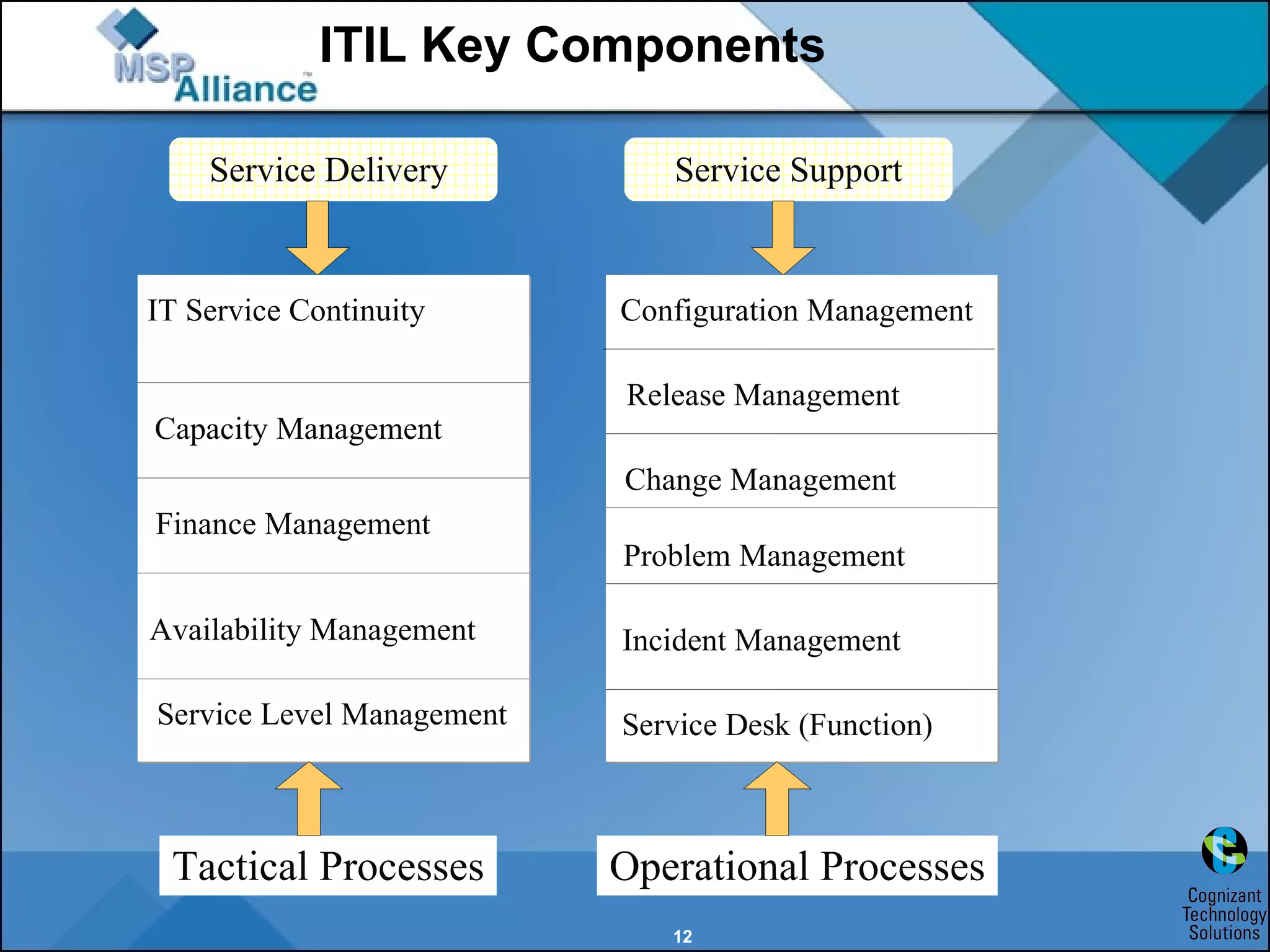
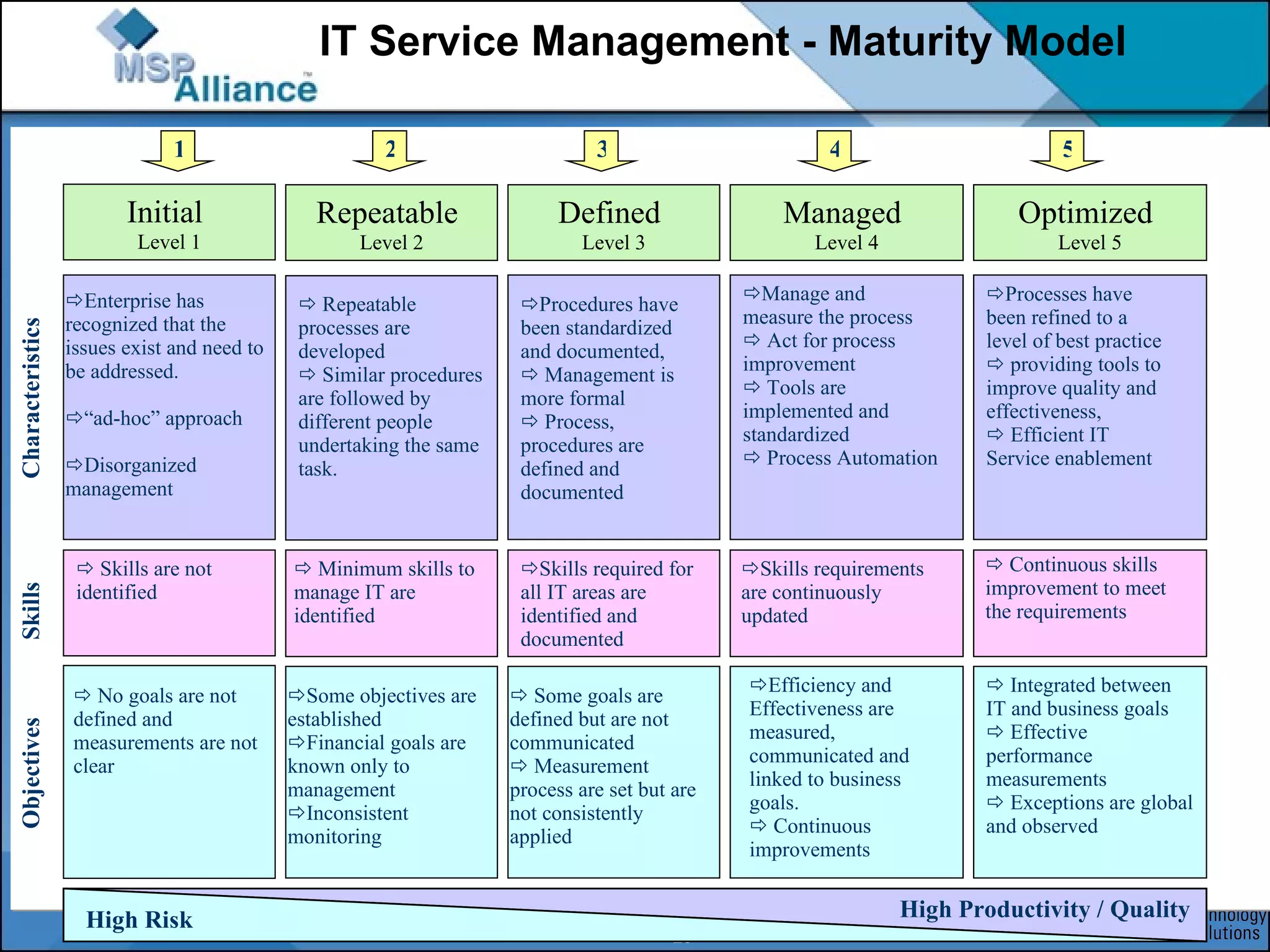
The document discusses IT service management frameworks and standards including ITIL, ISO 20000, COBIT, and ISO 27001. It uses the example of an IT services company called InfraRemote to illustrate how implementing these frameworks can help address issues like unmet service level agreements, poor customer support, and a lack of processes. Adopting standards like ITIL can help formalize processes, align IT with business goals, improve service quality, and increase maturity from an initial ad-hoc level to optimized processes.























![For any questions or further details, Please contact [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mspitgoveranceandservicedeliveryprocess-123708158206-phpapp02/75/Msp-It-Goverance-And-Service-Delivery-Process-26-2048.jpg)