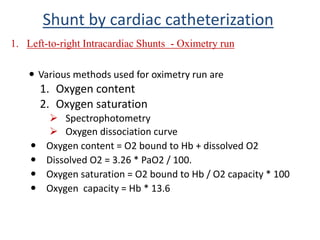
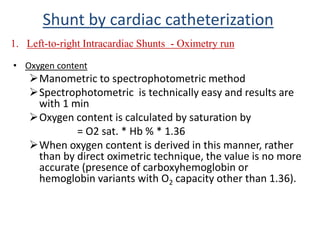
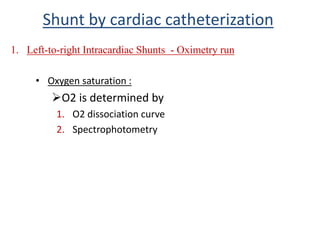
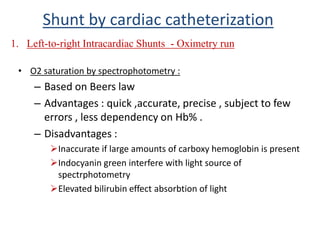
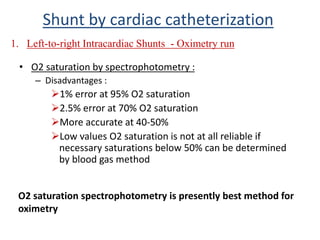
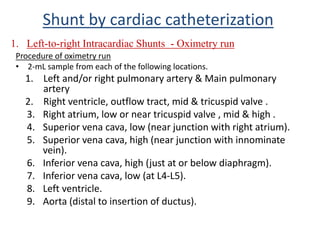
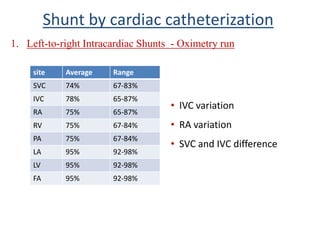
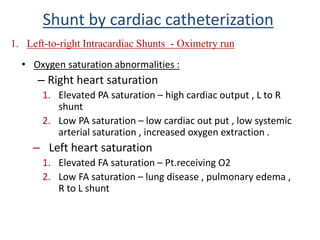
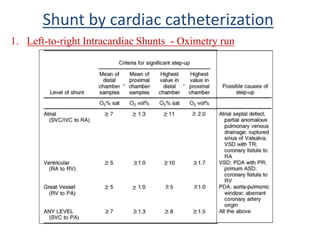
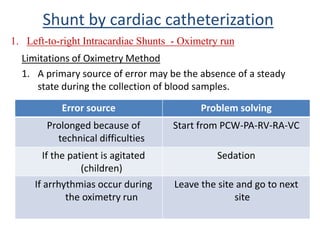
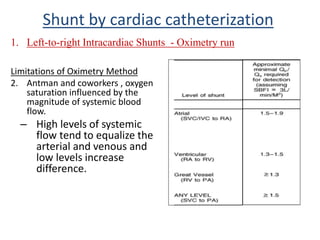
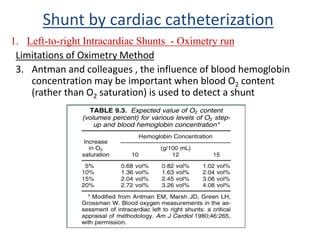
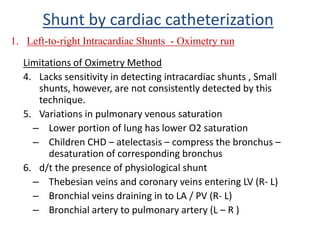
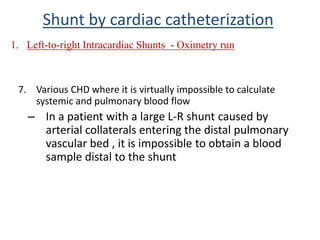
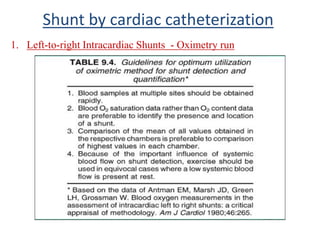
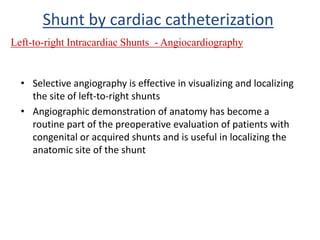
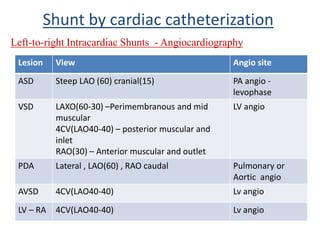
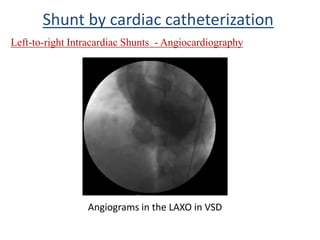
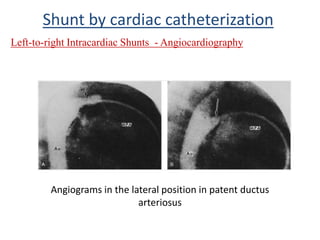
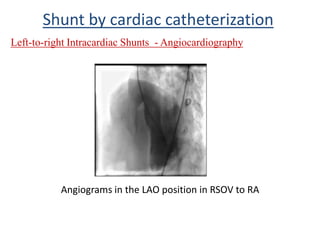
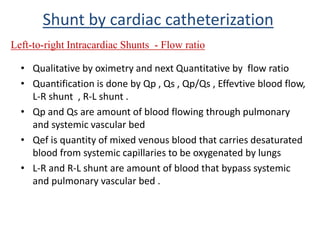
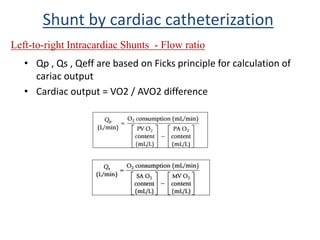
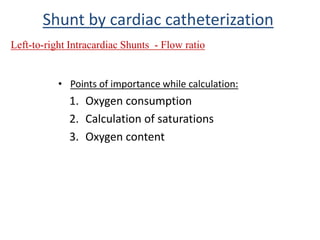
