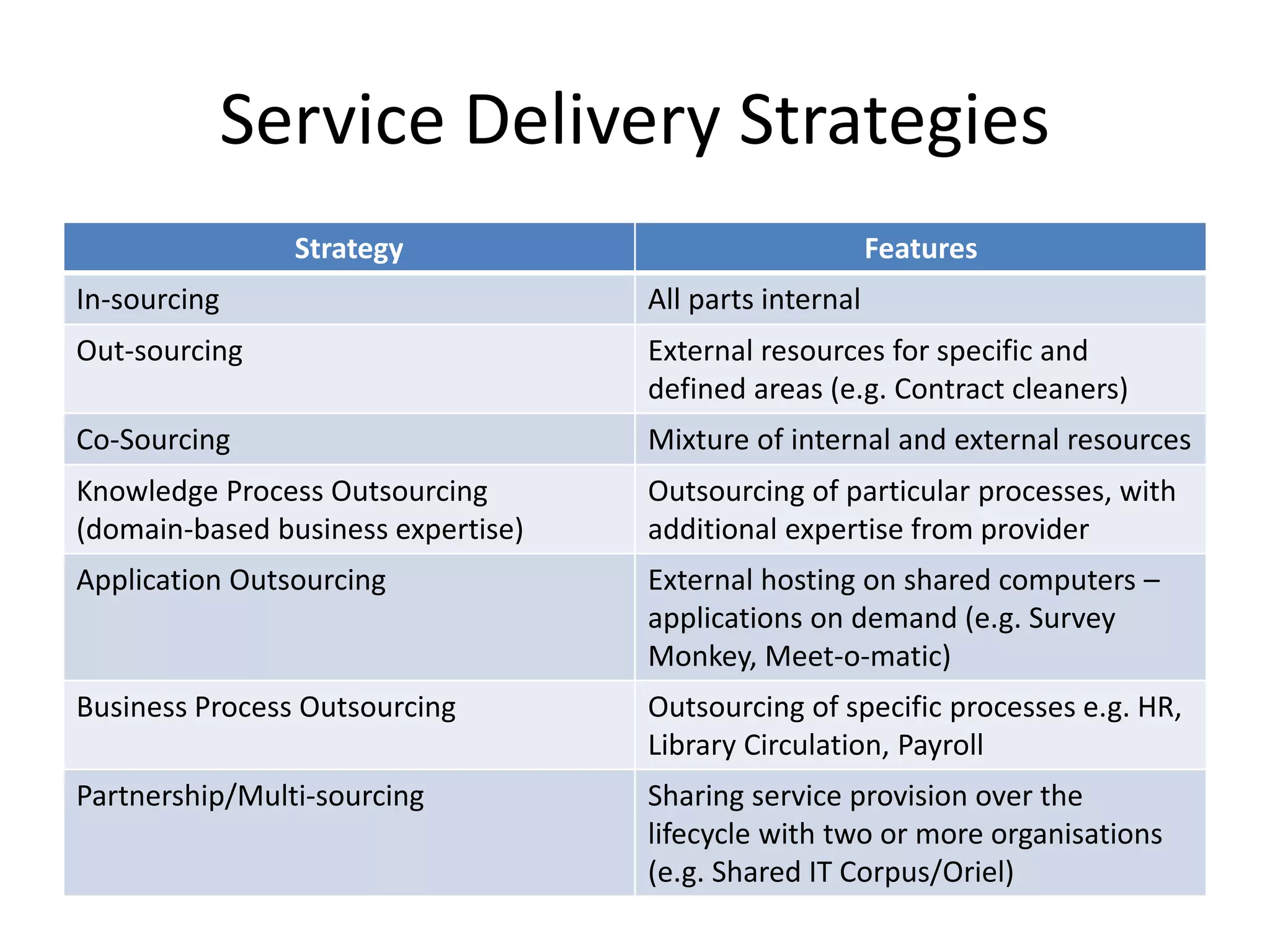
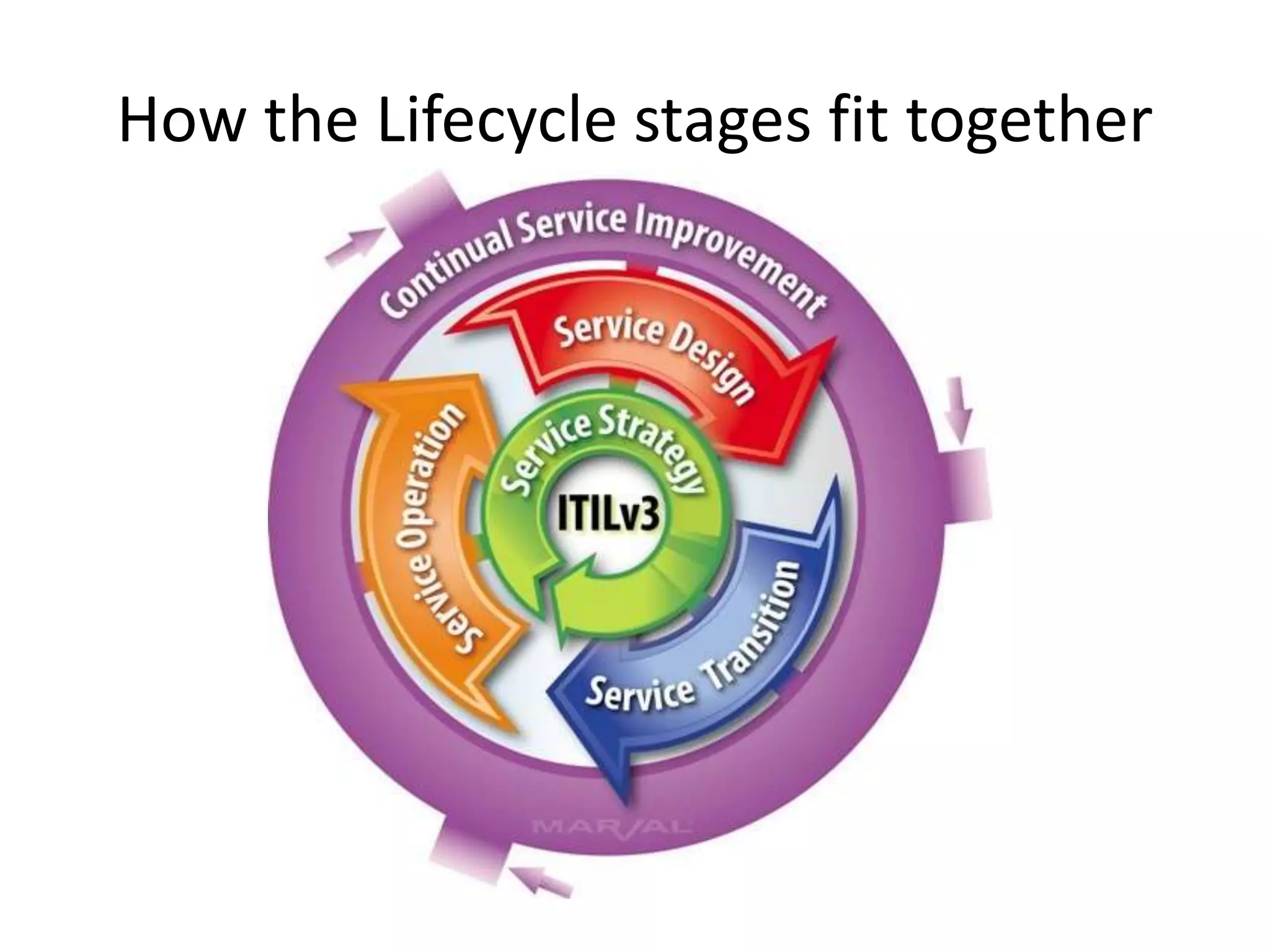
