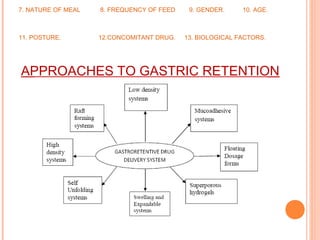
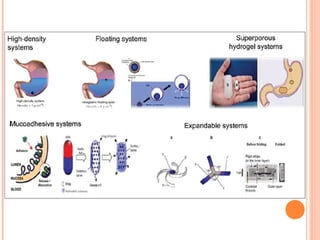
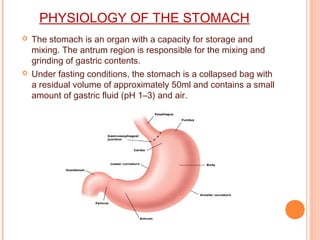
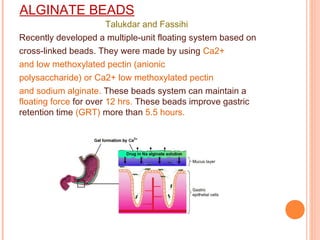
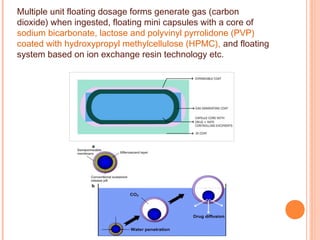
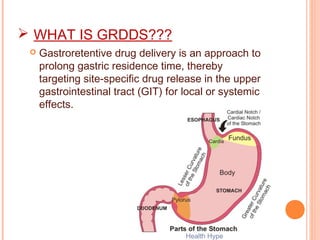
This document discusses gastroretentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS), which aim to prolong the gastric residence time of drugs to target drug release in the upper gastrointestinal tract. GRDDS are needed because oral drugs often have short gastric retention times and unpredictable emptying, resulting in incomplete drug release. The document outlines several approaches to achieving gastric retention, including floating, bioadhesive/mucoadhesive, expandable/unfoldable, and magnetic systems. It provides examples of drug candidates that could benefit from GRDDS and evaluates the advantages of these systems.



![1] DRUGS THAT HAVE VERY LIMITED ACID
SOLUBILITY
PHENYTOIN ETC.
2) DRUGS THAT SUFFER INSTABILITY IN THE
GASTRIC ENVIRONMENT E.G.
ERYTHROMYCIN ETC.
3) DRUGS INTENDED FOR SELECTIVE
RELEASE IN THE COLON
5-AMINO SALICYLIC ACID AND
CORTICOSTEROIDS
ETC.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE
GASTRORETENTIVE SYSTEM.
1. DENSITY.
2. SIZE.
3. SHAPE OF DOSAGE FORM.
4. SINGLE OR MULTIPLE UNIT FORMULATION.
5. FED OR UNFED STATE.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/164e9ddf-58c4-4032-a4ee-96885320c4b4-150217040244-conversion-gate01/85/Presentation-GRDDS-5-320.jpg)