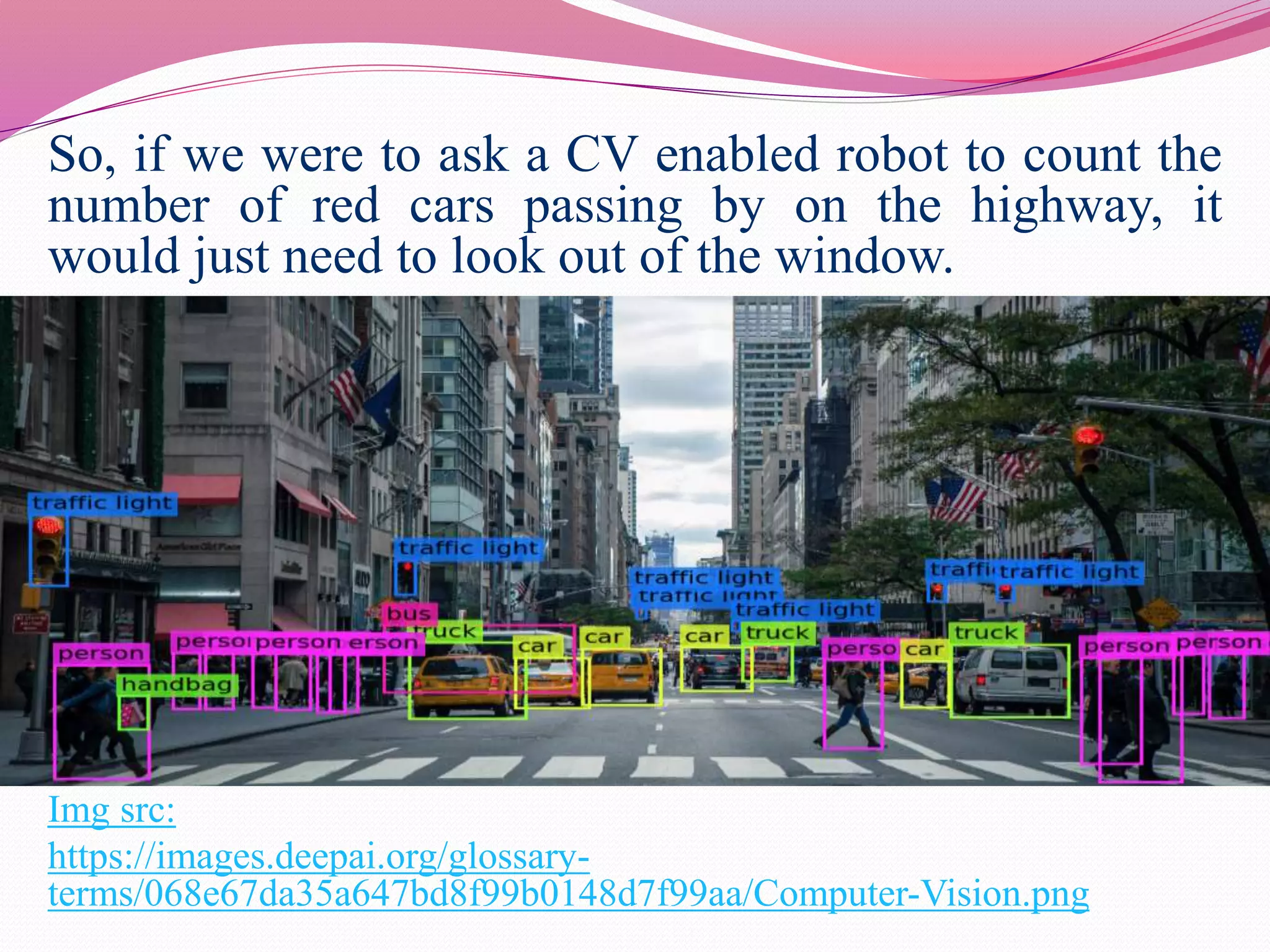
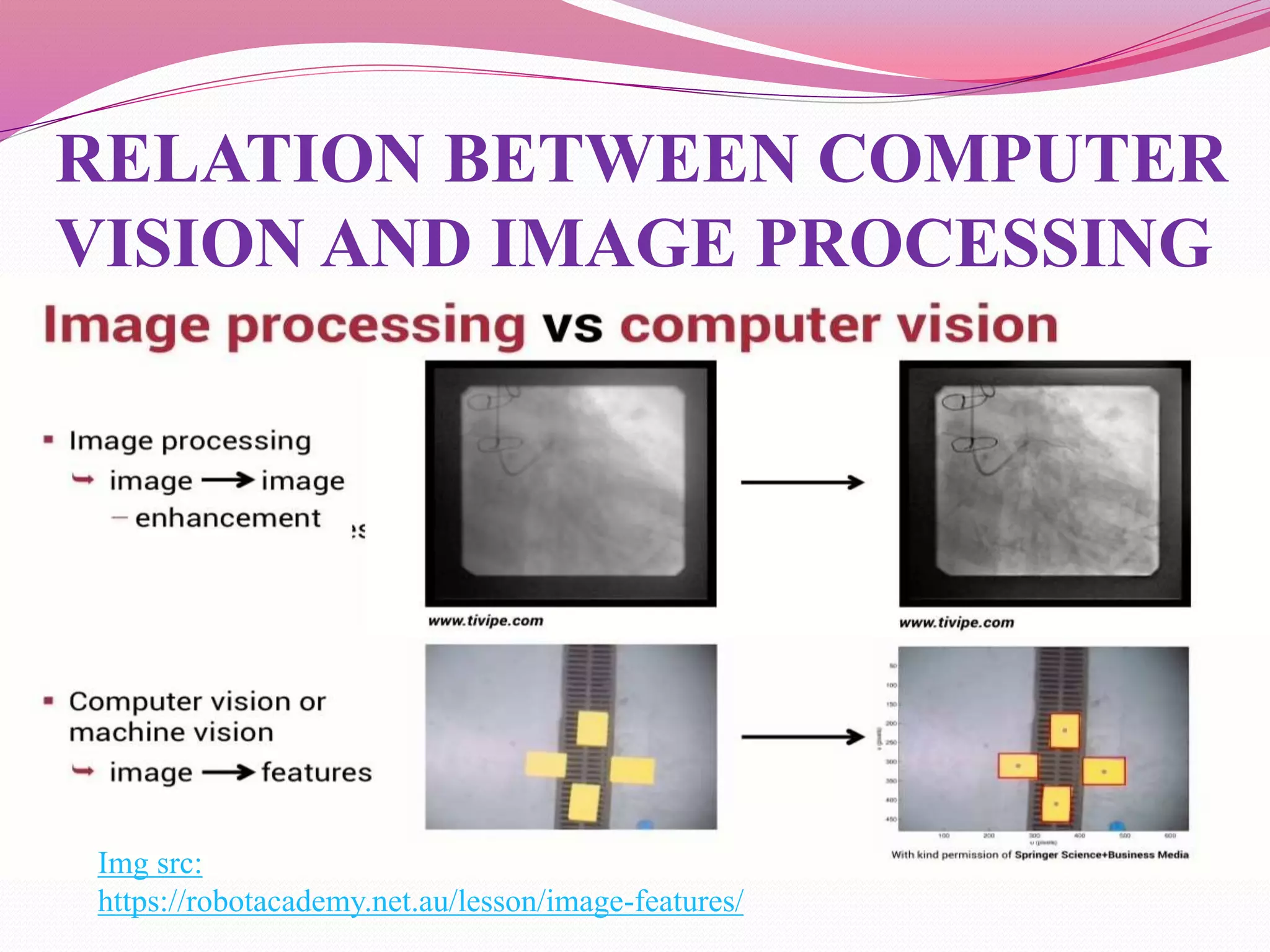
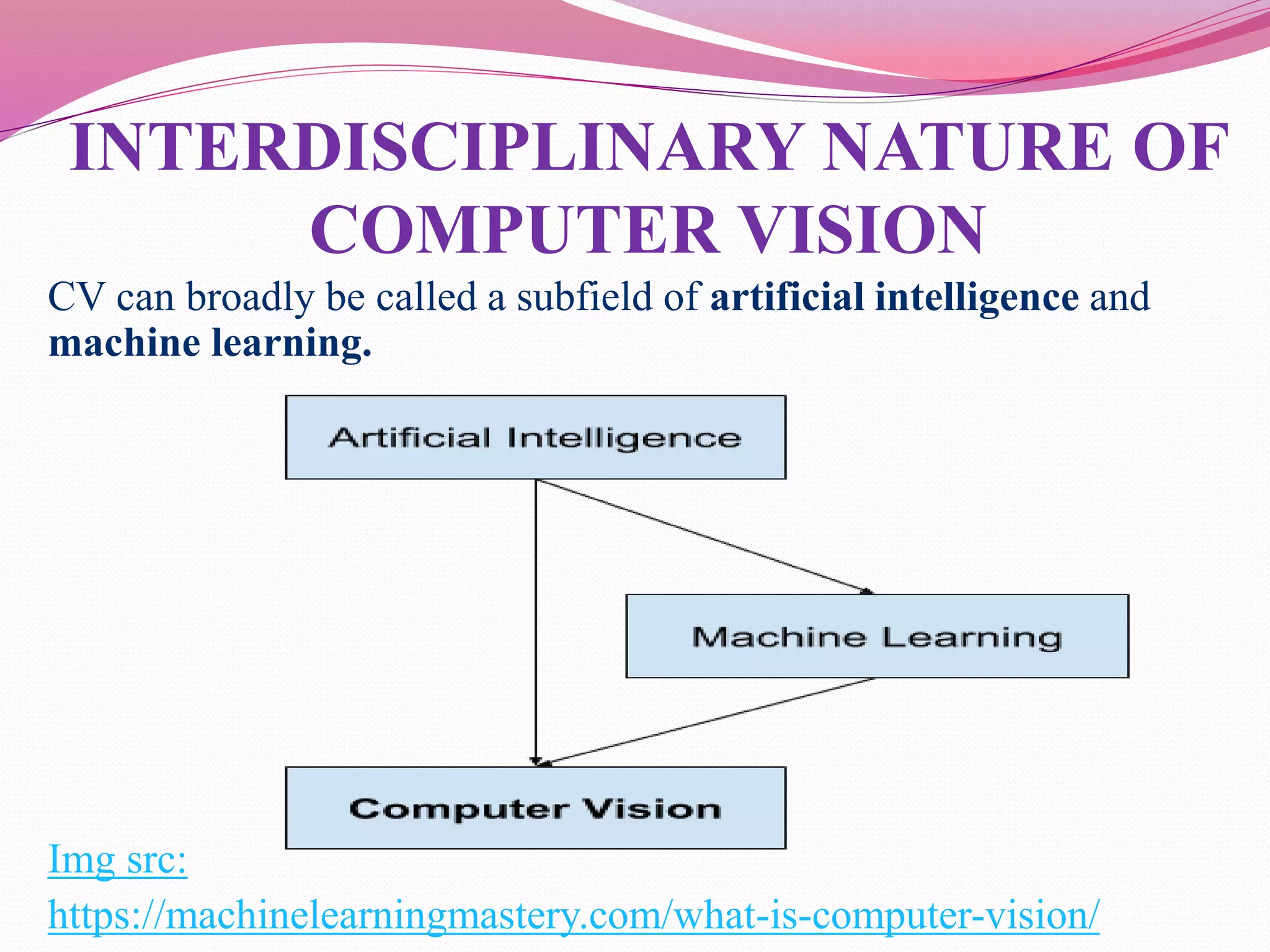
