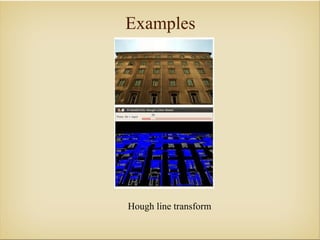
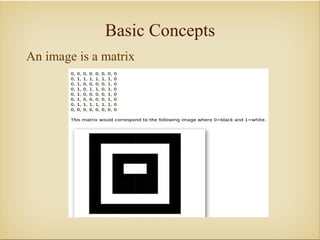
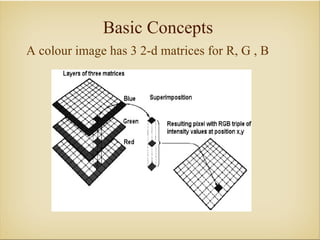
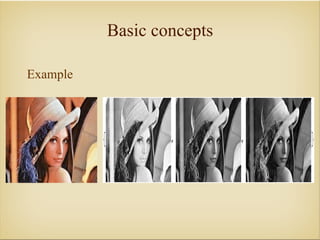
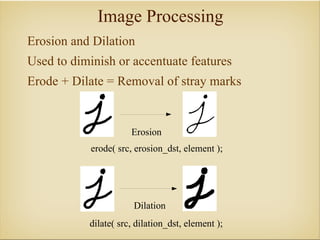
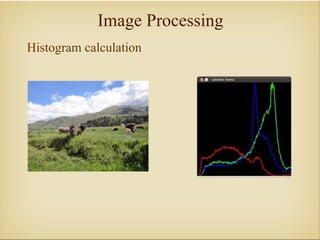
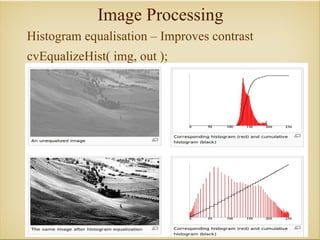
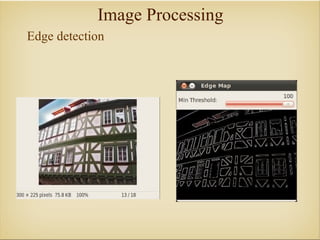
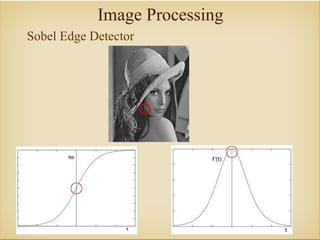
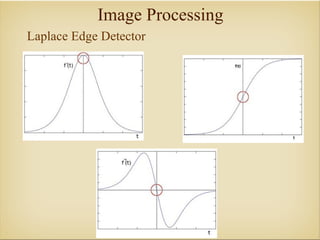
Image processing with OpenCV allows various techniques to manipulate digital images. Some key techniques include smoothing to remove noise, erosion and dilation to diminish or accentuate features, and edge detection algorithms like Sobel, Laplace, and Canny to find edges. The core OpenCV module provides functions for accessing pixel values, adjusting contrast and brightness, and drawing shapes. Feature detection identifies keypoints like edges, corners, and blobs, then describes the details around them for later matching against other images. Common algorithms include SURF, SIFT, and BRIEF for feature extraction and description and FLANN and BruteForce for feature matching.