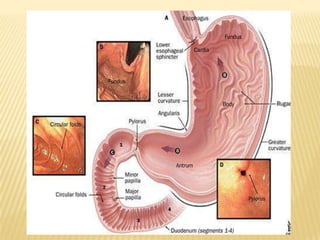
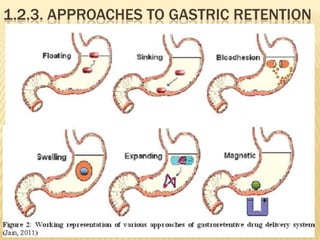
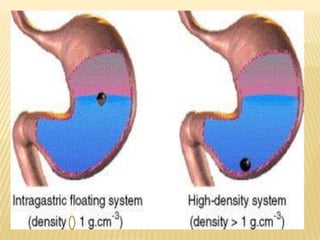
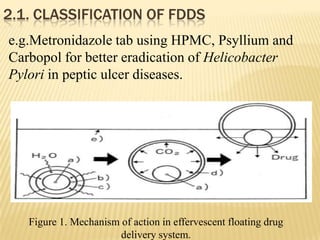
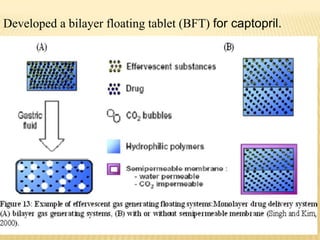
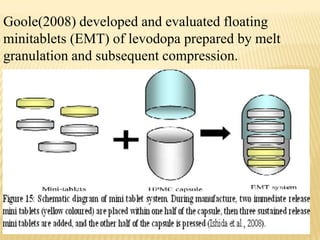
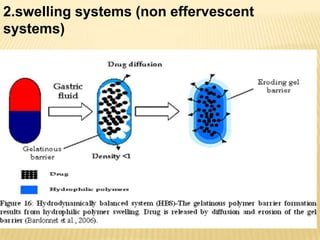
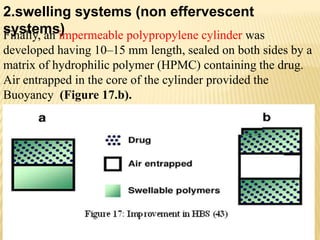
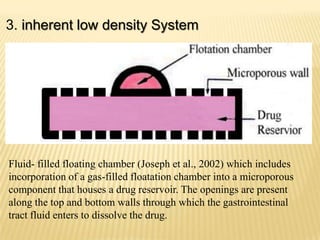
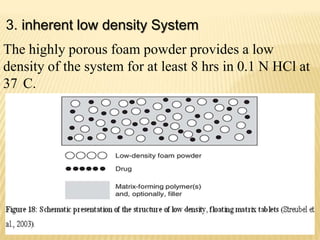
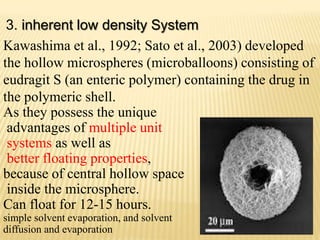
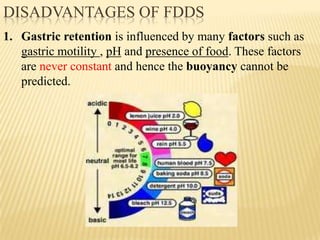
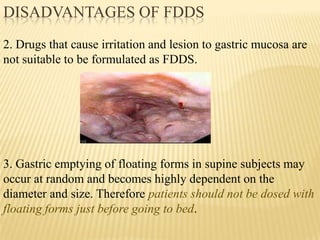
This document provides an overview of floating drug delivery systems (FDDS). It defines FDDS as systems that can remain in the gastric region for several hours, prolonging the gastric residence time of drugs. The document classifies FDDS into two main types - effervescent systems that use gas formation and non-effervescent systems that use swelling polymers. It lists advantages such as improved drug absorption and controlled delivery. The document also summarizes some research articles on developing FDDS for various drugs.