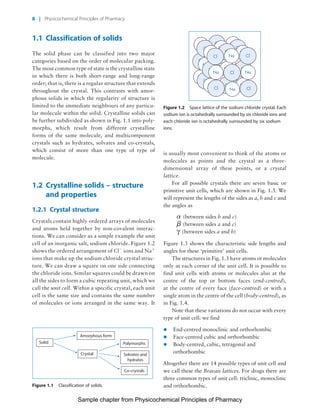
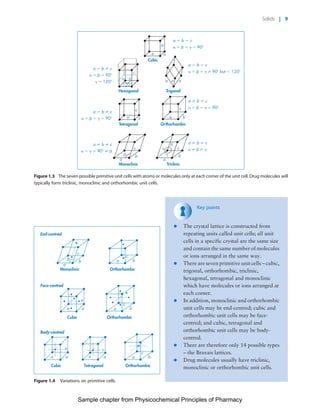
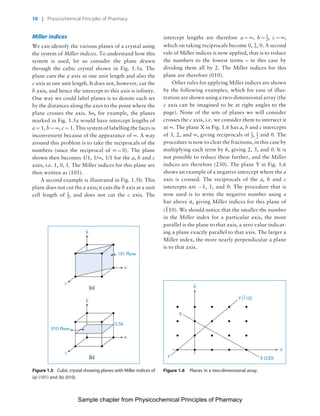
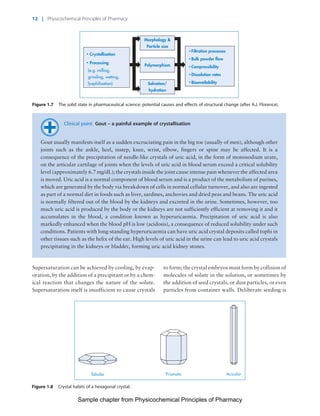
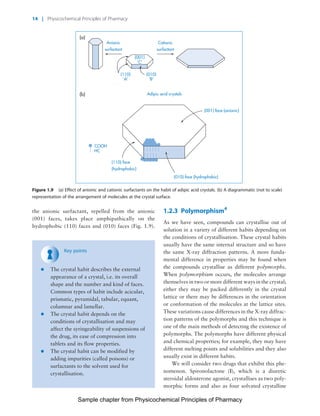
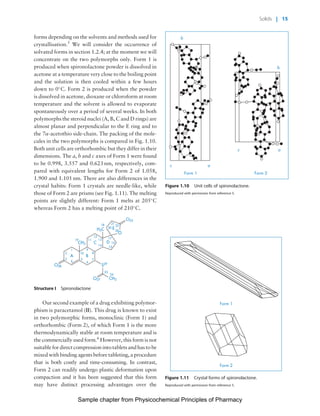
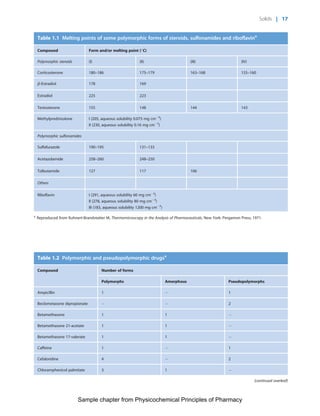
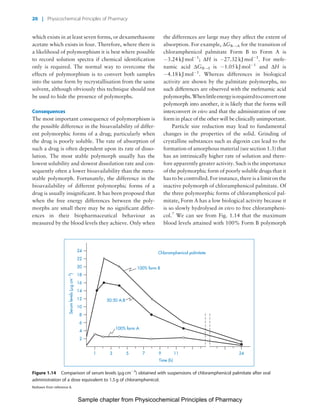
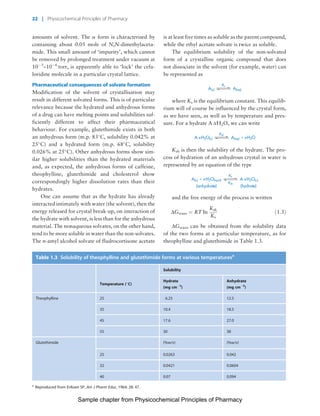
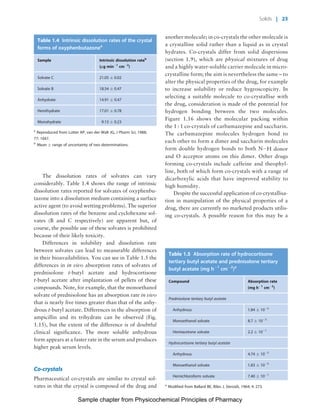
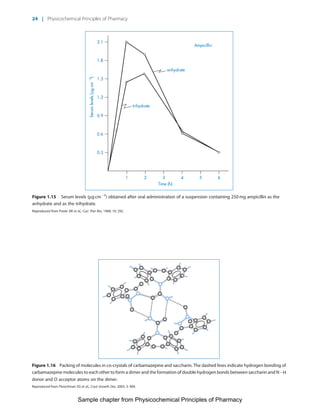
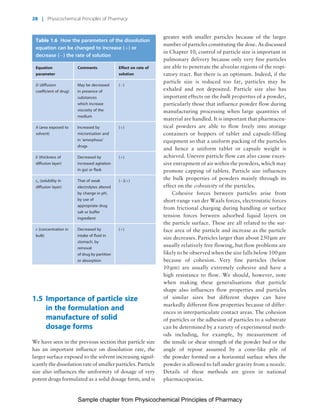
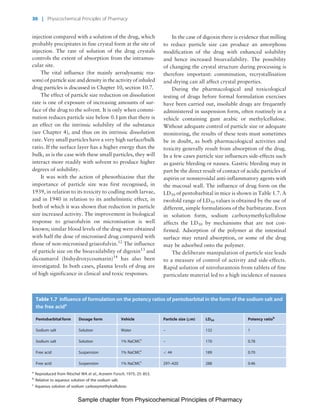
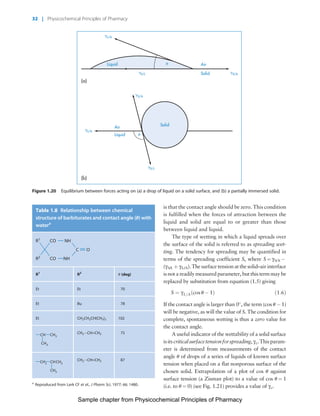
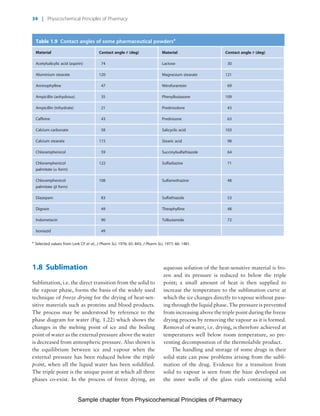
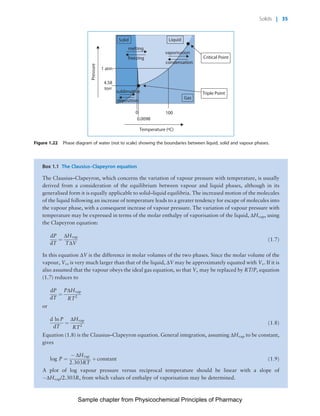
The document discusses the classification and properties of solid-state drugs and excipients. Crystalline solids can exist as polymorphs, hydrates, or co-crystals, consisting of short- and long-range molecular ordering. Amorphous solids lack long-range order. Particle size affects dissolution, absorption, and formulation. Miller indices are used to identify crystal planes by their intercepts with unit cell axes. Key properties like stability, solubility, and bioavailability can depend on a drug's solid-state form and characteristics.