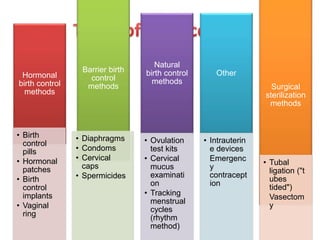
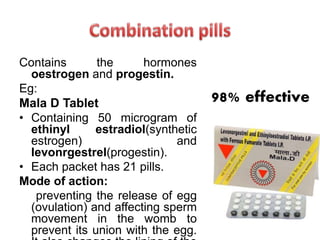
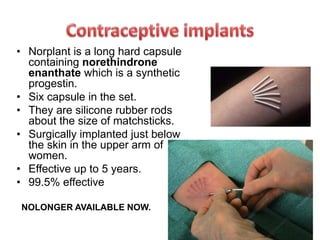
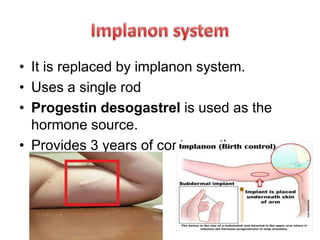
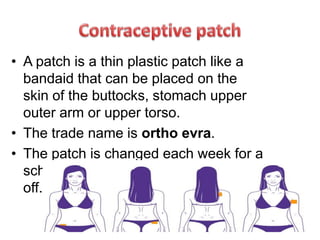
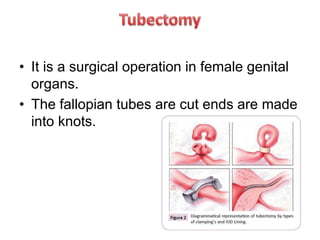
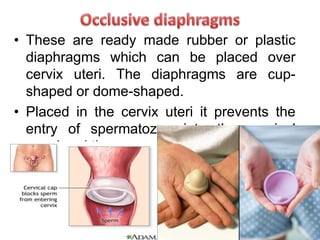
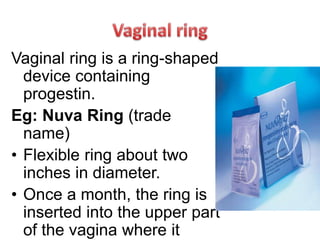
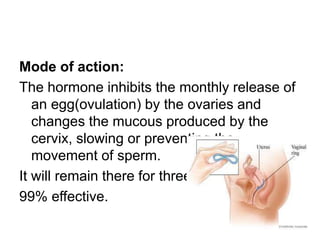
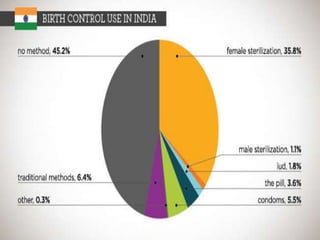
Population growth is steadily increasing, which can be controlled by decreasing births. The best way is birth control, which prevents fertilization through various methods like intrauterine devices, hormonal methods, barriers, natural methods, emergency contraception, surgical sterilization, and vaccines currently in development. Common birth control methods include copper-T or Lippes loop IUDs inserted in the uterus, hormonal pills, injections, implants and patches, male condoms, female sterilization procedures like tubectomy, and male vasectomy.