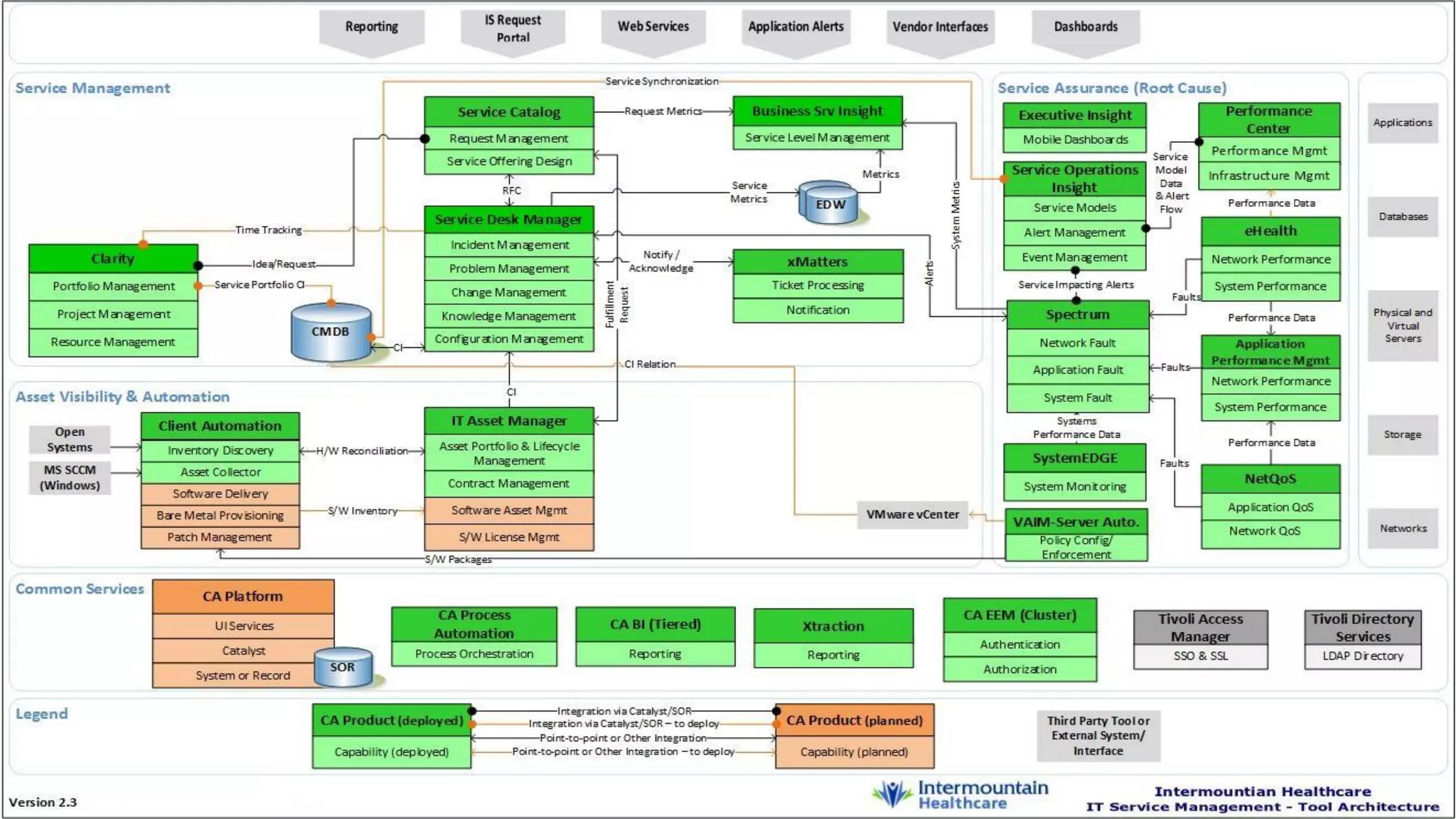
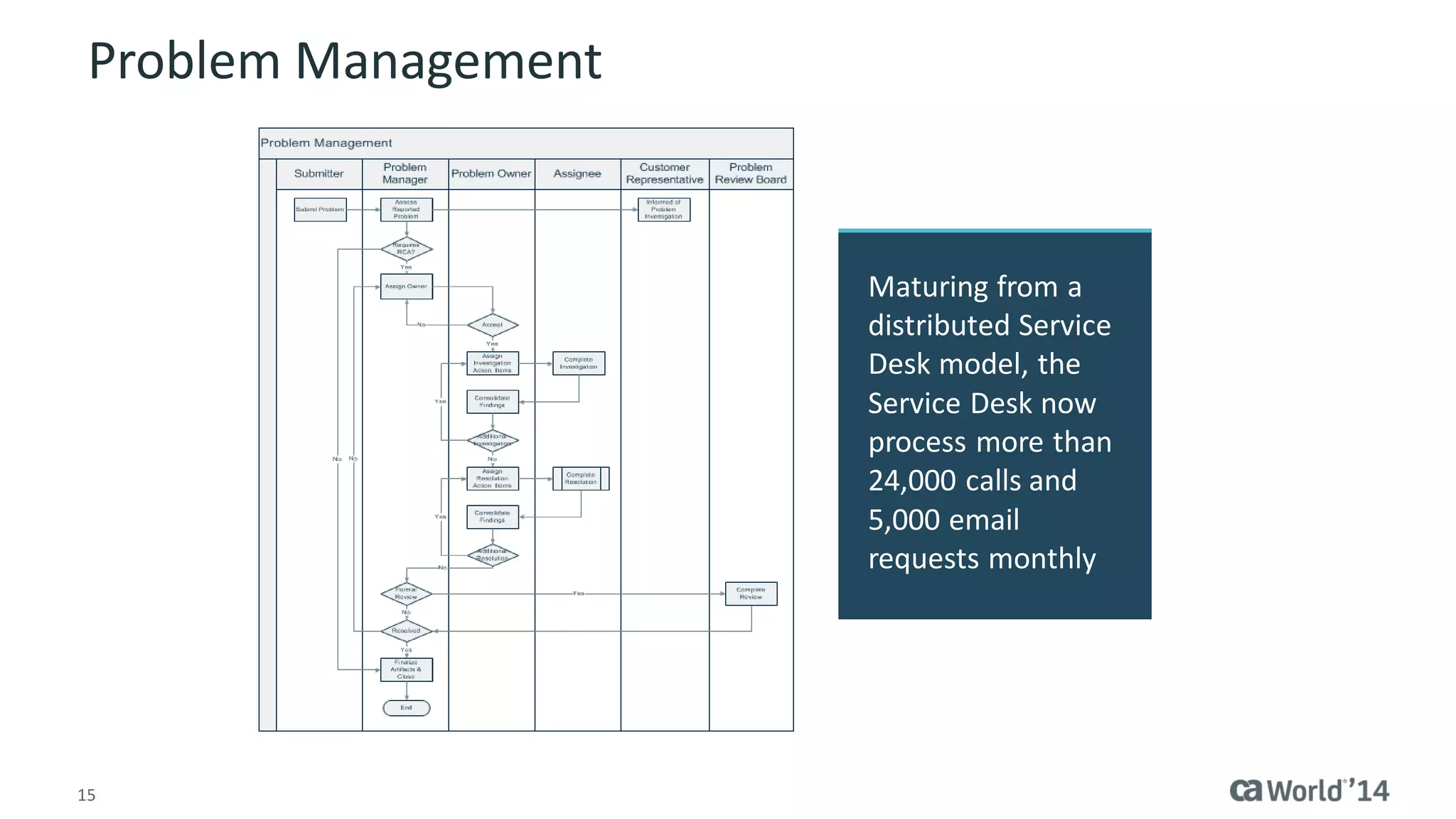
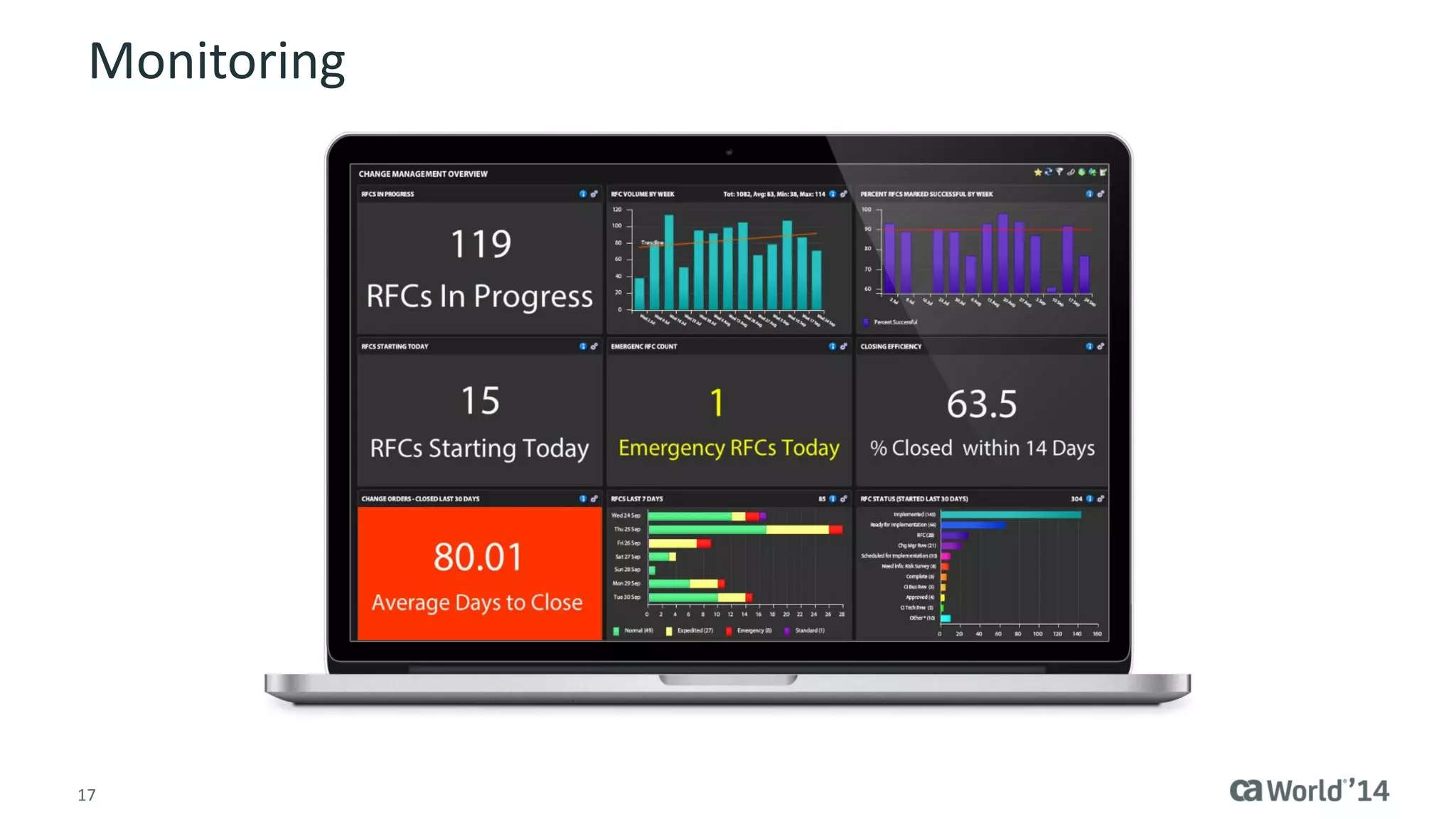
