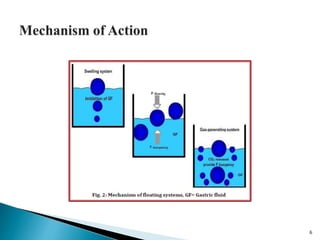
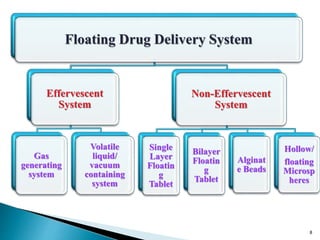
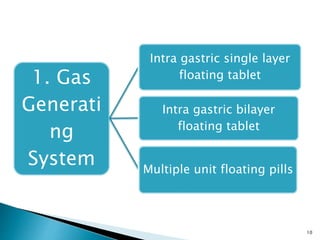
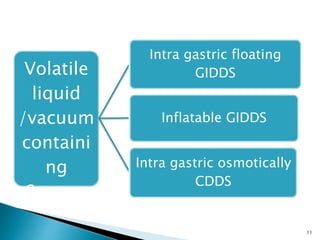
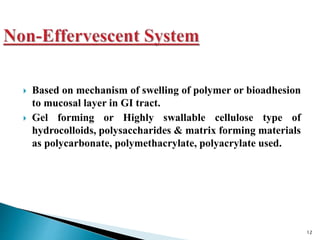
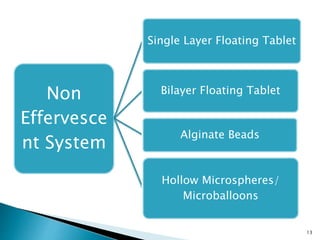
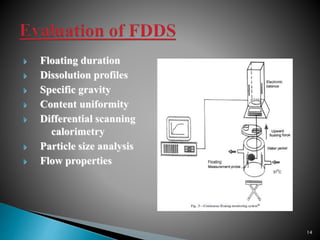
The document discusses floating drug delivery systems (FDDS), emphasizing their importance in enhancing oral drug bioavailability by improving gastric retention time. It categorizes FDDS into effervescent and non-effervescent types, each with specific mechanisms and formulations for drug release. The advantages include reduced side effects and improved patient compliance through decreased dosing frequency, although certain drug conditions and gastrointestinal factors can limit their effectiveness.