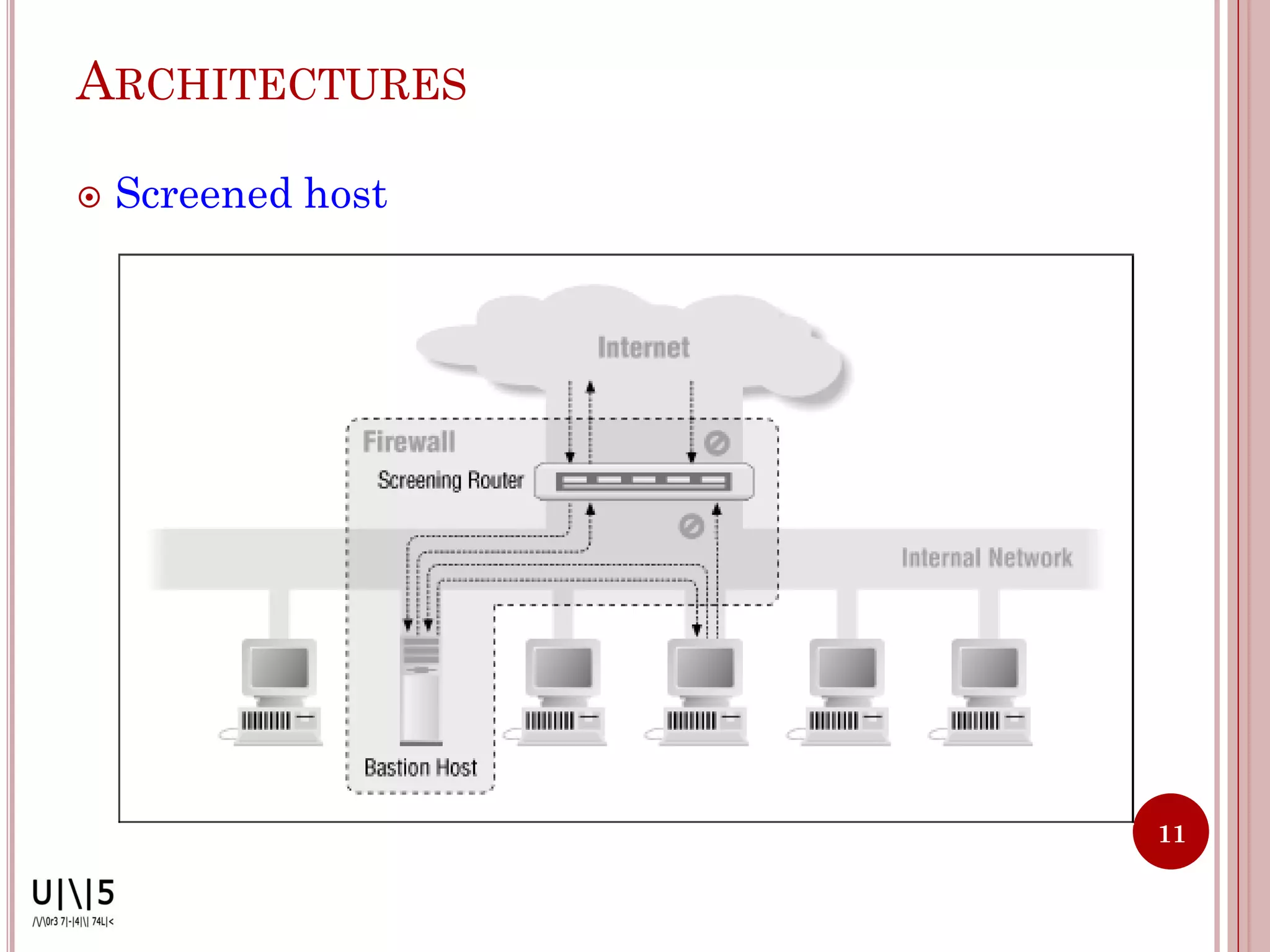
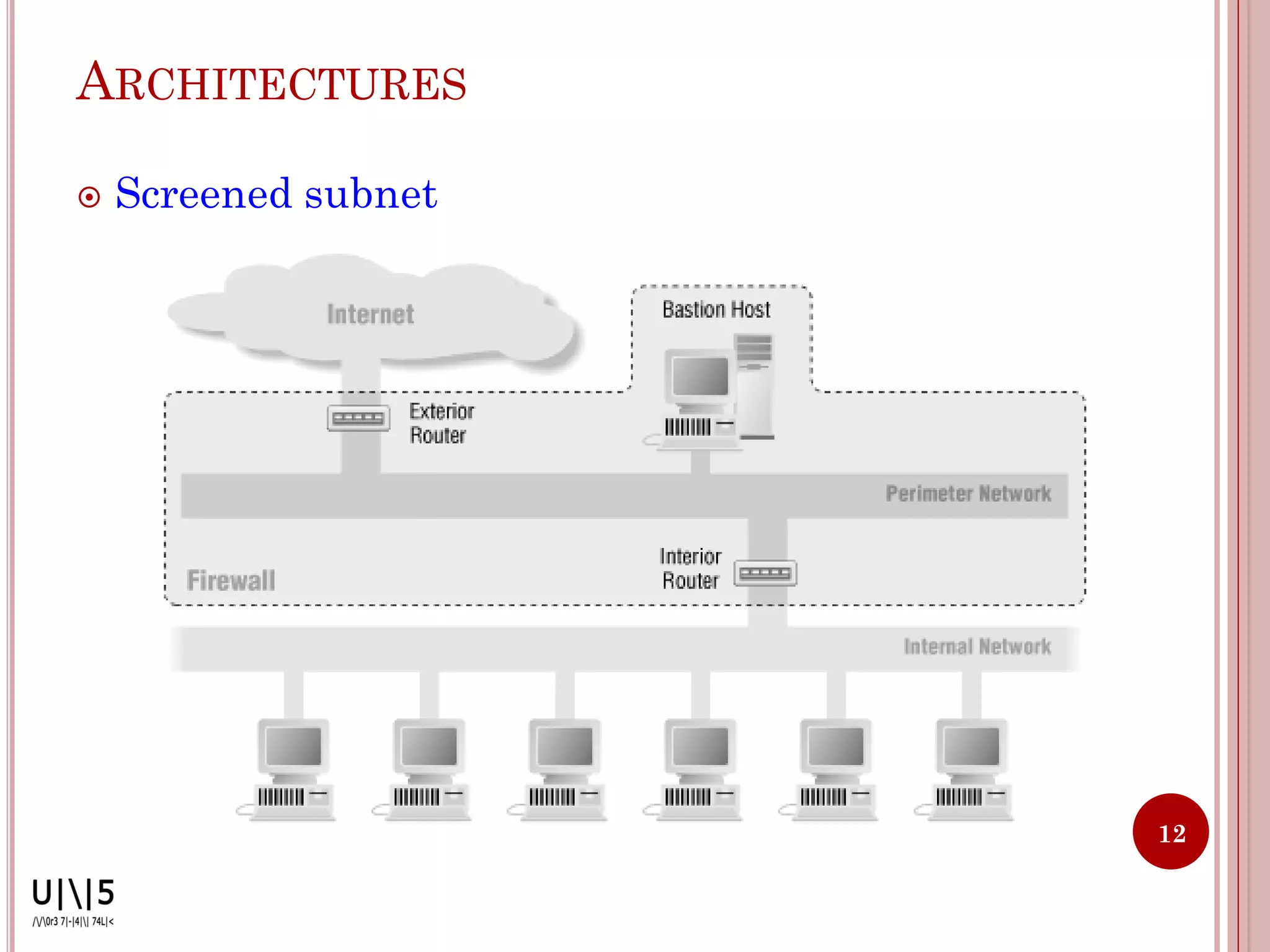
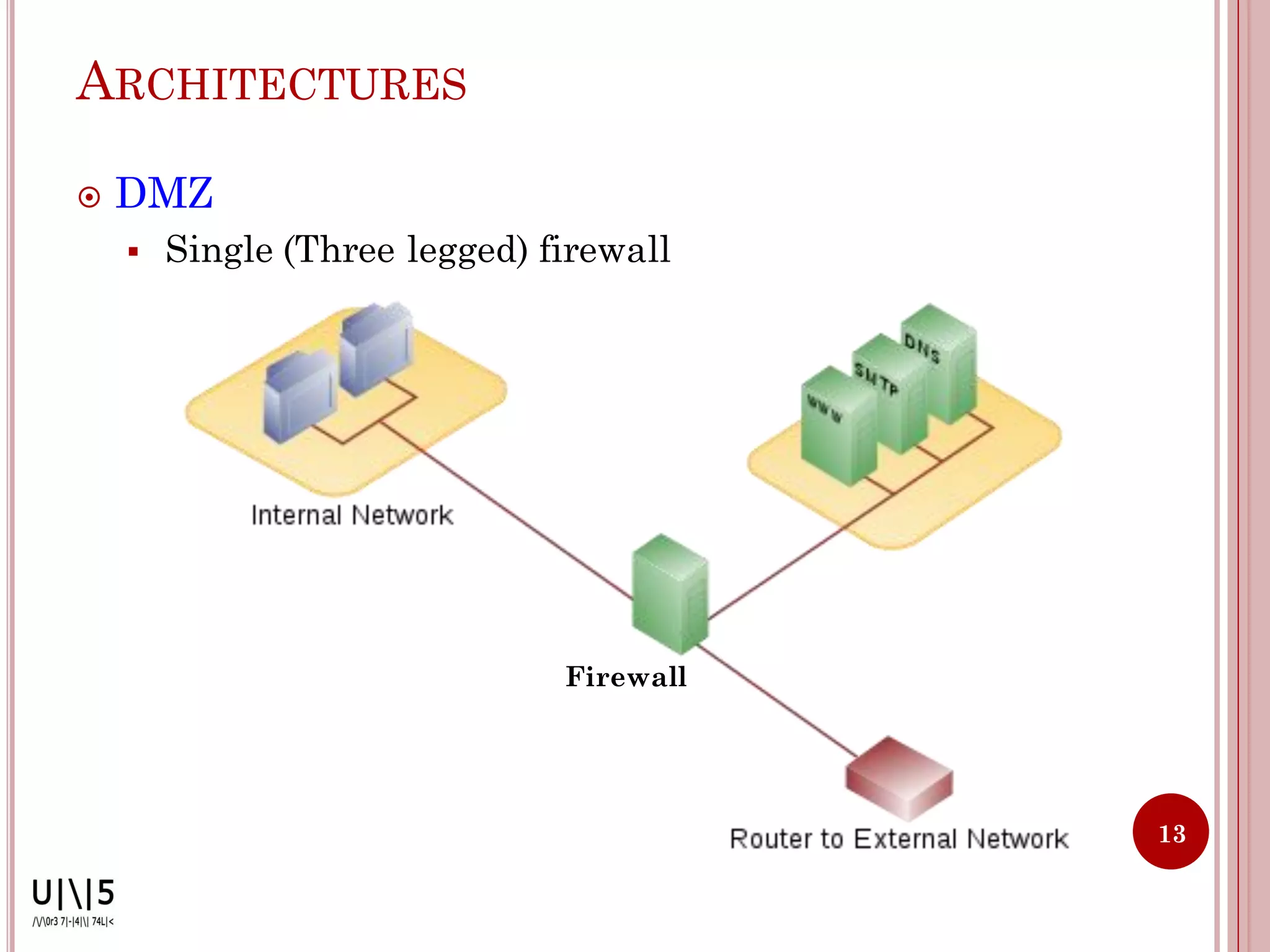
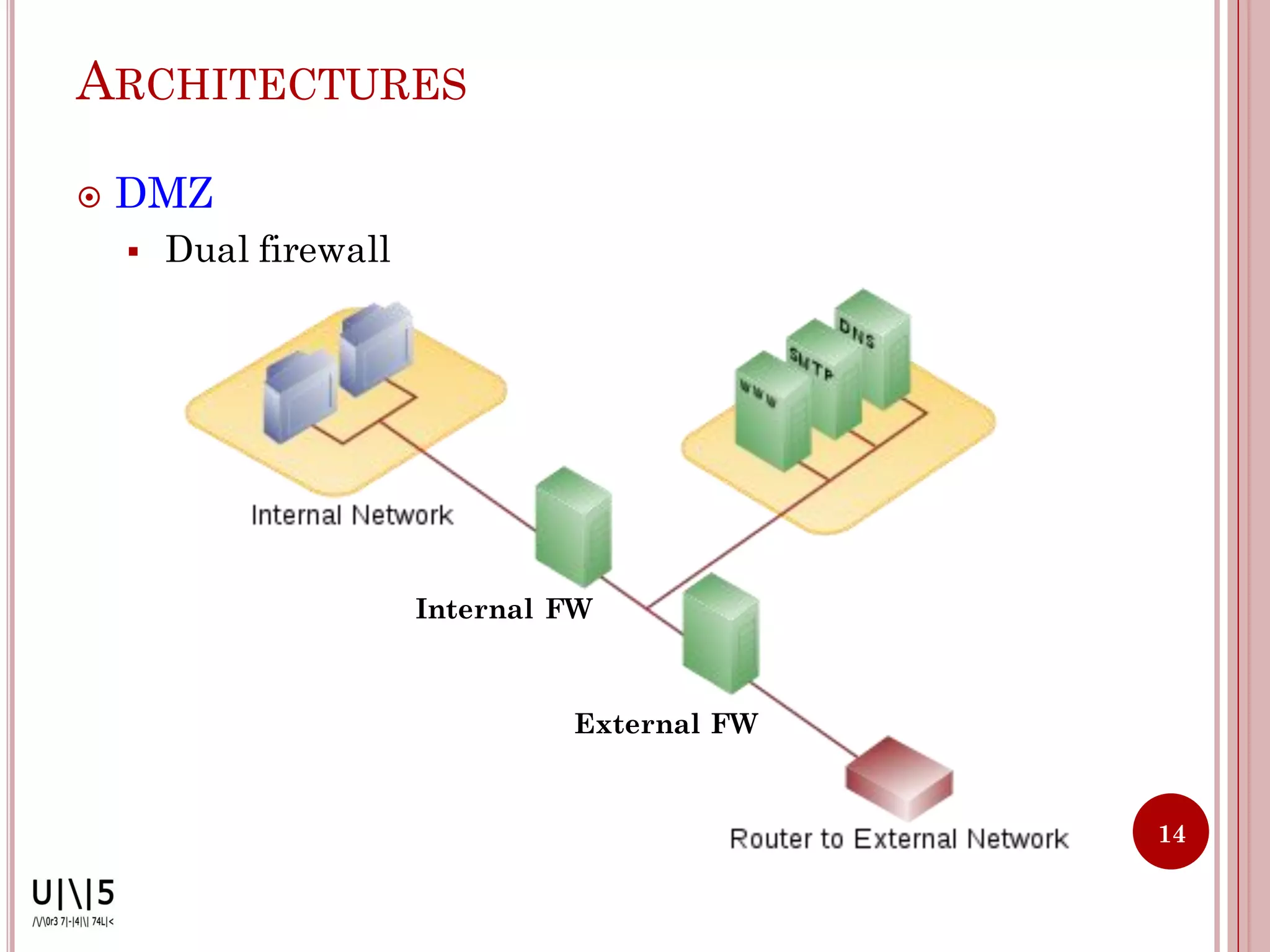
- Common firewall architectures include single-box, screened host, screened subnet, DMZ, and dual firewall setups. Firewalls have limitations and cannot protect against all internal/external threats.









![REFERENCES
[1] Firewall Fundamentals, Cisco Press (2006)
[2] Tactical Perimeter Defense, Element K (2007)
[3] Module 16 of CEH v7, EC-Council (2010)
[4] Building Internet Firewalls 2nd Edition, O'Reilly
(2000)
[5] Guidelines on Firewalls and Firewall Policy, NIST
(2009)
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firewallfundamentalsmanthang-110925033552-phpapp01/75/Firewall-fundamentals-18-2048.jpg)