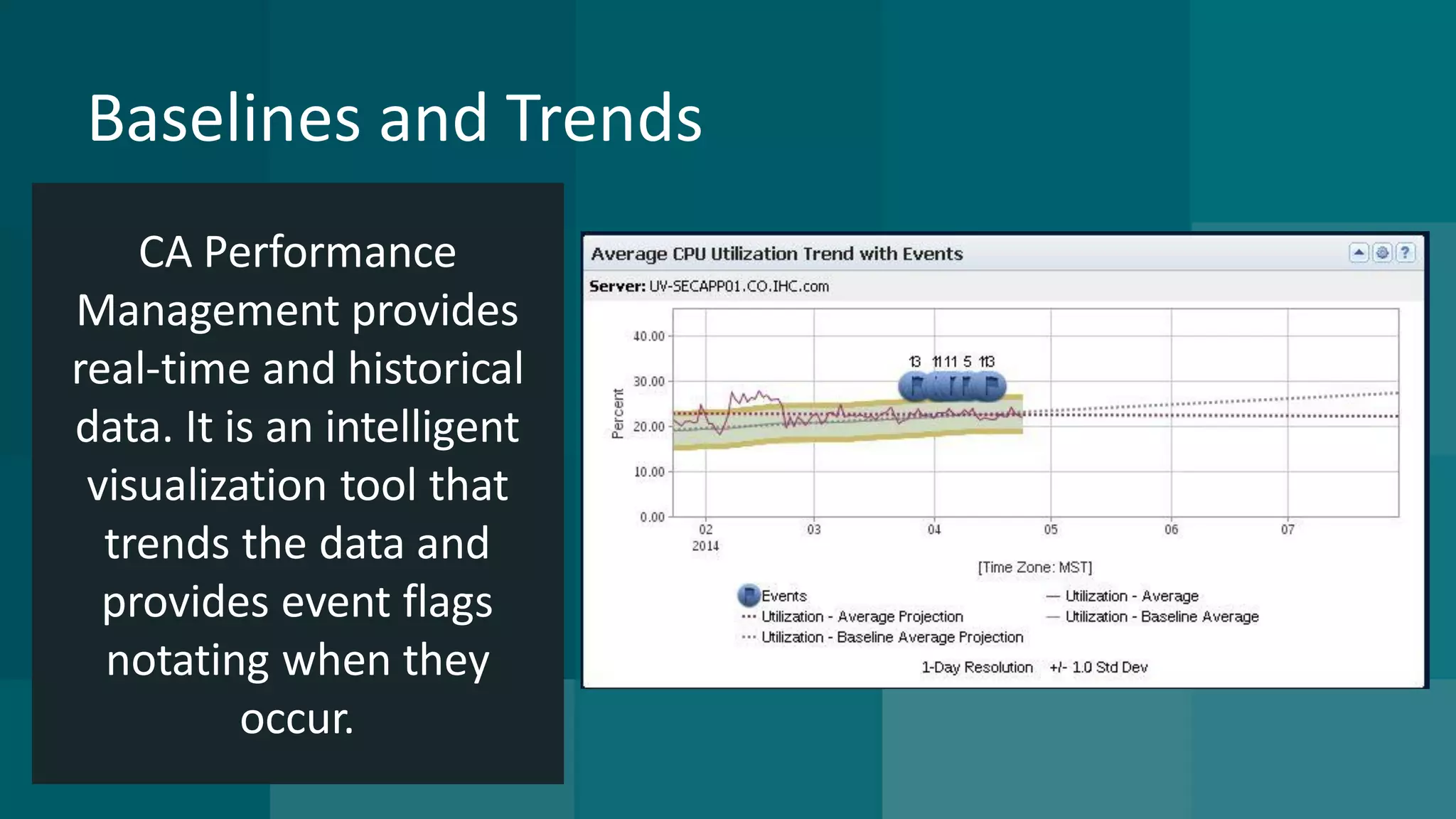
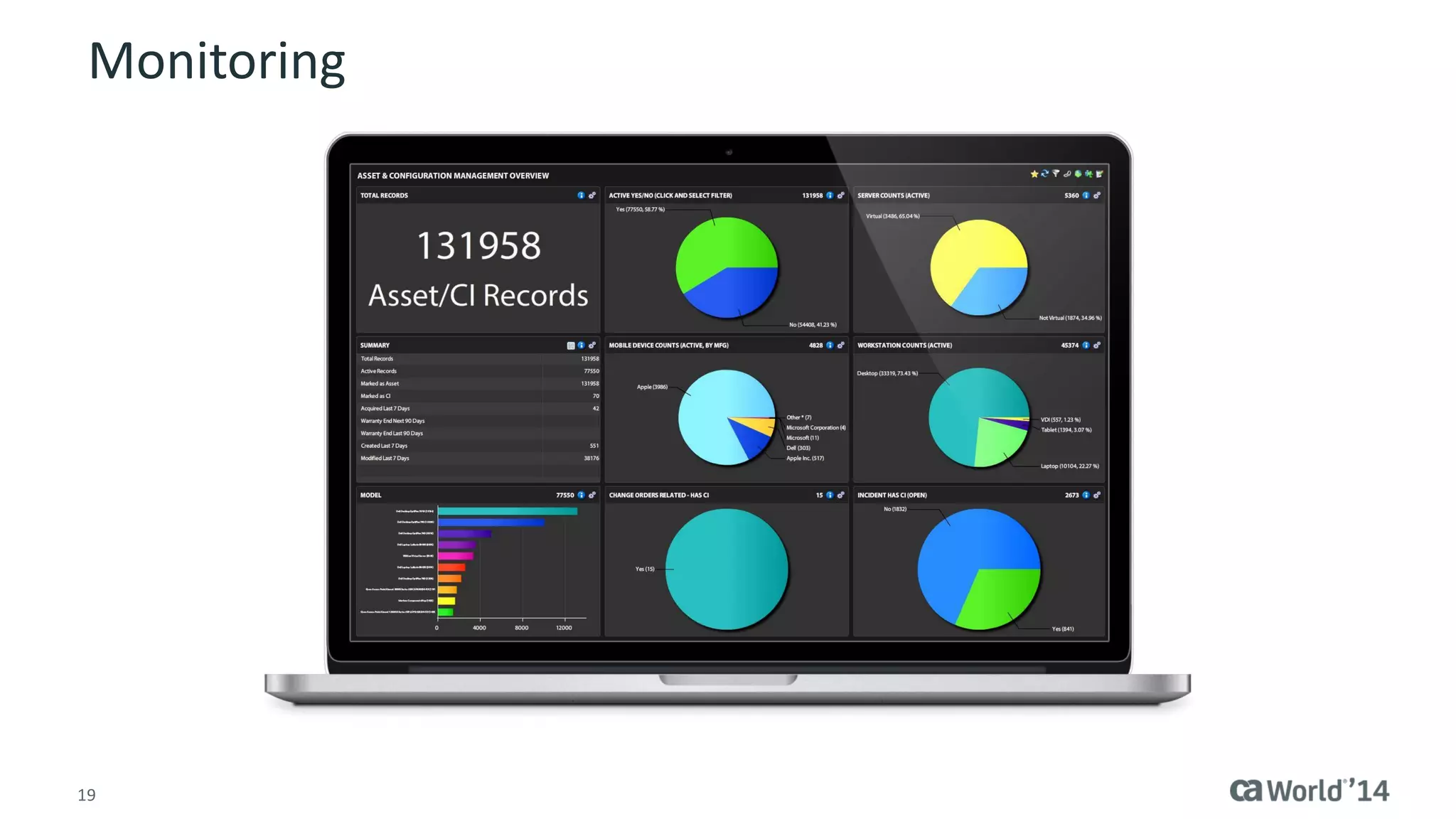
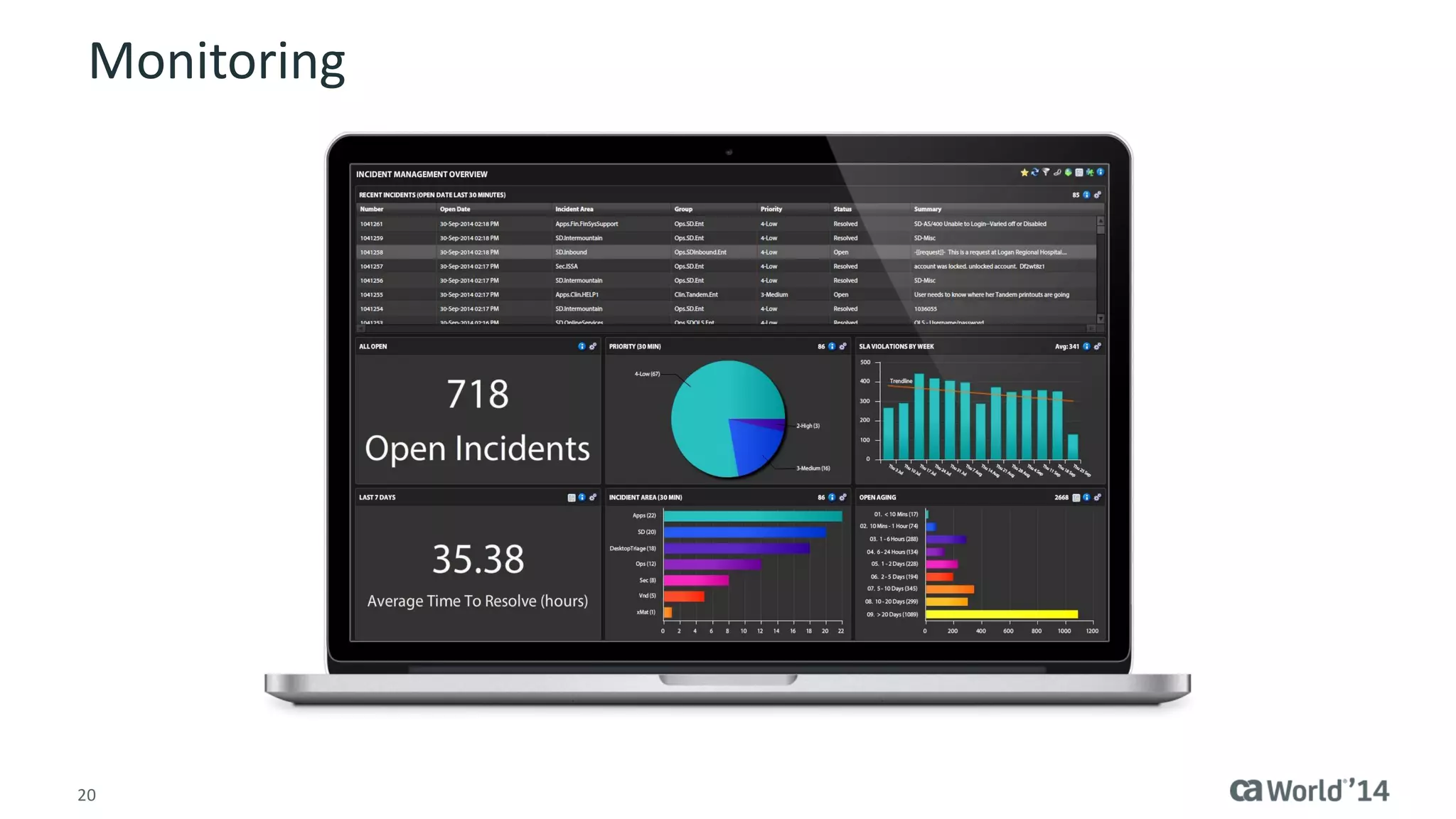
