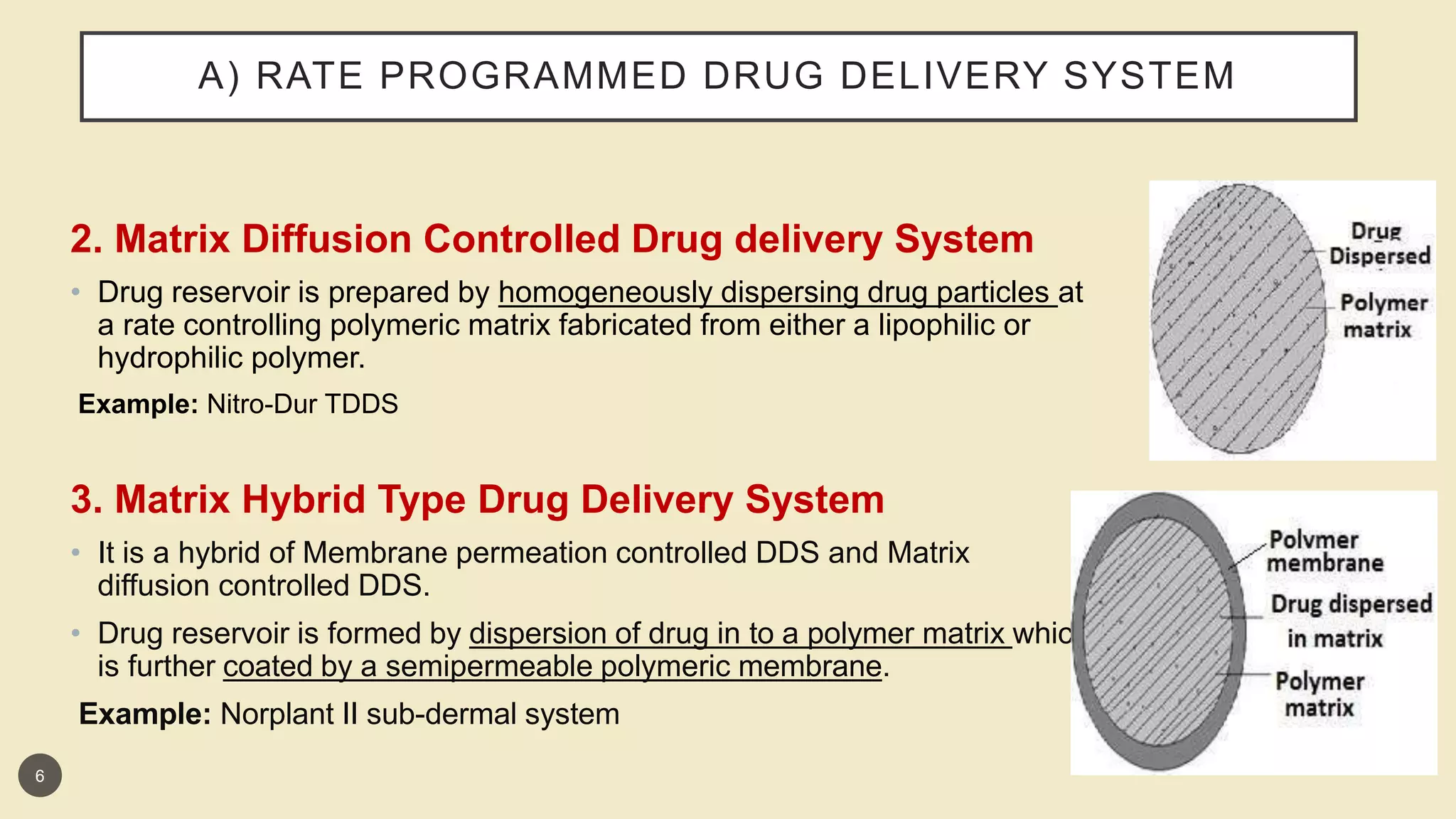
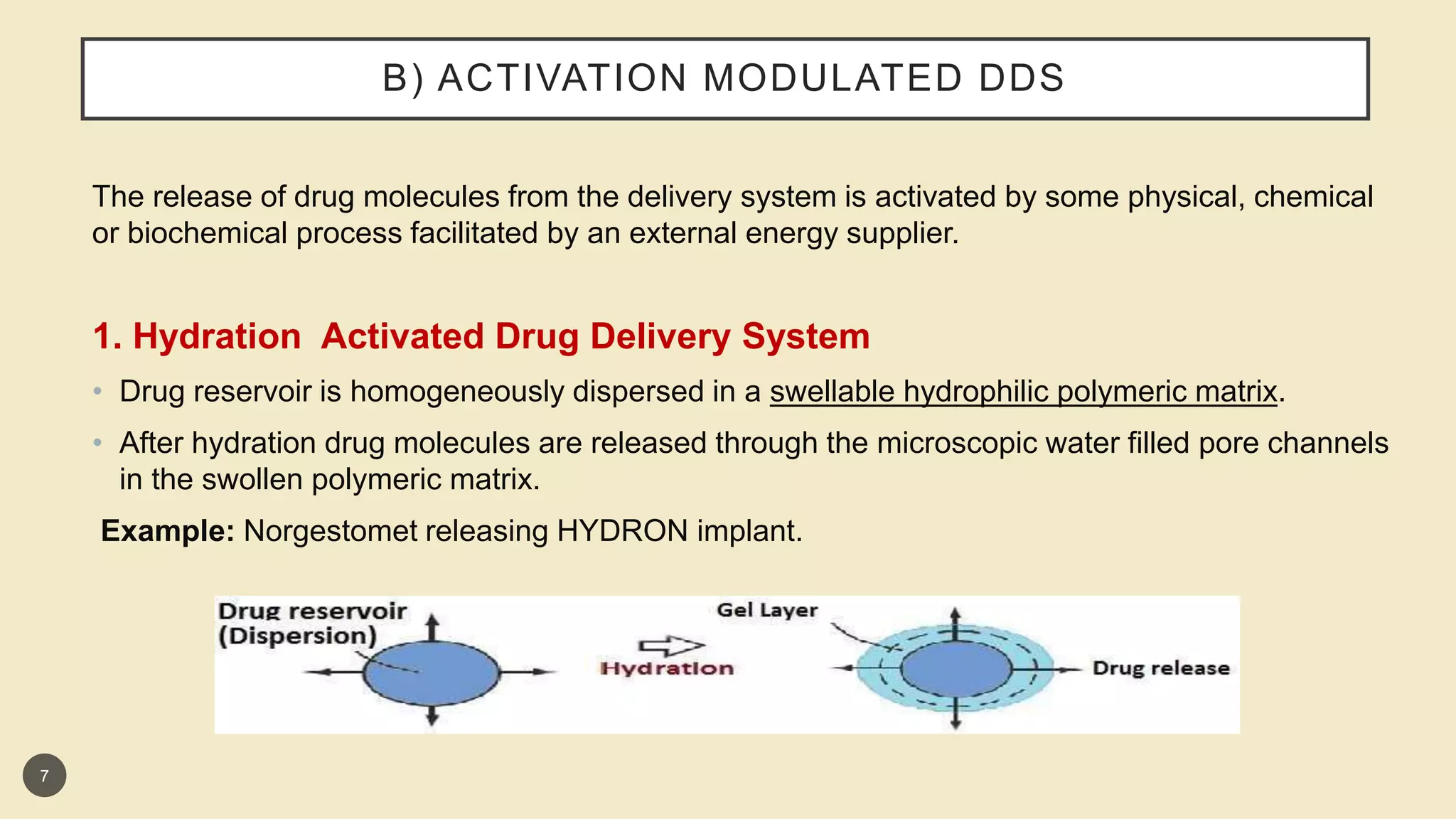
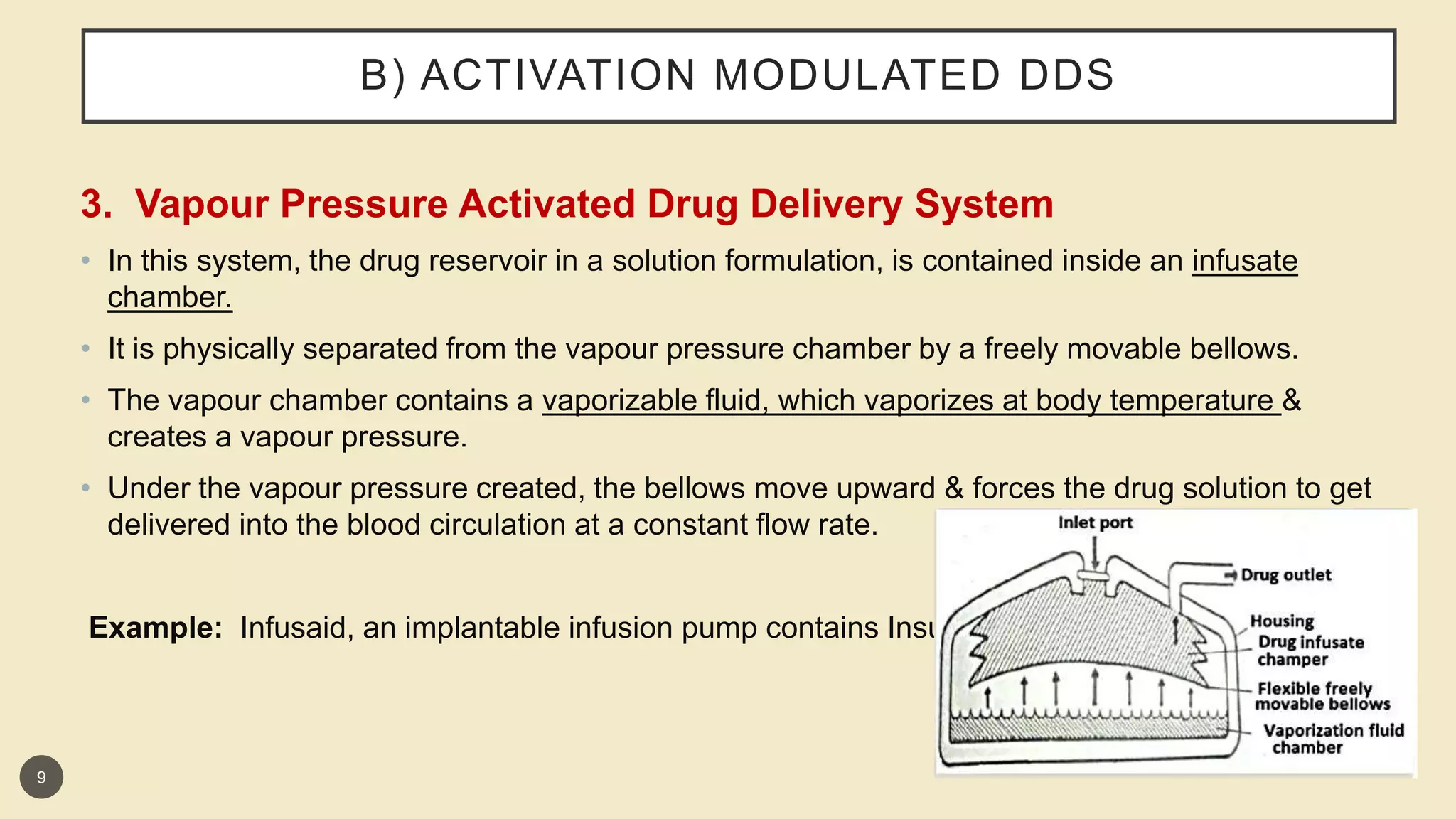
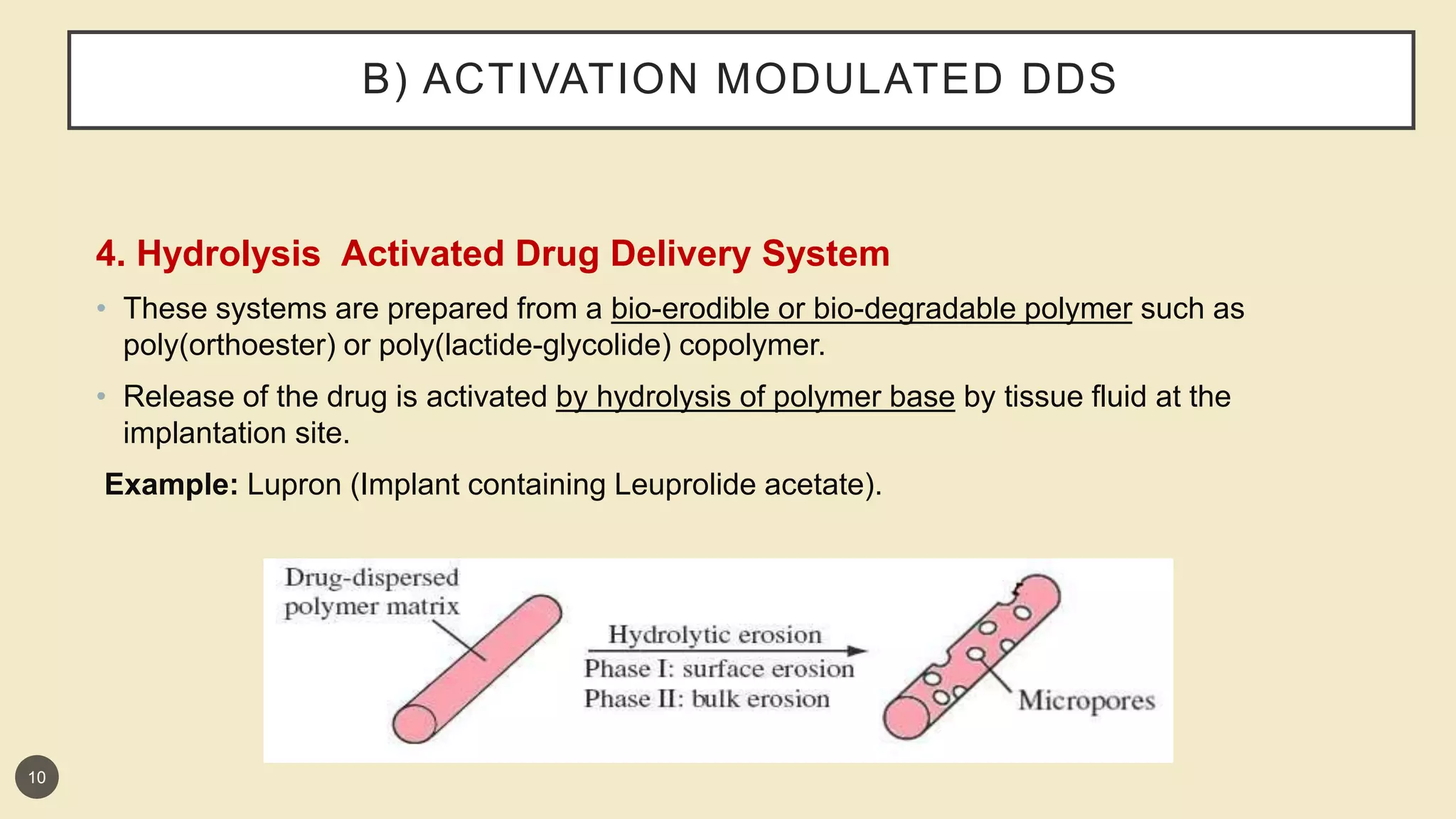
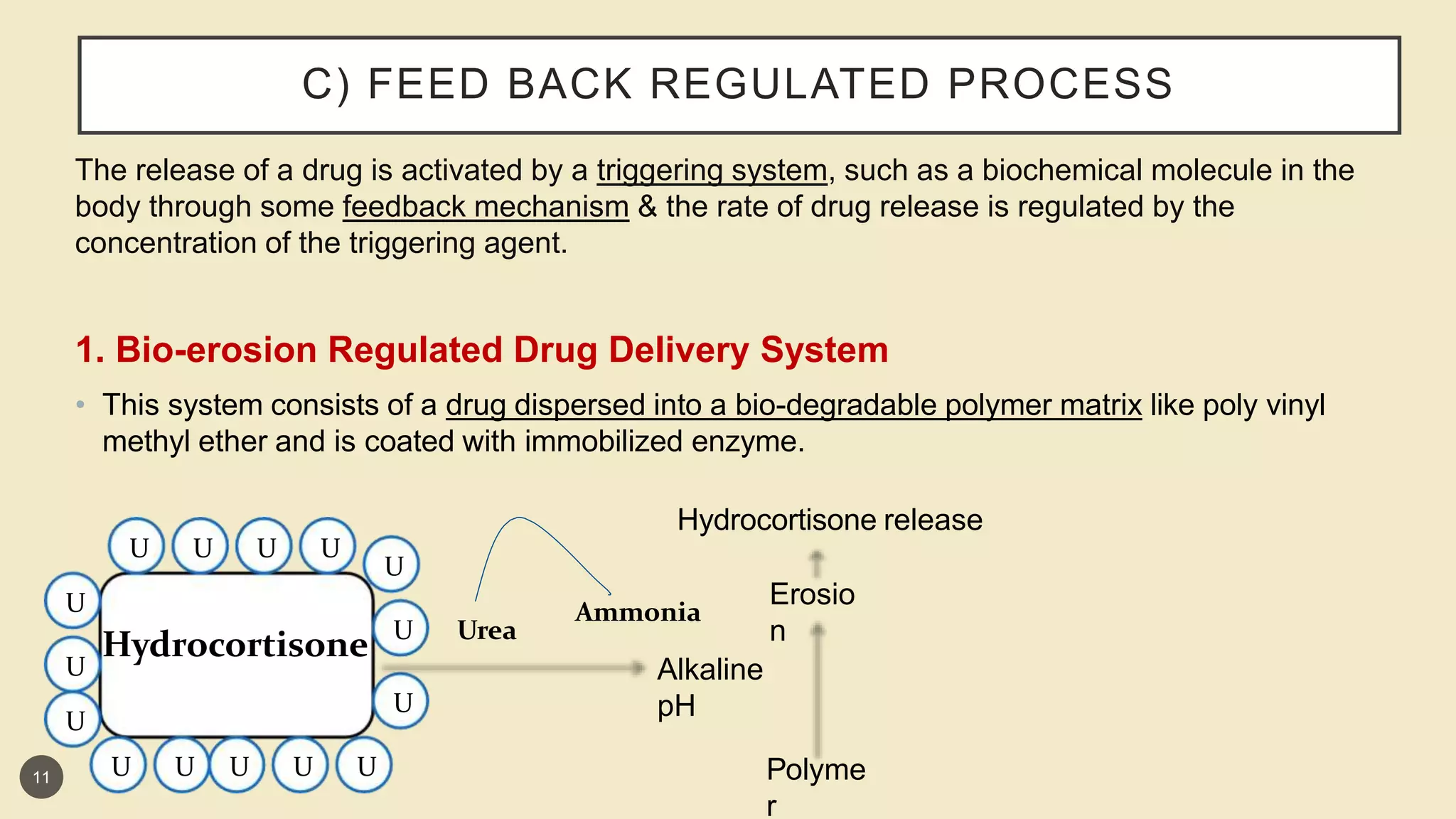
This presentation discusses implantable drug delivery systems. It begins by defining implants as solid masses of purified drug intended for implantation via minor surgery or large bore needle to provide continuous drug release over long periods. Implants are well-suited for drugs like insulin, steroids, antibiotics, and analgesics. The presentation covers advantages like controlled delivery, improved compliance and stability. It also discusses types of implant systems including rate-programmed, activation-modulated, and feedback-regulated devices. Various mechanisms for controlling drug release like diffusion, hydration and enzymatic reactions are described. The conclusion emphasizes implants can provide targeted delivery without limitations of other administration methods.