The document outlines the fundamentals and advantages of iris recognition technology, highlighting its uniqueness, stability, and non-invasive nature. Developed by pioneers including John Daugman, the technology involves several stages such as image acquisition, iris localization, normalization, feature extraction, and pattern matching. Currently, the project is in the iris localization phase using a dataset from the Chinese University of Hong Kong.



![History
Iris Recognition system was first proposed
by Flom and Safir in 1987. [1][3][4]
In the year 1994, John Daugman patented
his "biometrics personal identification
system based on iris analysis"[1][3][4].
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irismajor-150723071314-lva1-app6892/85/iris-recognition-system-as-means-of-unique-identification-4-320.jpg)


![8
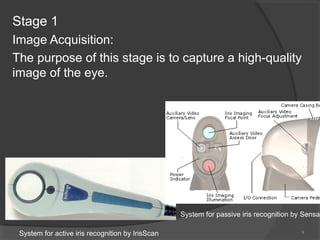
Stages
[2]
Stages of iris based recognition algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irismajor-150723071314-lva1-app6892/85/iris-recognition-system-as-means-of-unique-identification-8-320.jpg)
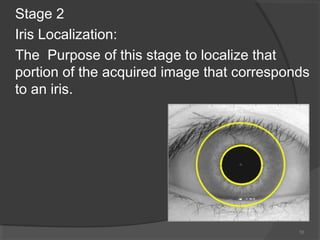





![Some of localized iris images are
16
Captured image
[5]
Eye image with circles
for localization of iris](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irismajor-150723071314-lva1-app6892/85/iris-recognition-system-as-means-of-unique-identification-16-320.jpg)
![17
Captured image Eye image with circles
for localization of iris
[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irismajor-150723071314-lva1-app6892/85/iris-recognition-system-as-means-of-unique-identification-17-320.jpg)
![REFERENCES
[1]J. Daugman , How iris recognition works, IEEE Trans. On Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology., Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 21-30, January 2004.
[2]Gargi Amoli, Nitin Thapliyal, Nidhi Sethi, “Iris Preprocessing “, International Journal of Advanced
Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering . ,Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2012 ISSN:
2277 128X page 301-304.
[3] J. Daugman, ―High Confidence Visual Recognition of Persons by a Test of Statistical
Independence , IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 15, No.11,‖
pp.1148-1161, 1993.
[4] John Daugman, ―The importance of being random: statistical principles of iris recognition ,‖
Pattern Recognition 36 (2003) 279 – 291, 21 December 2001
[5] Dataset, Chinese University of Hong Kong, “http://www.mae.cuhk.edu.hk/~cvl/main_database.htm”
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irismajor-150723071314-lva1-app6892/85/iris-recognition-system-as-means-of-unique-identification-18-320.jpg)