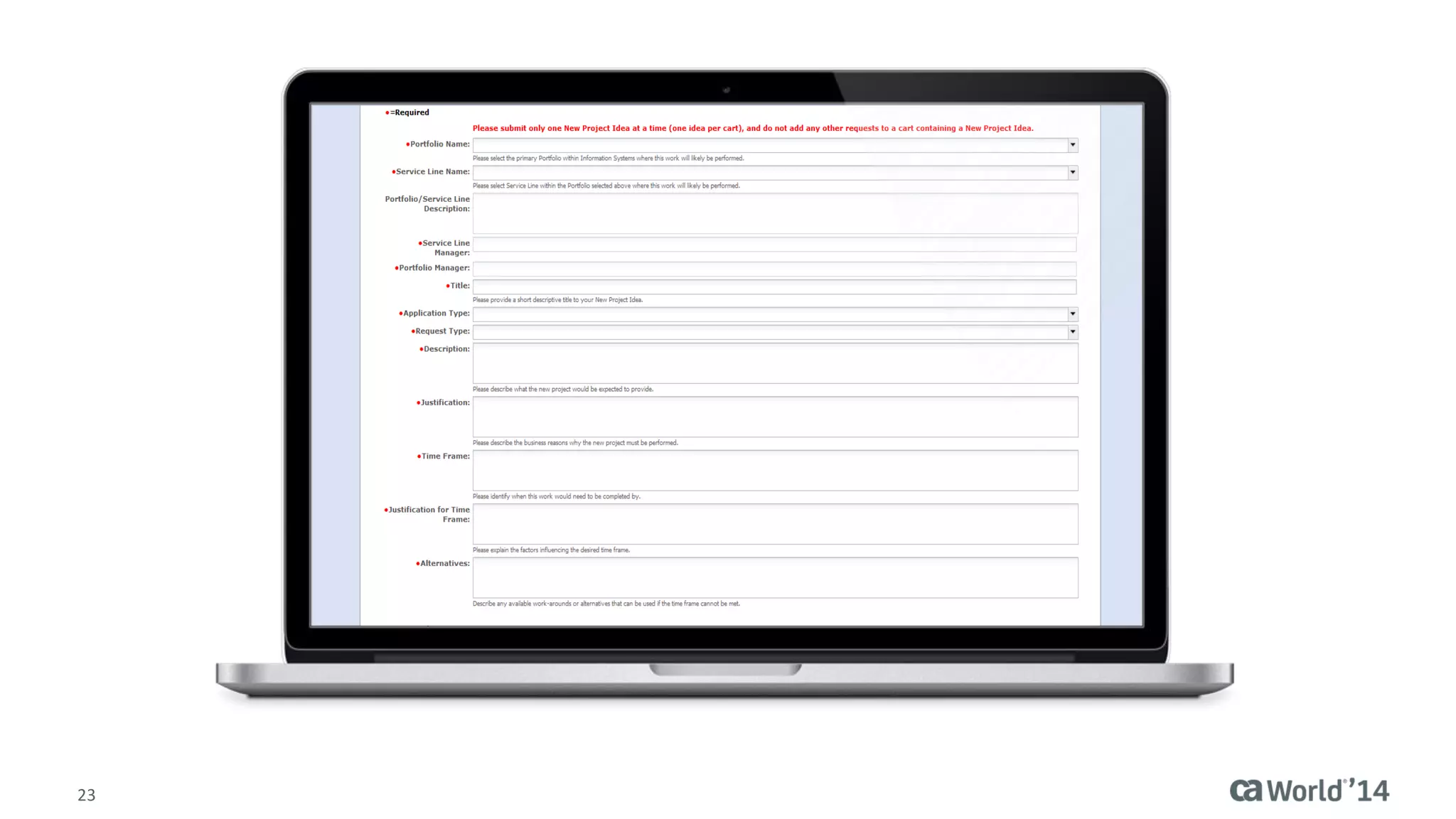
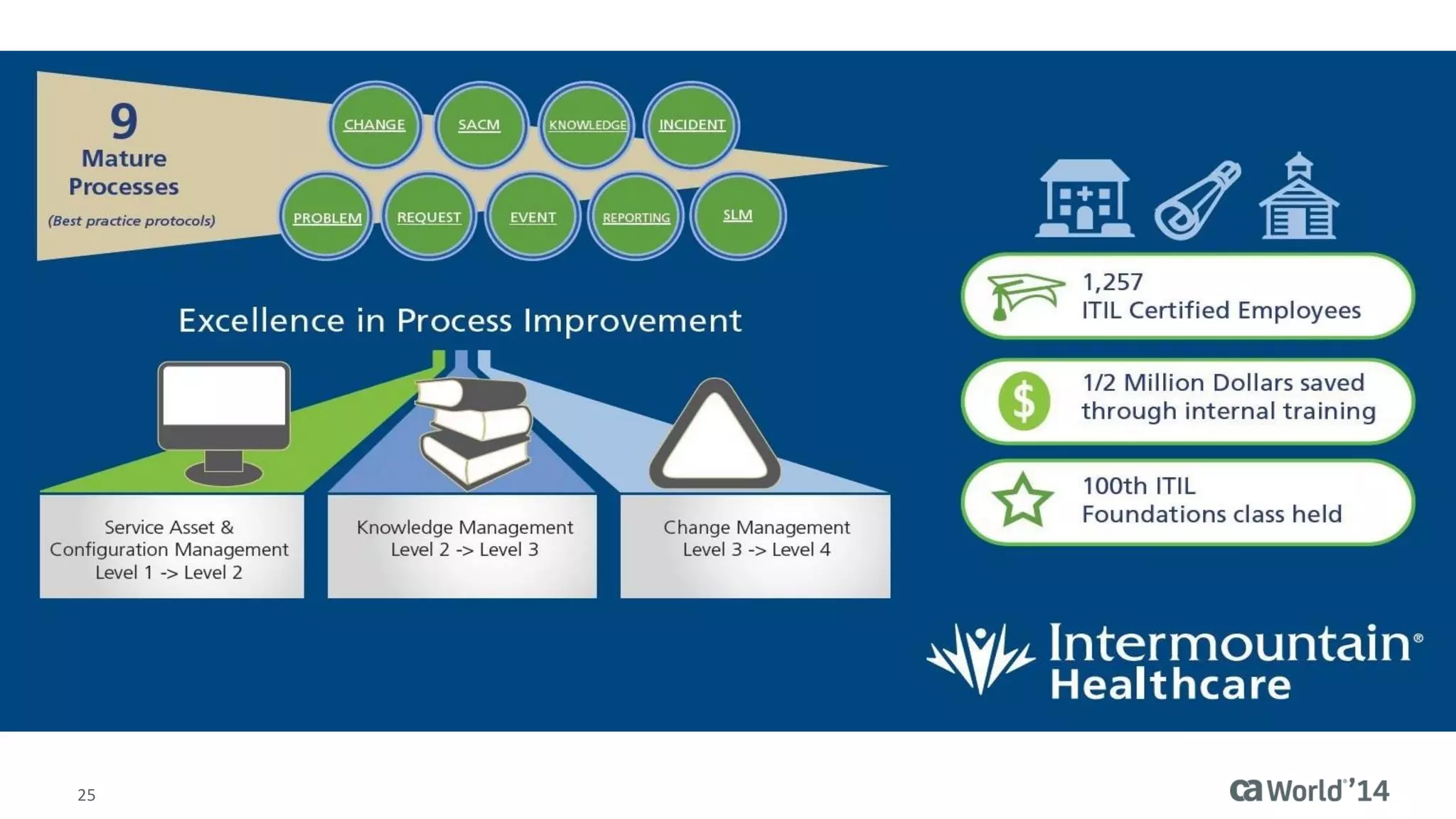
The document details the integration of IT service management (ITSM) at Intermountain Healthcare, emphasizing the necessity for a standardized, ITIL-oriented approach to enhance efficiency and improve service delivery. It highlights the challenges faced during the implementation, such as inconsistent executive support and inadequate documentation, and outlines the strategies employed to address these issues, including ITIL certification for staff and the establishment of a dedicated service management organization. The outcome includes improved communication, better management of requests and changes, and enhanced operational efficiency across IT services.