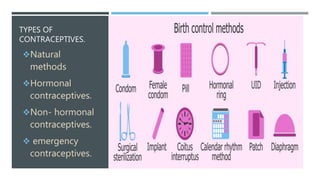
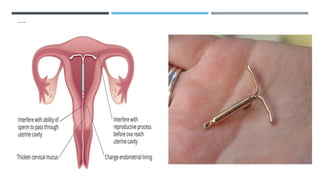
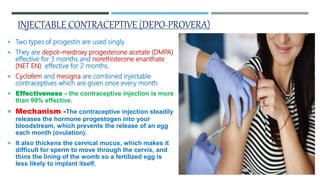
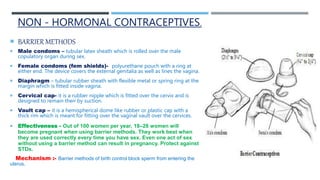
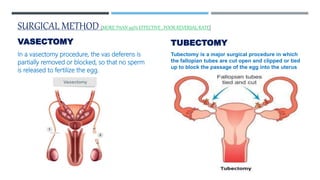
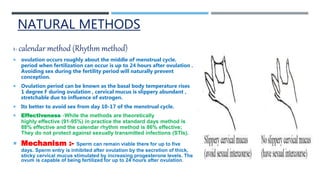
This document discusses various contraceptive types and their mechanisms of action. It describes the characteristics of ideal contraceptives and defines contraception. The main types discussed are hormonal methods like oral pills, patches, rings and IUDs; barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms; fertility awareness methods; emergency contraception; and surgical sterilization. Hormonal contraceptives work mainly by preventing ovulation while barrier methods block sperm from entering the uterus. Natural methods avoid sex during the fertile window but have a higher typical use failure rate than other methods.