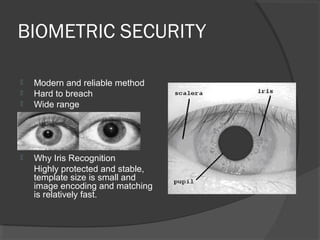
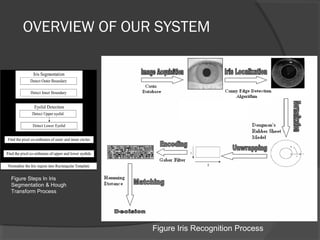
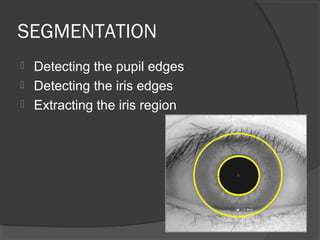
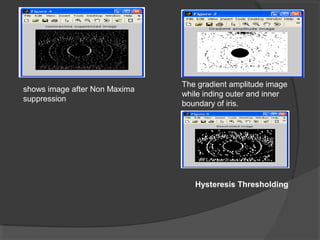
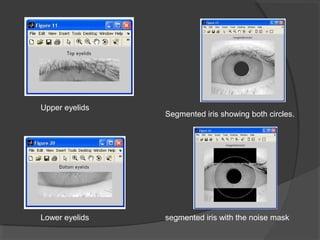
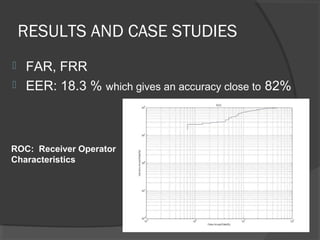
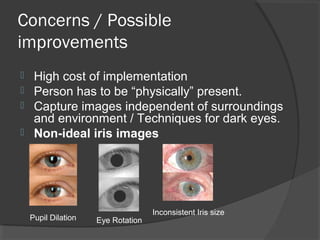
This document discusses iris recognition as a biometric security method. It provides an overview of how iris recognition works, including segmentation of the iris region, normalization, and feature extraction and matching. The accuracy of iris recognition is close to 82%, with an equal error rate of 18.3%. While iris recognition has advantages like the uniqueness and stability of iris patterns, concerns include the high cost of implementation and challenges with non-ideal iris images under different lighting conditions.






![REFERENCES
1] Wildes, R.P, “Iris Recognition: An Emerging
Biometric Technology”, Proceedings of the IEEE,
VOL. 85, NO. 9, September 1997, pp. 1348-1363.
2] John G. Daugman. How Iris Recognition Works.
Proceedings of 2002 International Conference on
Image Processing, Vol. 1, 2002.
5) J. Daugman “High confidence visual recognition of
persons by a test of statistical independence ,”IEEE
Trans. Pattern Analyse Machine Intell., vol. 15, pp.
1148–1161, Nov. 1993.
6) R. Wildes, “Iris recognition: an emerging biometric](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalirisrecognition-141124011742-conversion-gate01/85/Final-iris-recognition-14-320.jpg)