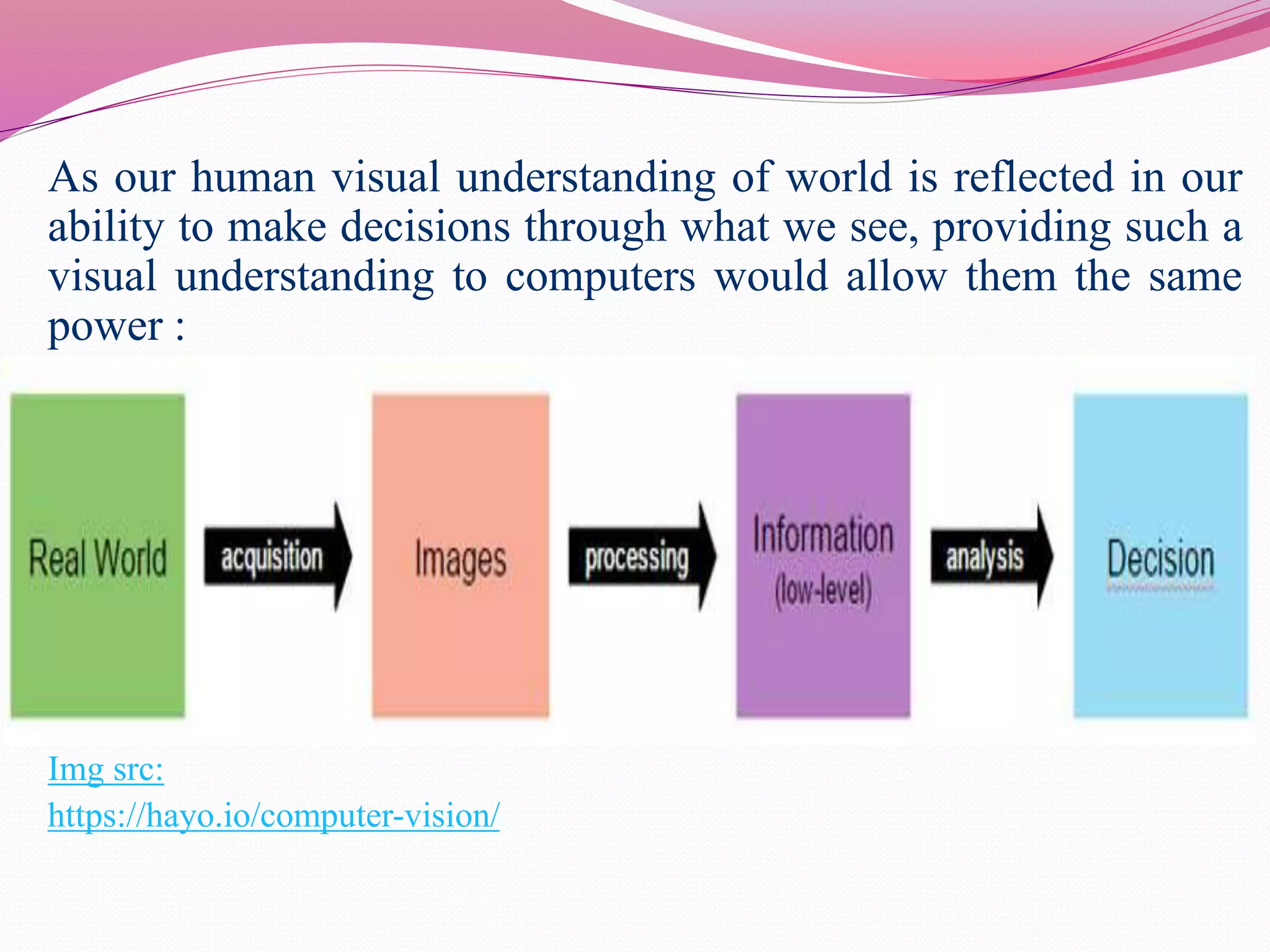
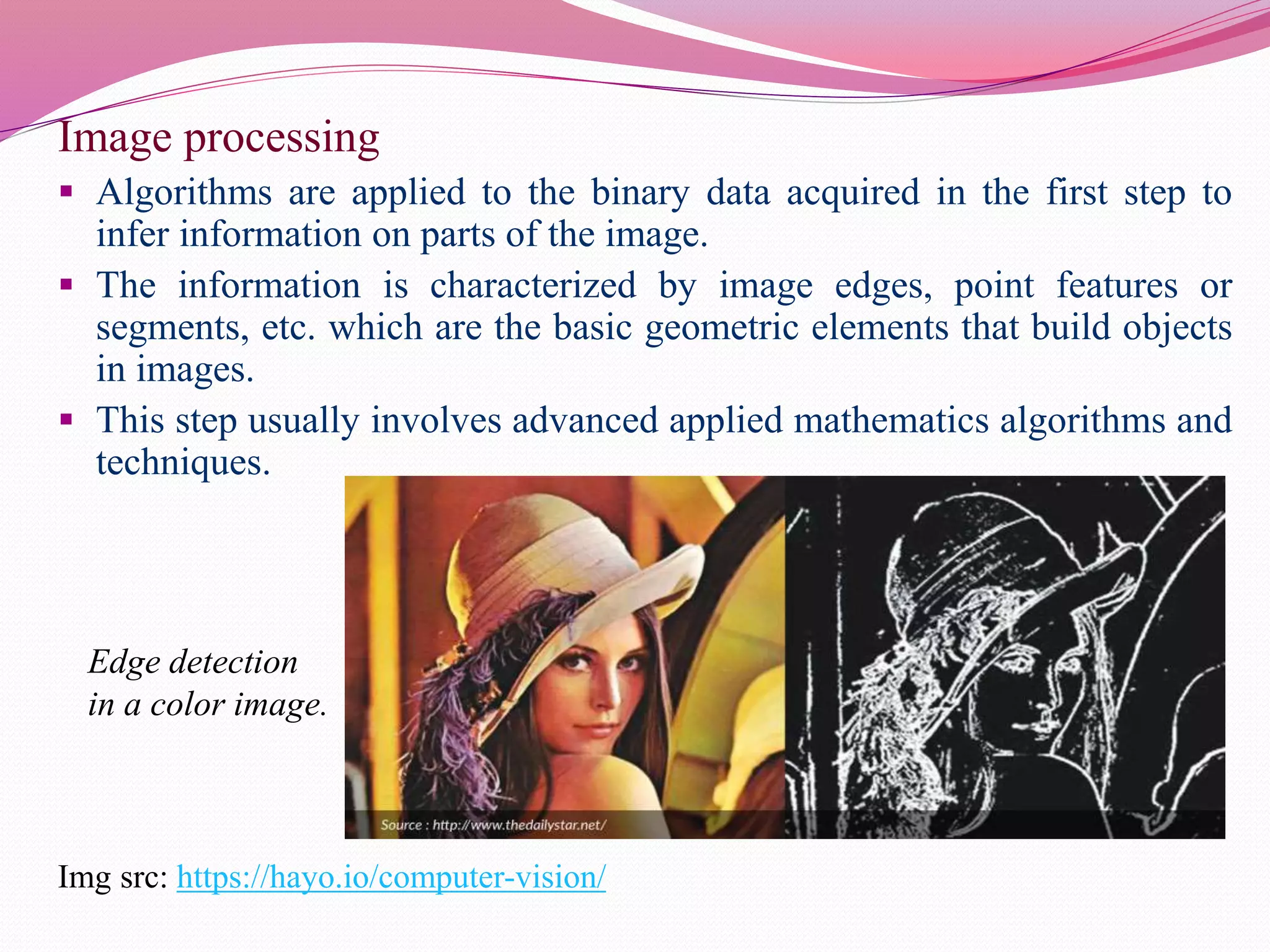
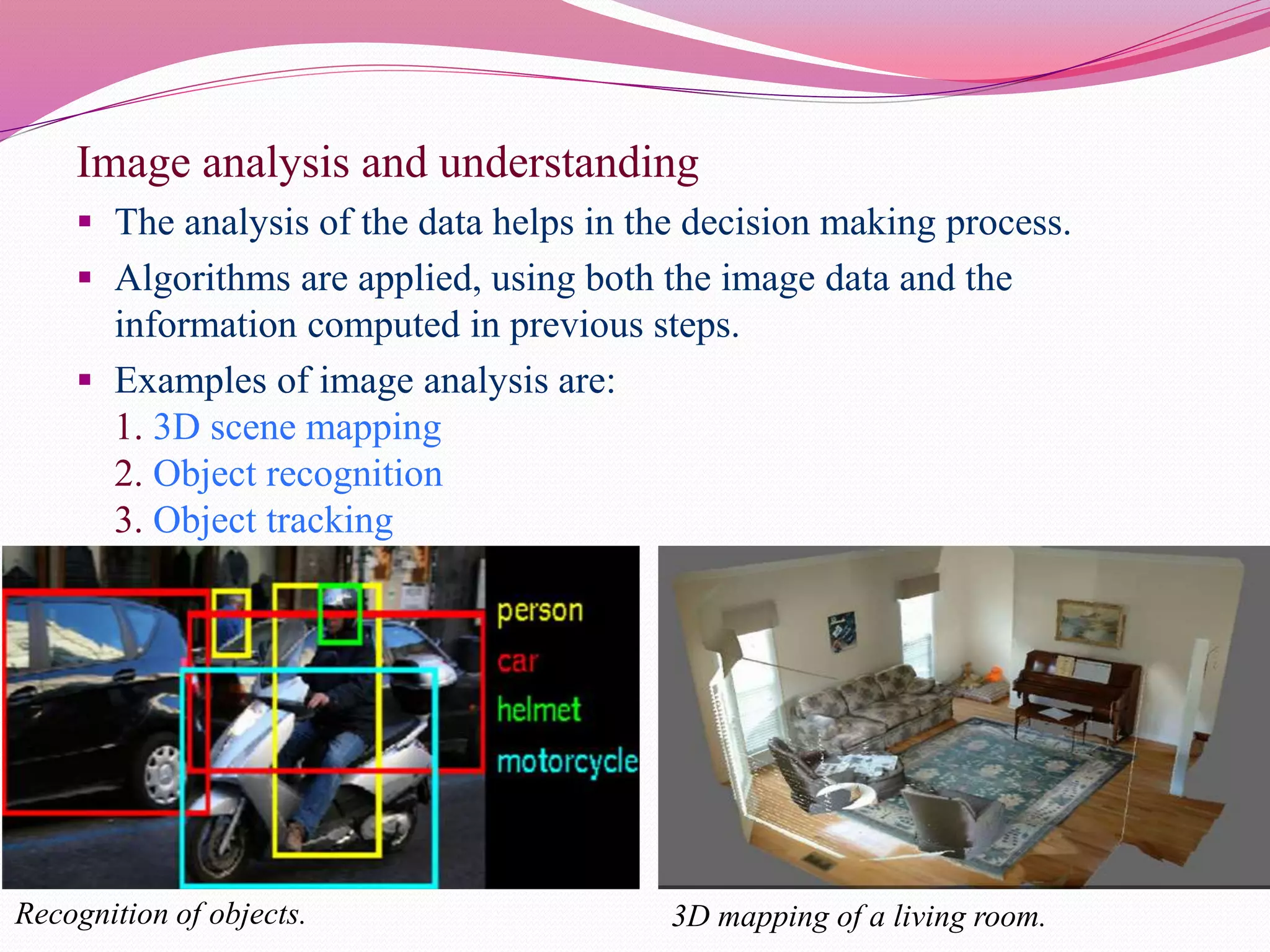
