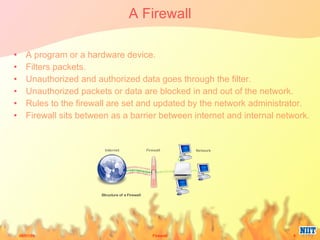
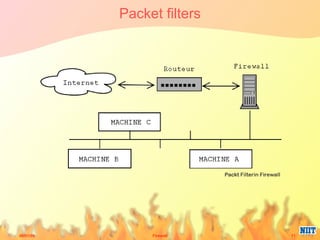
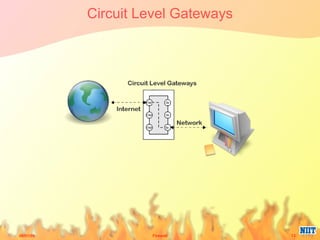
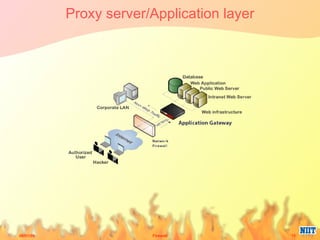
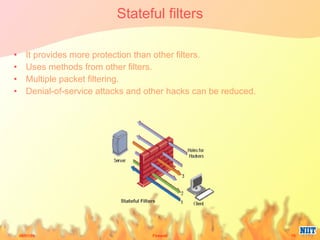
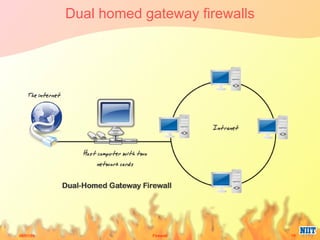
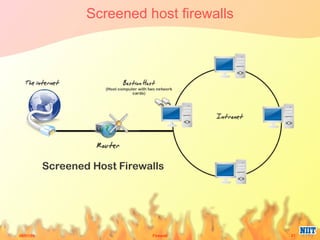
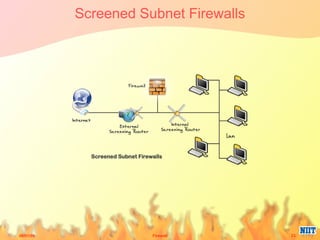
Firewalls have evolved from metal sheets used in the 19th century to protect buildings from fire, to software and hardware used today to filter network traffic and protect computers and networks. Key developments included the growth of the internet in the 1980s which led to the implementation of firewalls in routers to control network data traffic and allocate networks. Different types of firewalls evolved to suit various network sizes, from personal firewalls on individual computers to enterprise firewalls capable of handling thousands of users across multiple firewalls. Future firewalls may be integrated directly into devices like personal computers and supercomputers.