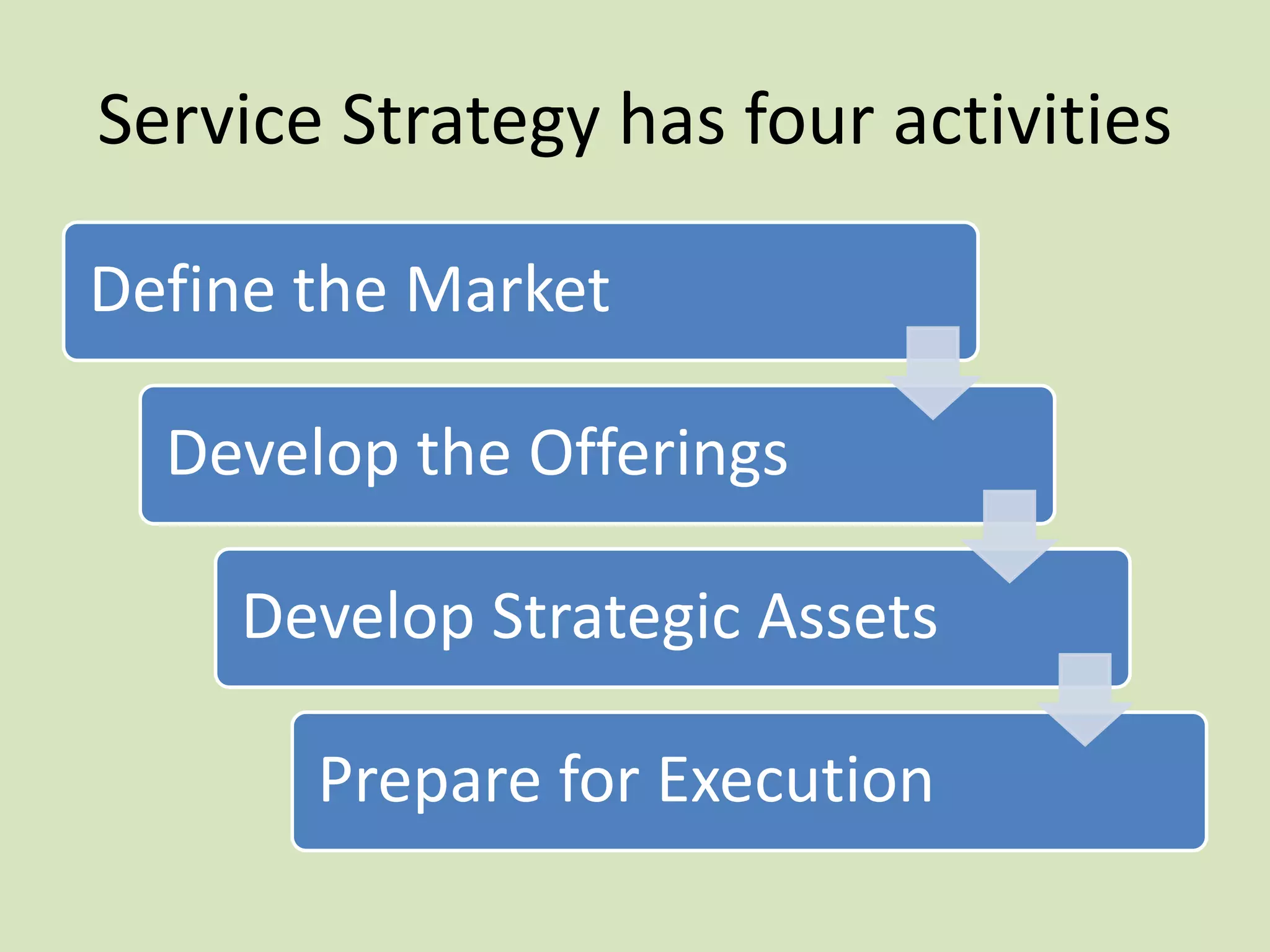
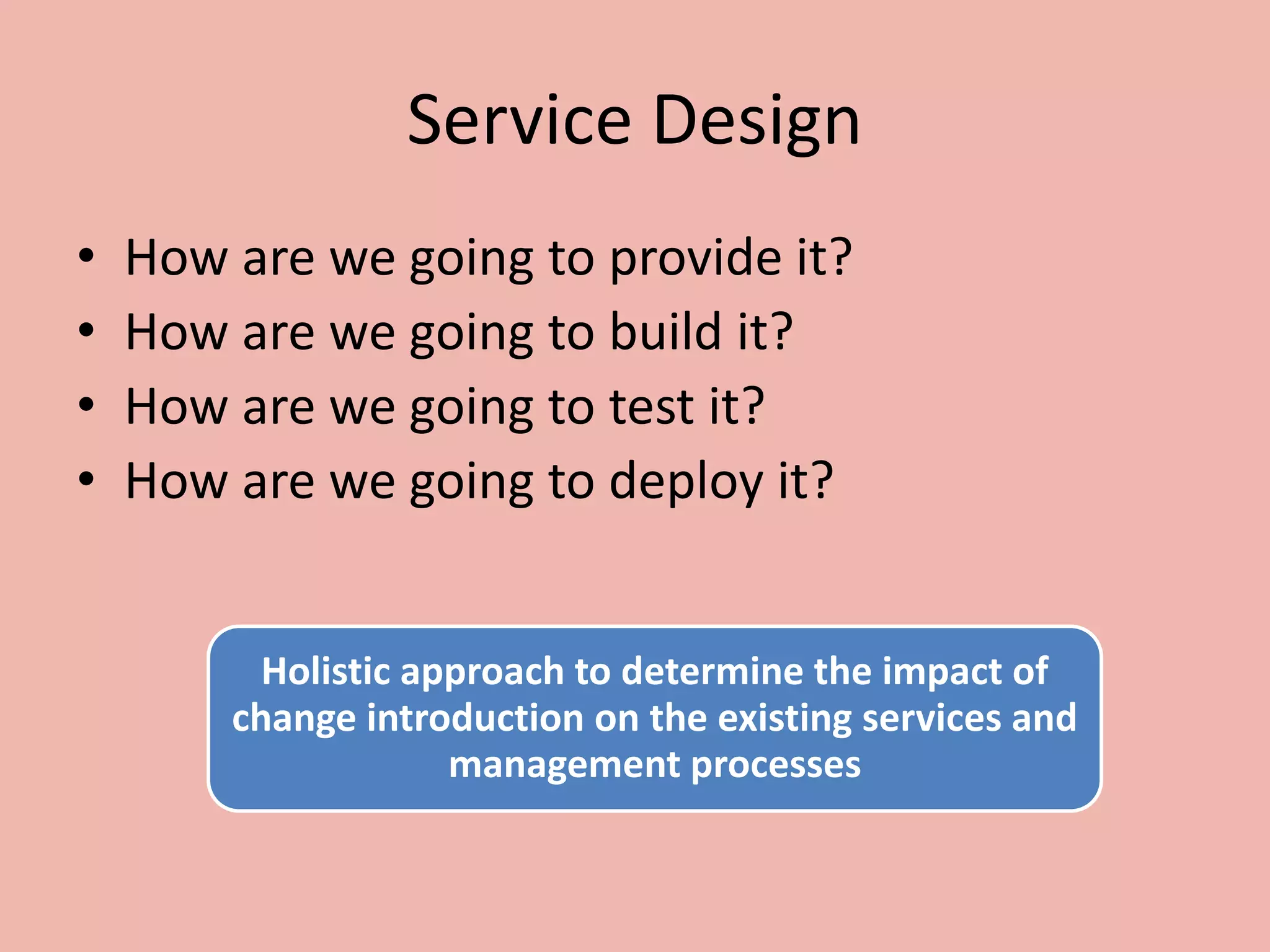
