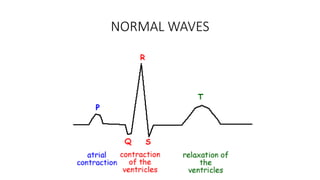
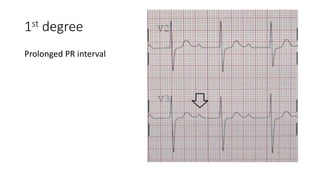
This document discusses different types of arrhythmias, including tachyarrhythmias like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia. It describes the causes, complications, and treatment options for each type. The document also covers bradyarrhythmias such as different degrees of atrioventricular block and sick sinus syndrome. Normal ECG findings are reviewed as well as how to properly read an ECG.