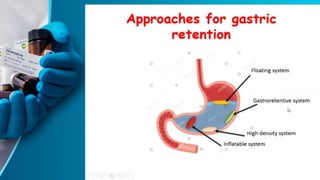
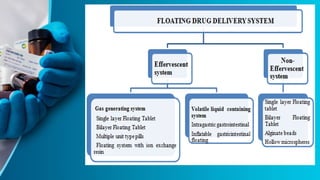
This document discusses floating tablet technology as a novel oral drug delivery system for controlled release. Floating tablets are gastroretentive drug delivery systems that float on the gastric contents and remain in the stomach for an extended period of time, allowing for sustained drug release at the absorption site. Some key advantages of floating tablets include improved bioavailability, increased duration of drug release, and minimized drug degradation in the colon. The document reviews different types of floating systems and polymers used in their formulation. It also discusses evaluation tests and provides examples of research on developing floating tablets with silymarin as a model drug.