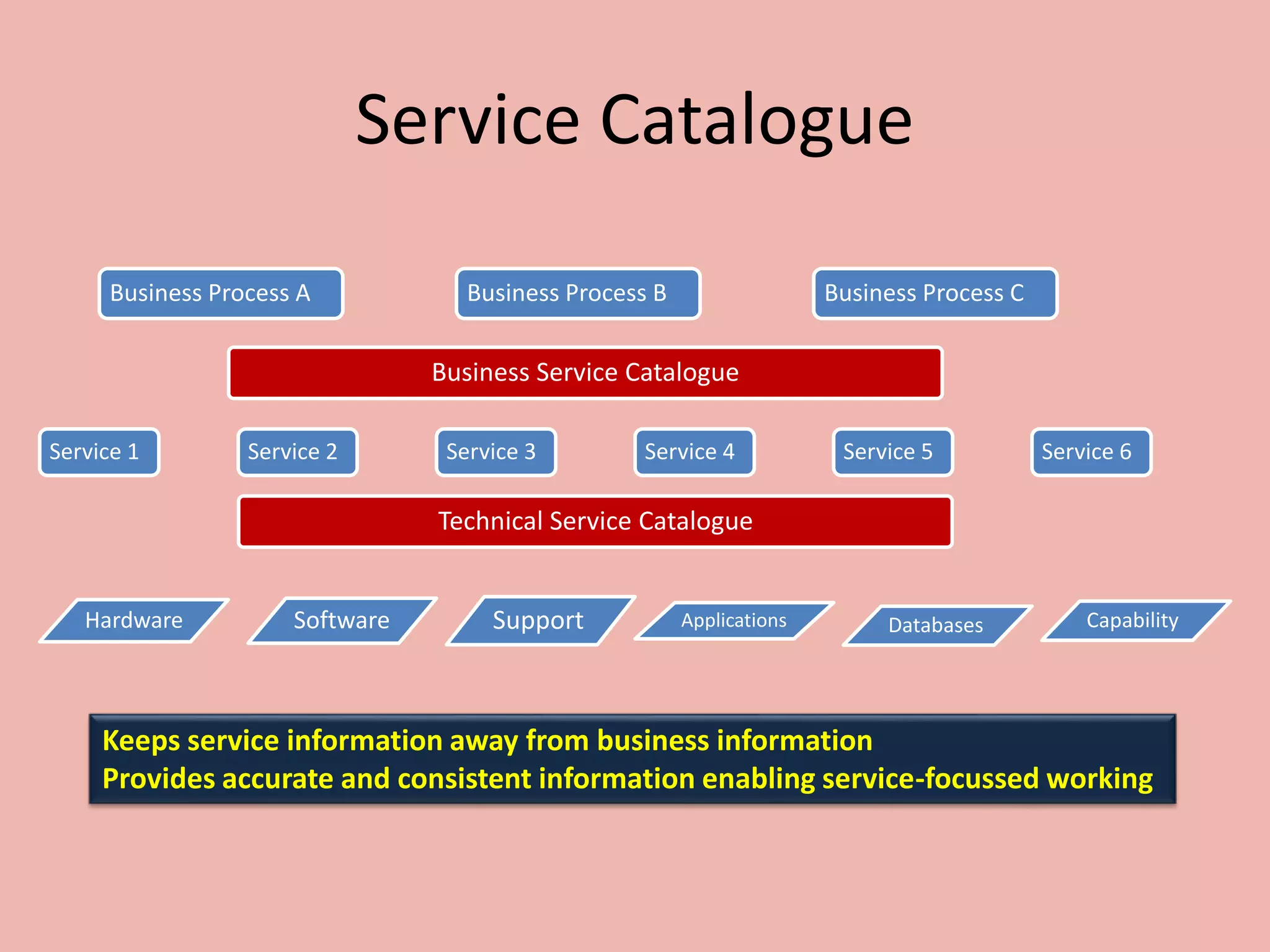
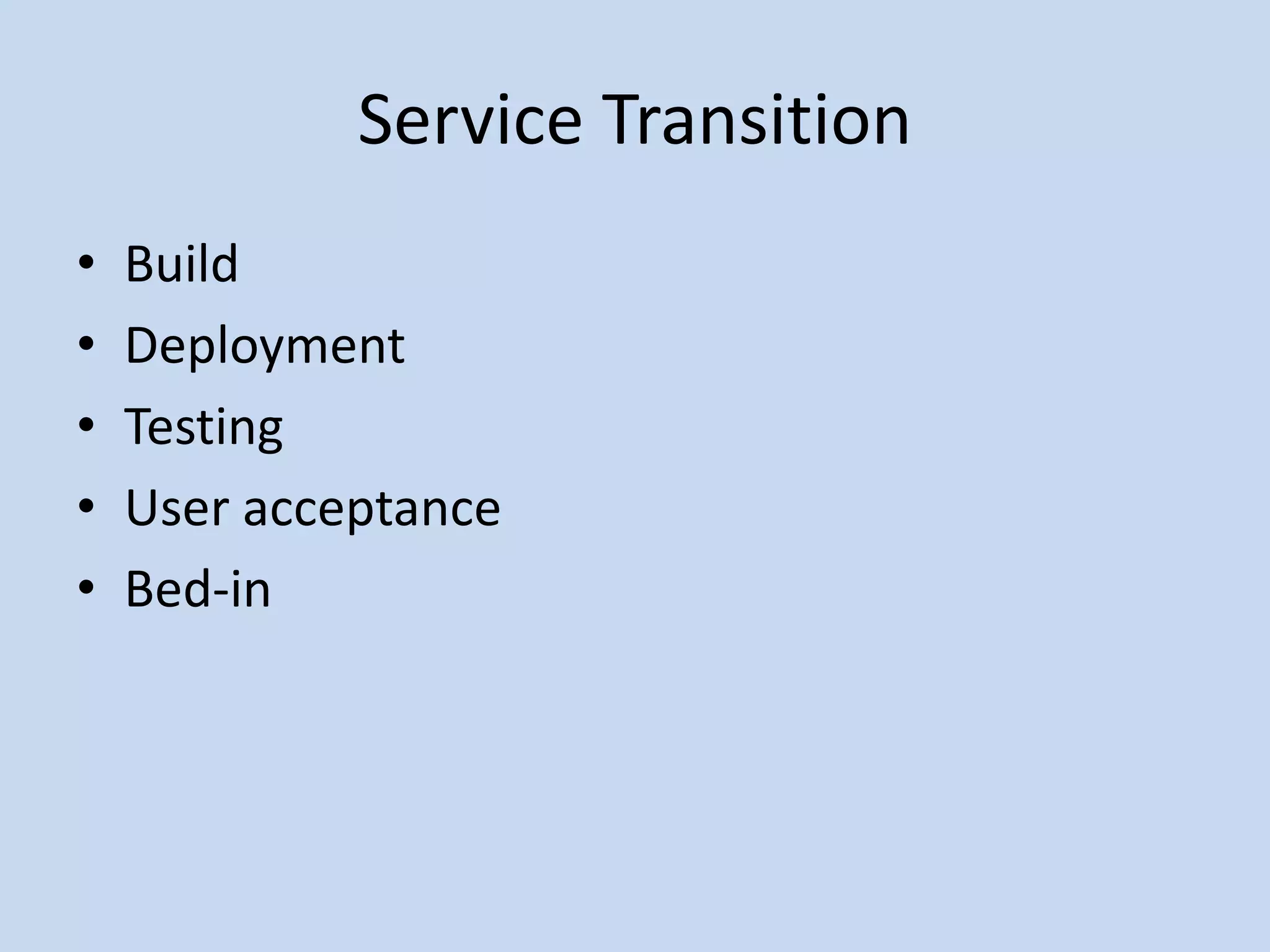