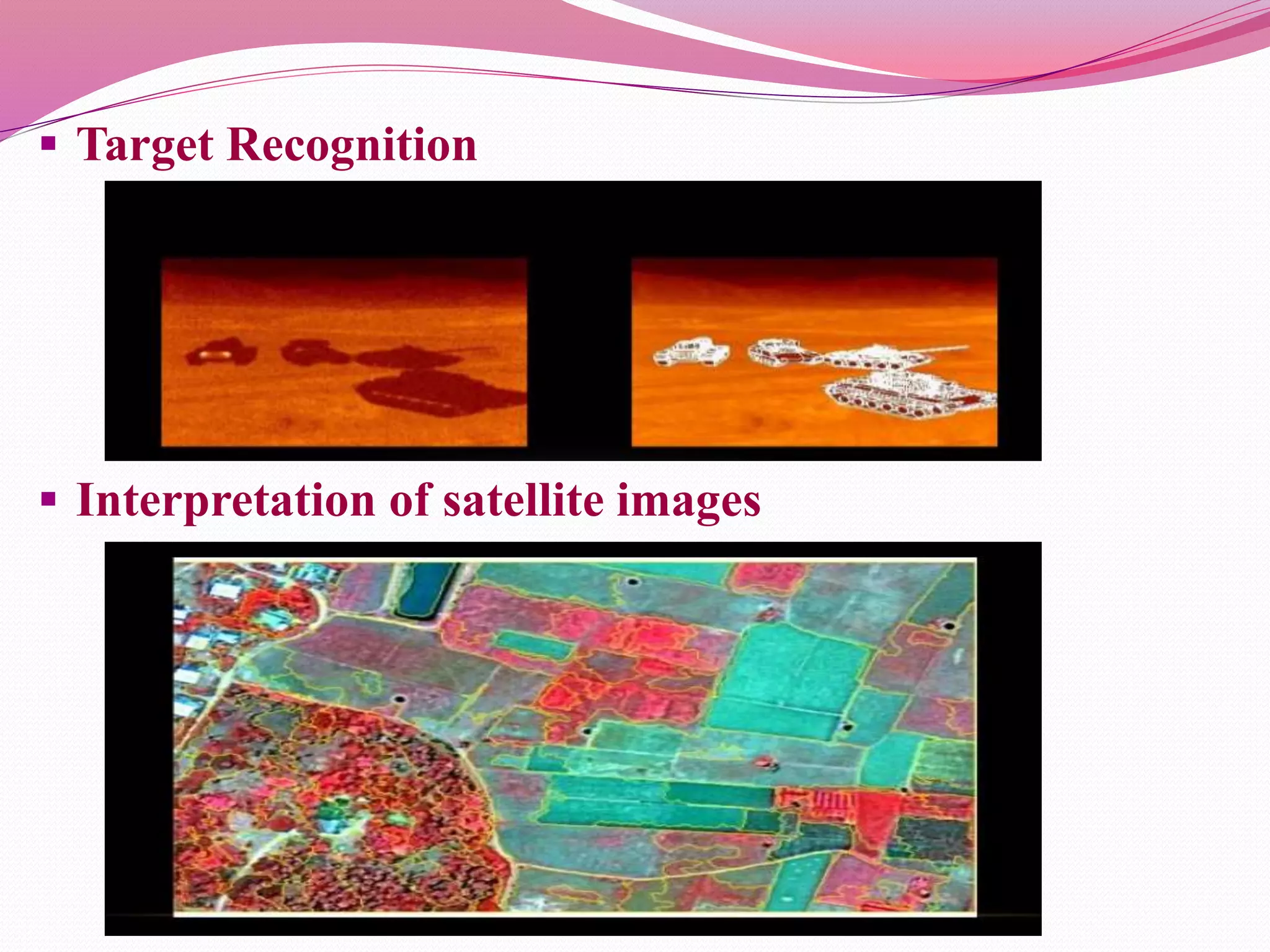
Computer vision is the automation of human visual perception to allow computers to analyze and understand digital images. The goal is to emulate the human visual system through techniques like deep learning. Computer vision involves image acquisition, processing, and analysis to interpret images beyond just recording them. It has applications in areas like object detection, facial recognition, medical imaging, and self-driving cars. While it provides advantages like unique customer experiences, it also raises privacy concerns regarding how the data used is collected and stored.