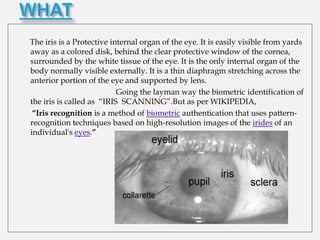
This document summarizes the history and technology of iris recognition biometrics. It discusses how the iris was first proposed as a biometric in the 1930s, was featured in Bond films in the 1980s, and was patented and implemented in ATMs in the late 1980s. The iris is described as a protected internal organ that has many unique identifying features, making it very difficult to artificially duplicate. The document outlines the major parts of an iris recognition system and discusses many applications of the technology such as computer login, border control, and forensics. It concludes that iris recognition is extremely accurate and could be used for large-scale identification.