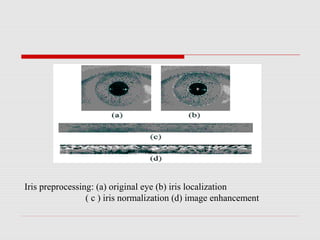
This document discusses iris biometrics for person identification. It begins by defining biometrics and explaining why they are used. It then focuses on iris biometrics, describing how the iris is unique, how iris recognition systems work to capture images and extract iris codes for identification, and the techniques involved like localization, normalization and enhancement. It compares iris recognition to other biometrics like fingerprints in terms of accuracy, stability, speed and security. It concludes by discussing current and future uses of iris biometrics with references.