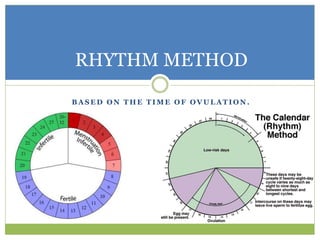
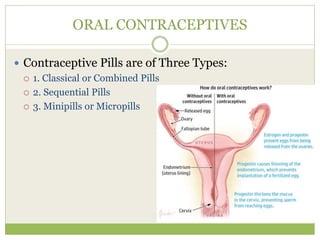
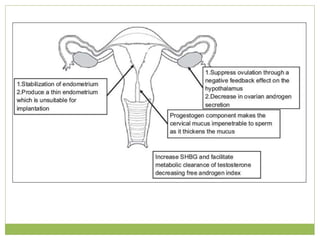
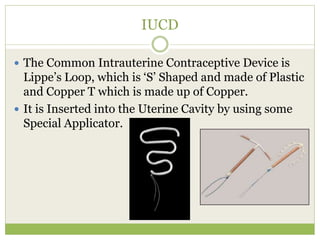
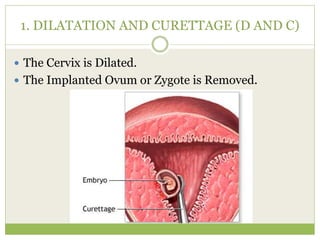
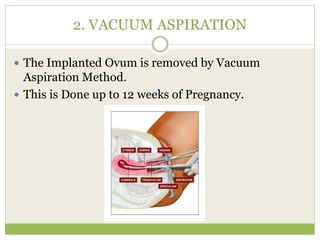
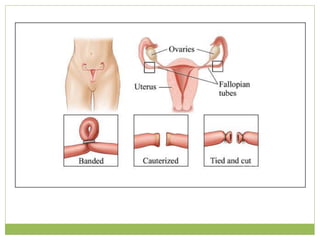
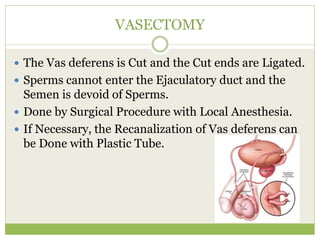
This document discusses various methods of fertility control, including natural methods like the rhythm method, barrier methods using condoms, spermicides, and IUDs. It also covers hormonal contraception using oral contraceptive pills, implants, and sterilization surgeries like tubectomy and vasectomy. The main mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages of each method are described. Permanent sterilization involves surgical procedures to cut and tie off the fallopian tubes or vas deferens.