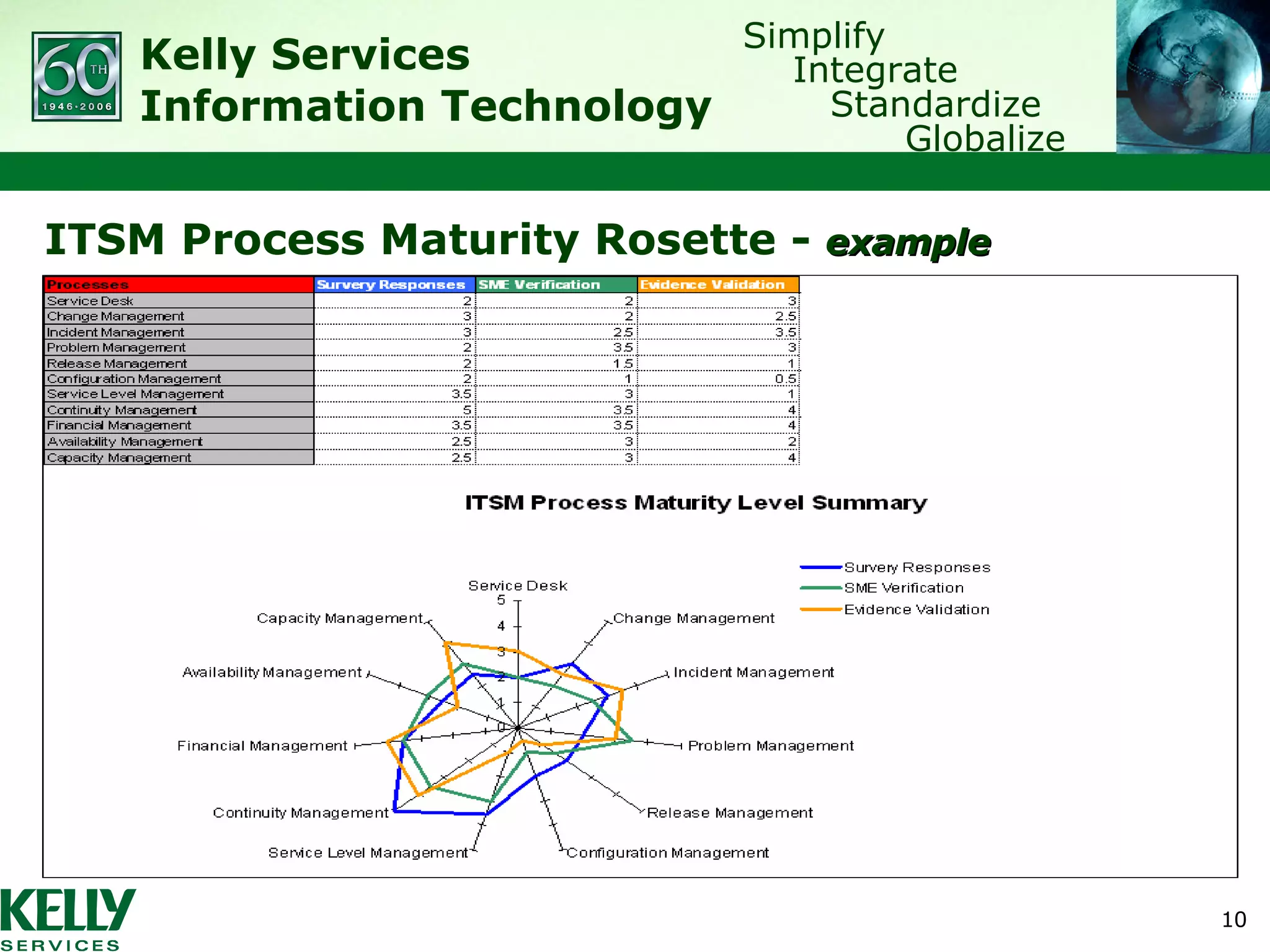
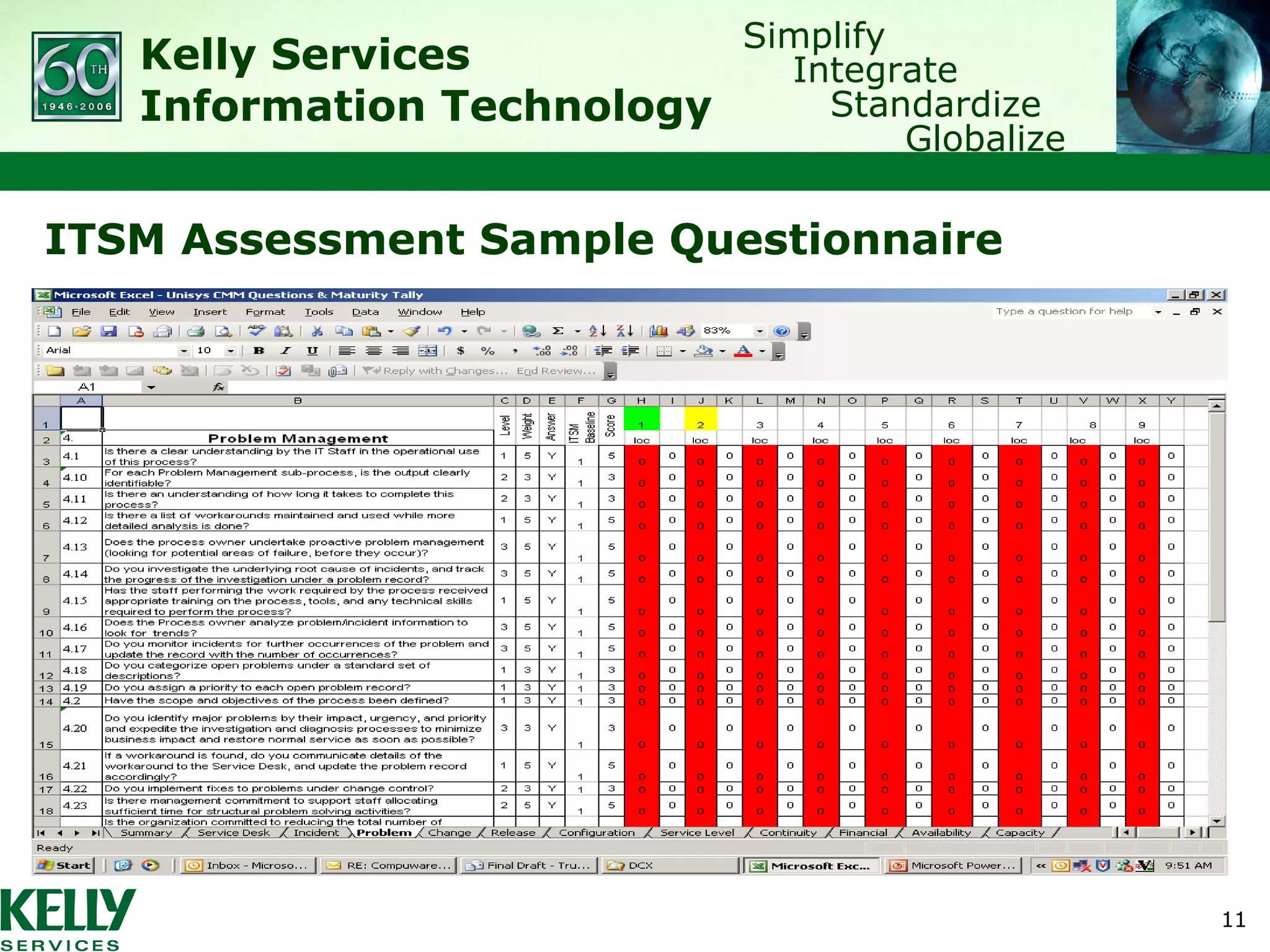
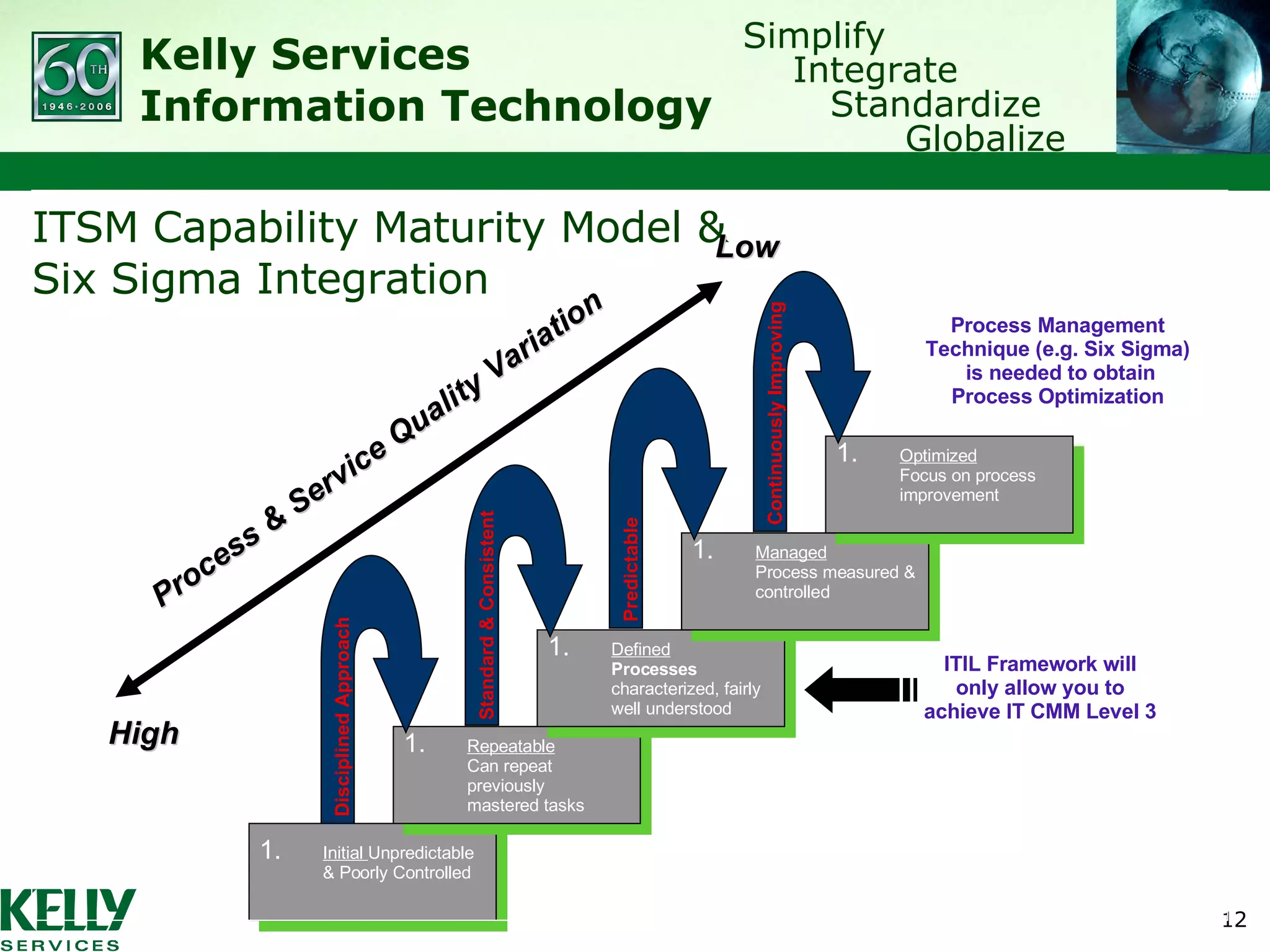
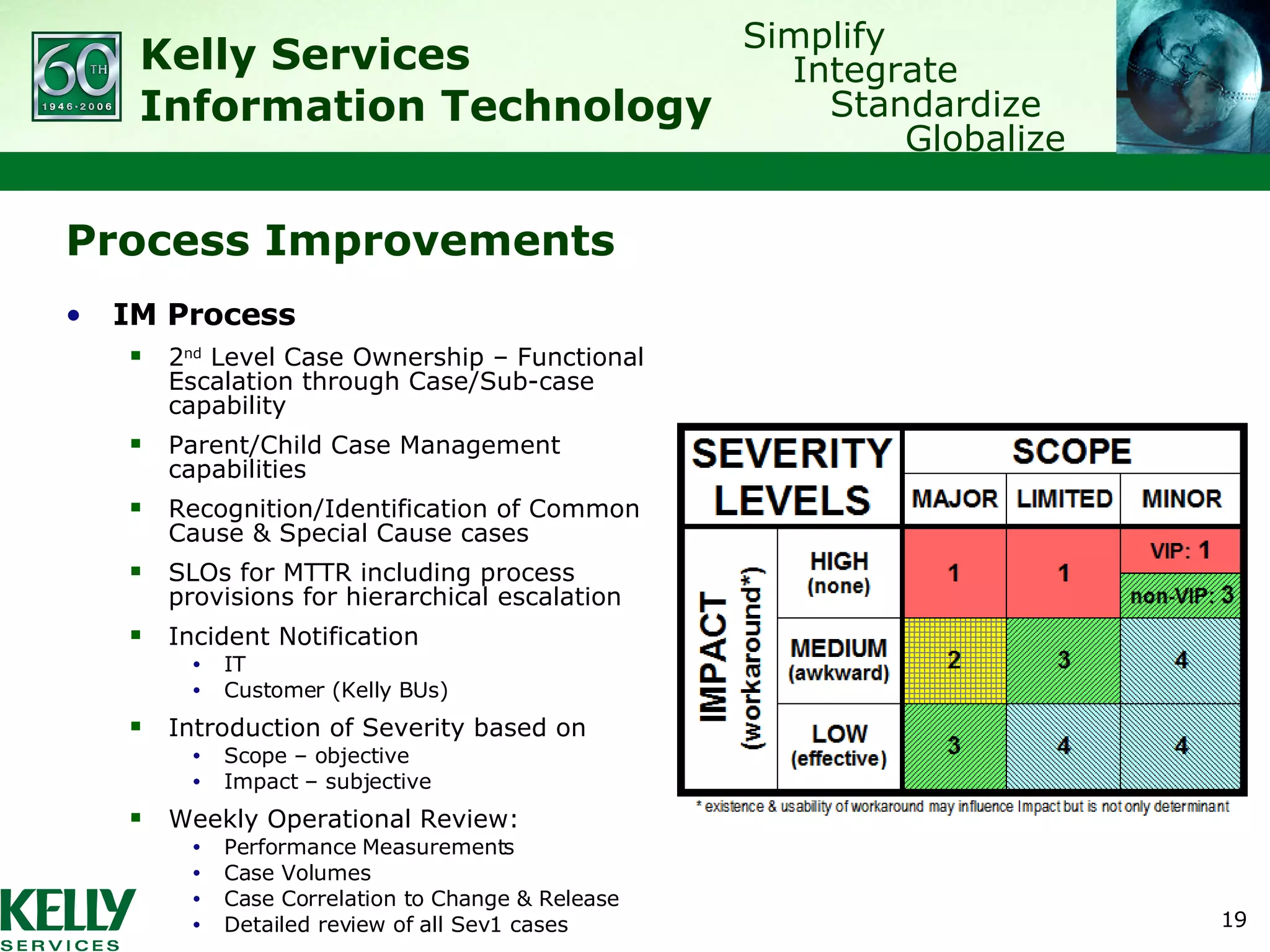
