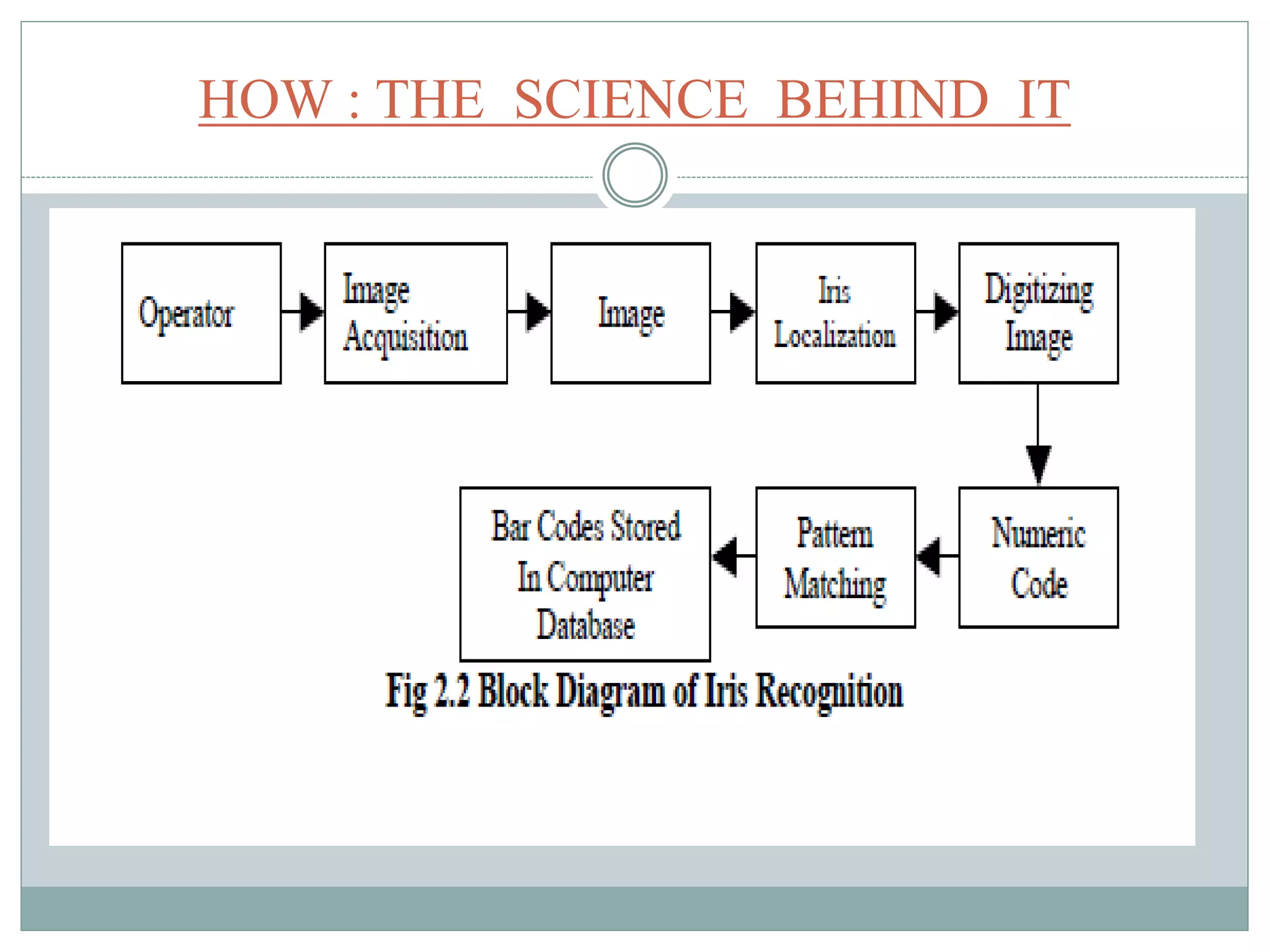
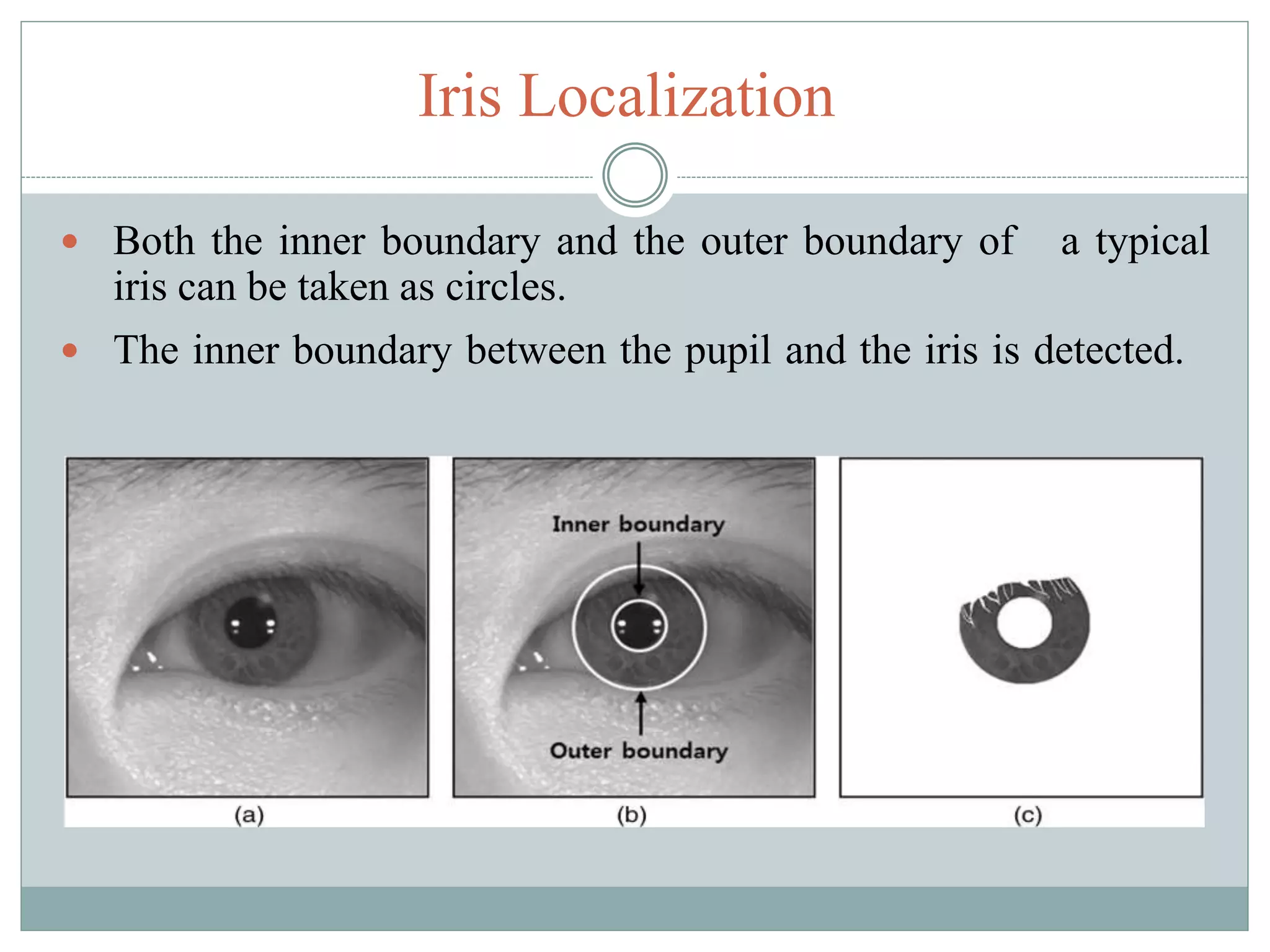
The document discusses iris recognition as a biometric method for uniquely identifying individuals based on the distinctive patterns of their irises. It highlights the anatomy of the human eye, the characteristics and uniqueness of the iris, and how iris recognition works scientifically. Additionally, it outlines the merits, demerits, and various applications of iris recognition technology, emphasizing its reliability and potential as a security measure.