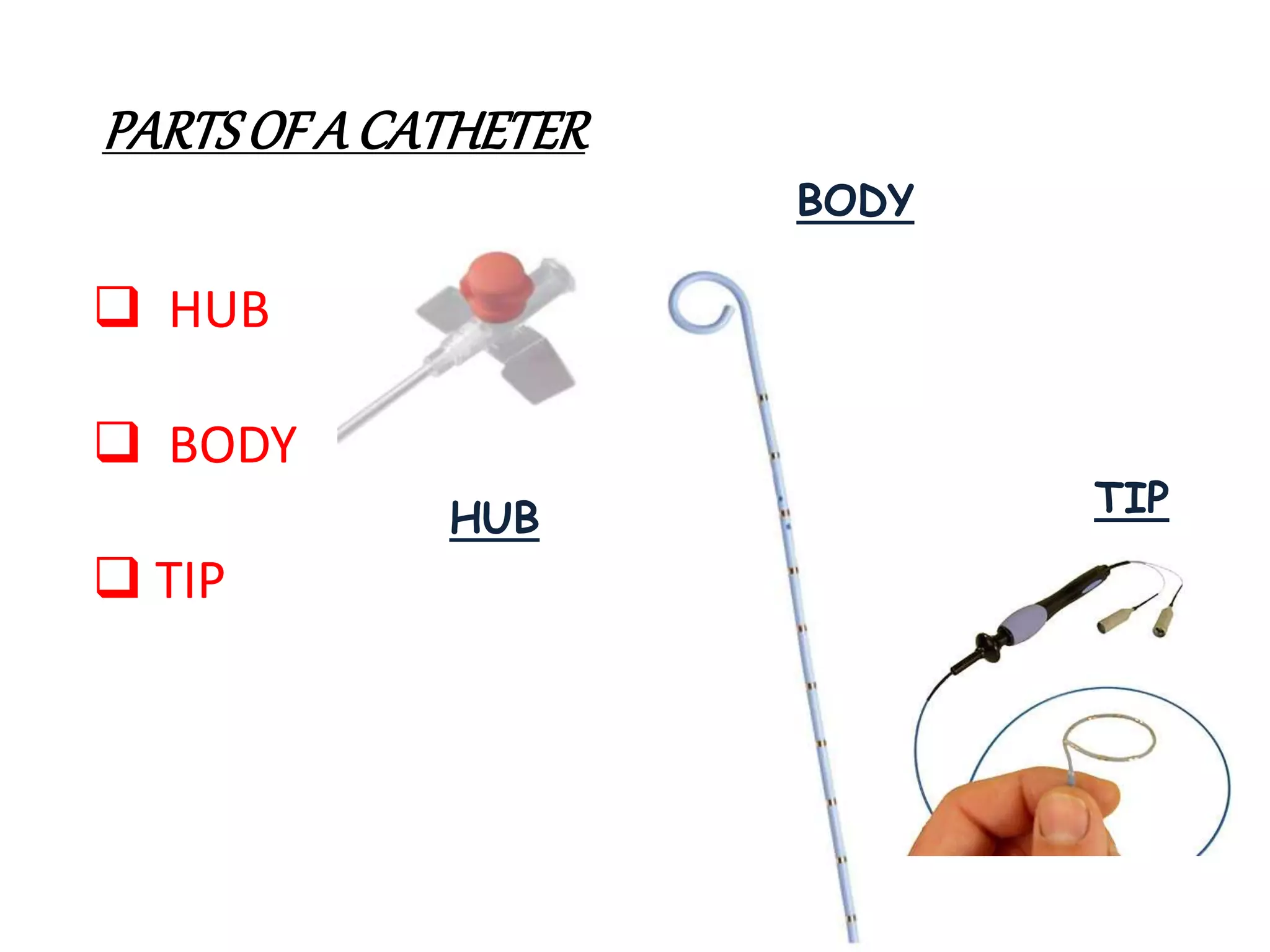
This document provides information about right heart catheters and angiographic catheters. It discusses the history of right heart catheters from 1929 to 1970. It then describes the diagnostic and therapeutic indications for right heart catheterization. The document outlines the parts of a catheter including the hub, body, and tip. It summarizes several general purpose catheters used for right heart catheterization including the Cournand, Goodale-Lubin, multipurpose, and Swan-Ganz balloon flotation catheters. Finally, it discusses several angiographic catheters used including the pigtail, NIH, Berman, Gensini, and Lehman catheters.



![• 1964- Ronald Bradley
• First person to describe the use of a
pulmonary-artery catheter in man
• Miniature catheter [extremely narrow portex
catheter (0·63 mm diam)] having no balloon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rightheartcatheters-220220054616/75/Right-heart-catheters-4-2048.jpg)









![Side Holes
ADVANTAGES
• Prevent catheter damping
[occlusion of coronary
ostium]
• Allow additional blood flow
out of tip, to perfuse artery
• Avoid catastrophic
dissections in the ostium of
artery
• Avoid disengagement
during injections
DISADVANTAGES
• False sense of security
becoz now aortic pressures
& not the coronary pressure
is being monitored
• Suboptimal opacification
• Makes catheter weak-
kinking at side holes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rightheartcatheters-220220054616/75/Right-heart-catheters-16-2048.jpg)