The document summarizes Kelly Services' transformation of its IT service desk to better align with ITIL best practices. Key points include:
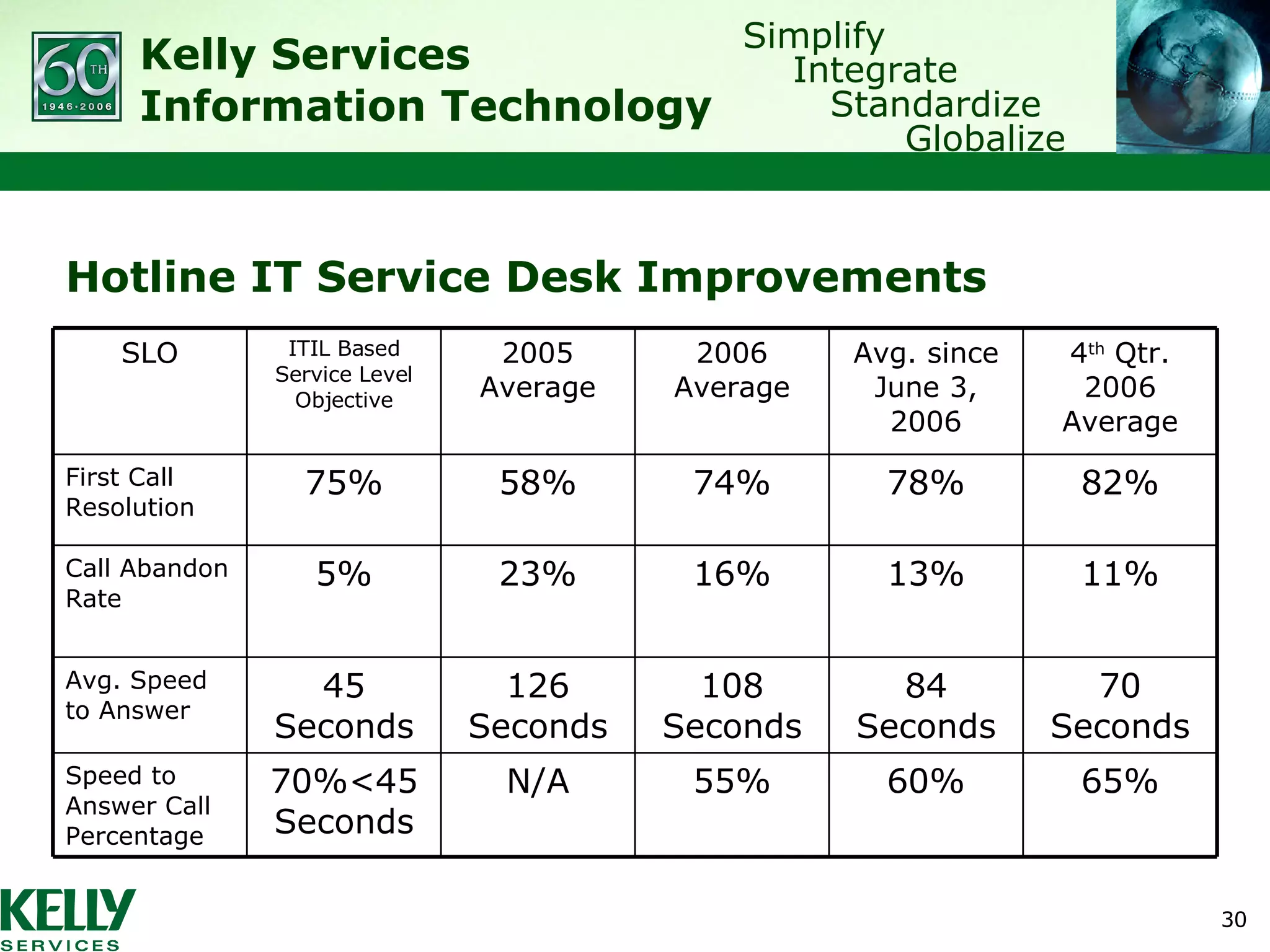
- Kelly conducted an assessment that found its previous service desk model lacked maturity and was inefficient
- It restructured the service desk into technical and business teams with specialized roles to improve incident and problem management
- Metrics like first call resolution, speed to answer, and customer satisfaction improved as a result of adopting ITIL processes and tools