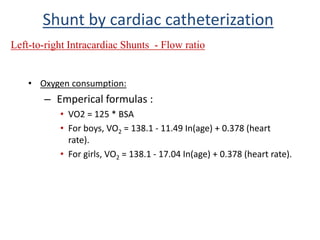
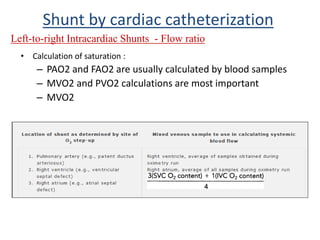
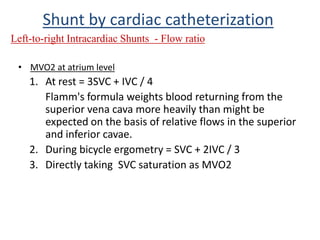
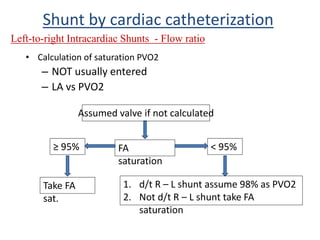
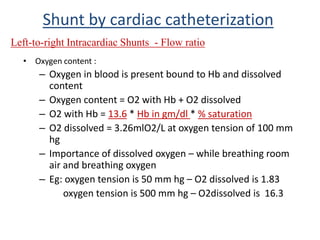
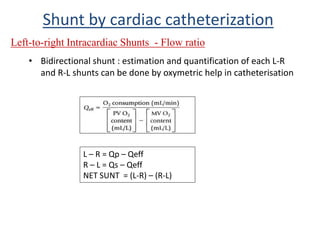
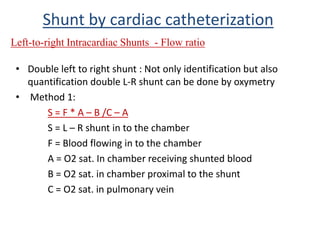
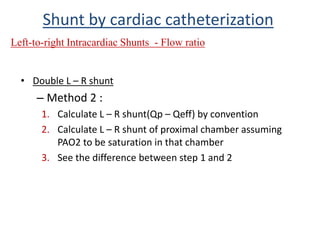
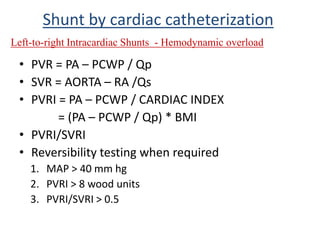
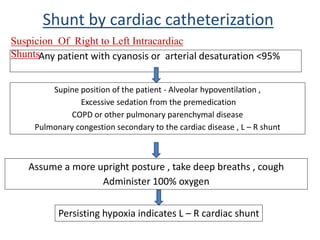
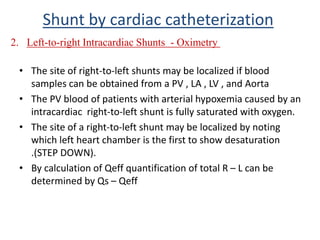
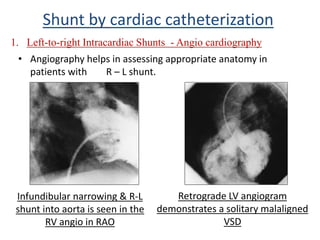
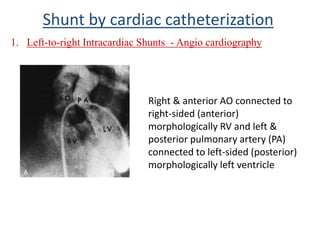
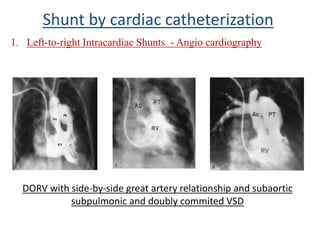
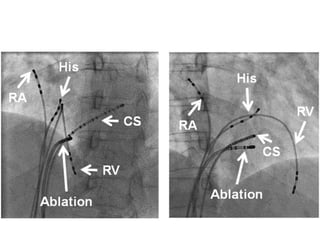
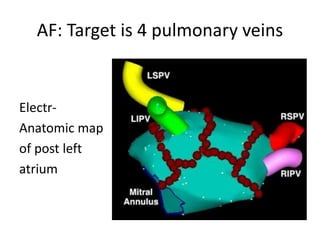
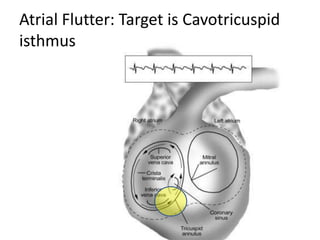
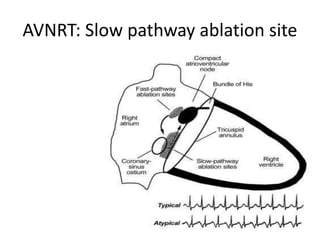
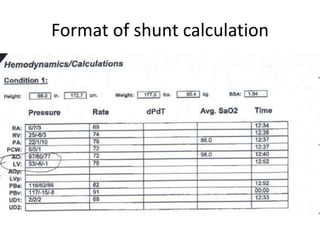
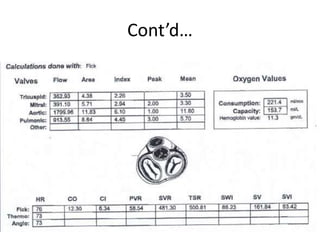
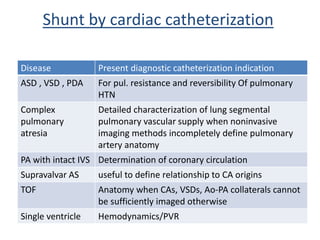
This document discusses the assessment of intracardiac shunts by cardiac catheterization. It describes how an oximetry run is performed to detect a left-to-right shunt by measuring oxygen saturation at various locations in the heart and great vessels. A significant step-up in oxygen saturation between the right atrium and ventricle or pulmonary artery suggests a left-to-right shunt. The document also discusses calculating shunt ratios using indicator dilution techniques and identifying shunt locations with angiography and pressure measurements. Complications of the procedure are outlined.























![Shunt by cardiac catheterization
1. Pulmonary artery [PA] blood oxygen saturation is >80%, the
possibility of a left-to-right intracardiac shunt should be considered
.
When to suspect cardiac L – R
shunt ?
Plan of management by catheterisation:
1. Diagnosis
2. Quantification of shunt
3. Hemodynamic load](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ffrrafshuntcalculationpvr-161206092015/85/Ffr-raf-shunt-calculation-pvr-43-320.jpg)