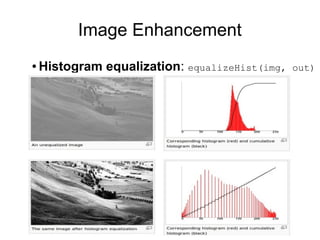
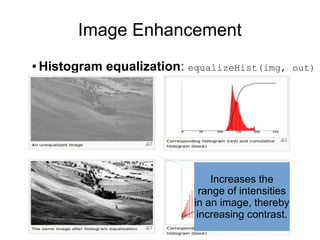
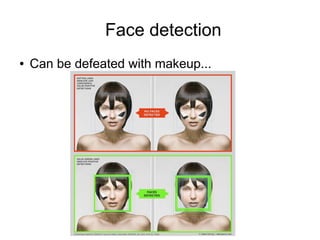
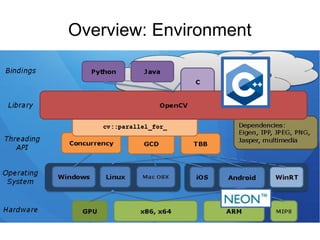
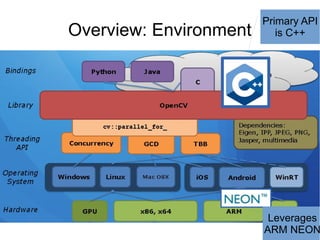
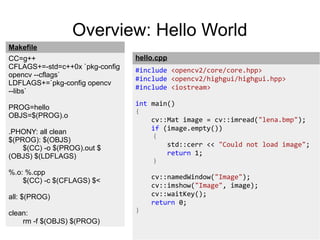
Open Source Computer Vision (OpenCV) is a BSD-licensed open source library for computer vision and image processing. The document outlines OpenCV's capabilities including image enhancement, object classification and tracking, and face detection and recognition. It provides examples of using OpenCV in C++ and Python to load and display images, detect faces, and enhance images. The document concludes that OpenCV is a cross-platform library with over 2,000 algorithms for computer vision and image processing tasks.









![Video from IP camera w/ RTSP!
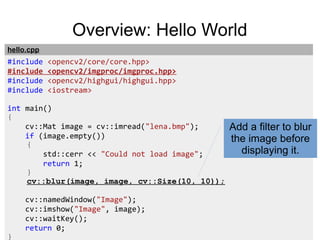
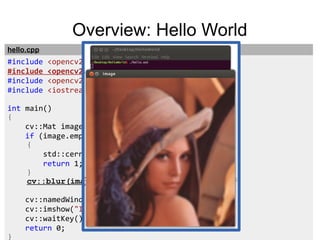
#include <opencv/cxcore.h>
#include <opencv/highgui.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
cv::Ptr<CvCapture> capture = cvCaptureFromFile(
"rtsp://admin:admin@10.10.32.33/video");
cv::namedWindow("Frame");
for (;;)
{
cv::Mat frame = cvQueryFrame(capture);
cv::imshow("Frame", frame);
if (cv::waitKey(1) >= 0)
break;
}
return 0;
}
Network comm.,
RTSP protocol, etc.
is all handled for you
so all you have to do
is process each
frame as an image
(a cv::Mat object).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opencvintro-131206011641-phpapp02/85/OpenCV-Introduction-16-320.jpg)