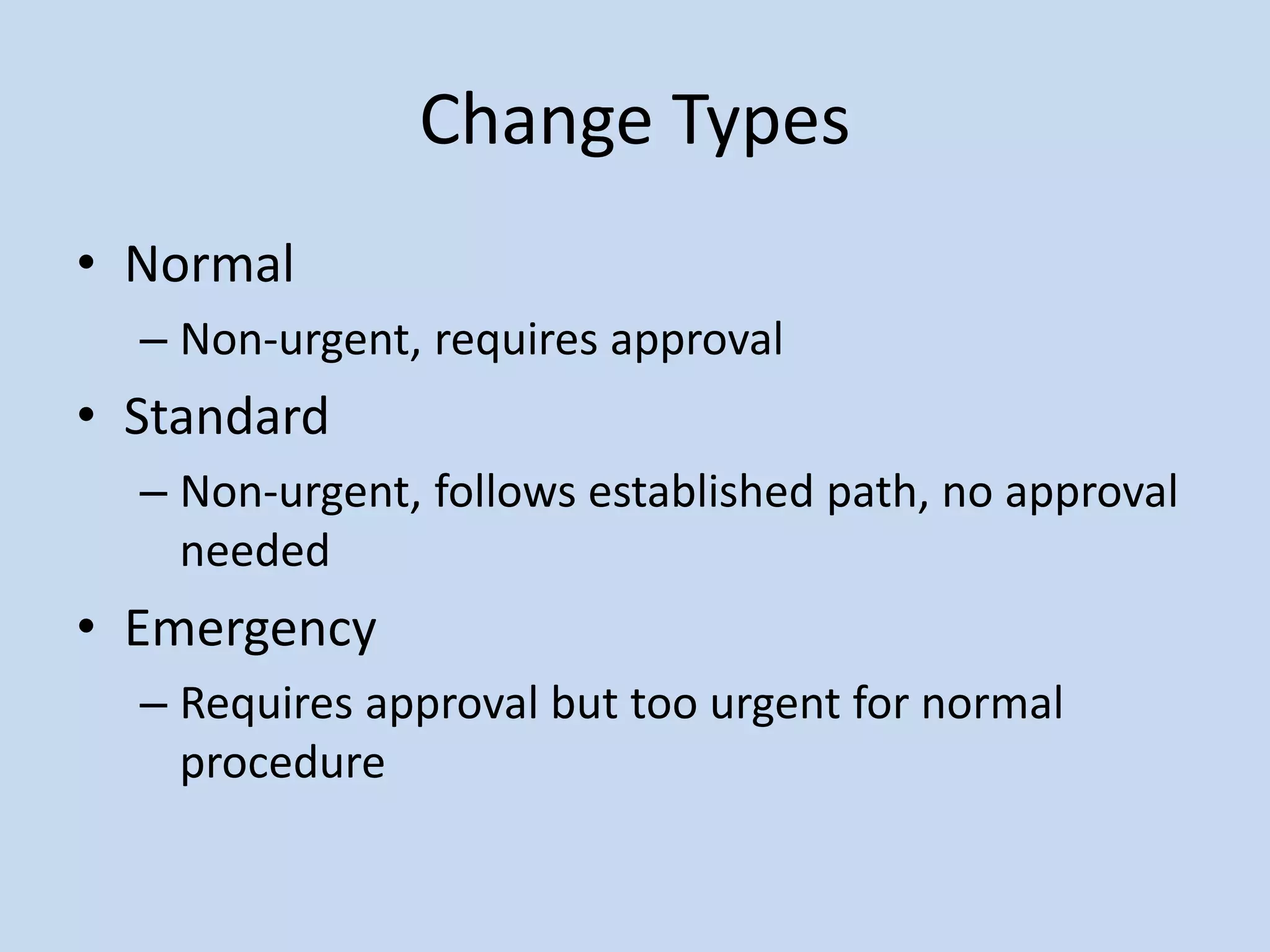
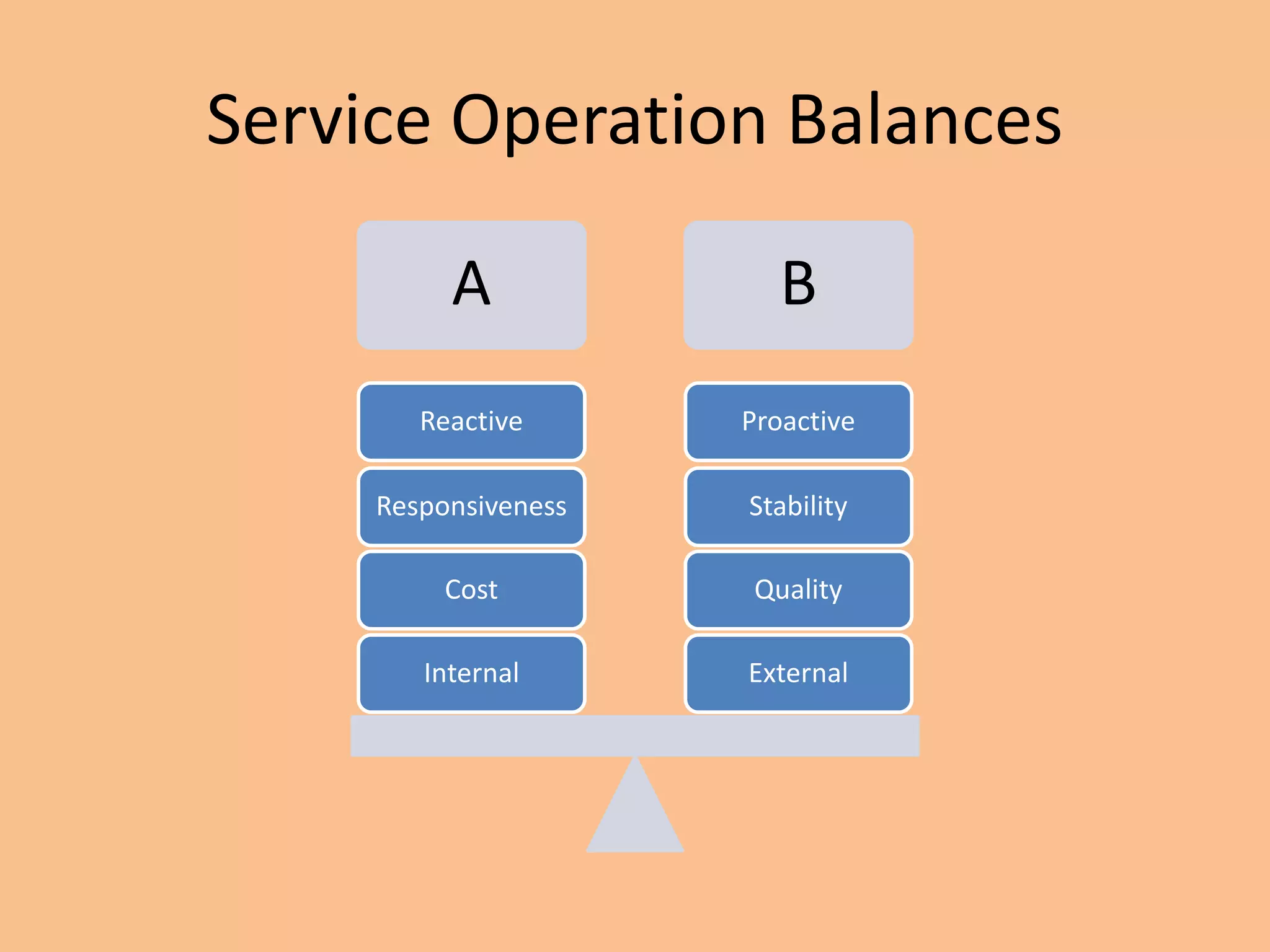
ITILv3 provides best practices for IT service management. It defines key concepts like service, service level agreements, and the IT service lifecycle. The service lifecycle consists of five stages - service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. ITIL aims to help organizations deliver high-quality IT services through standardized processes and roles.