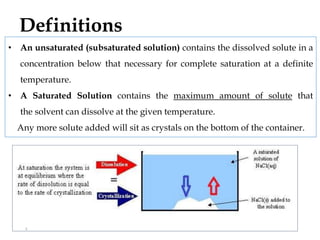
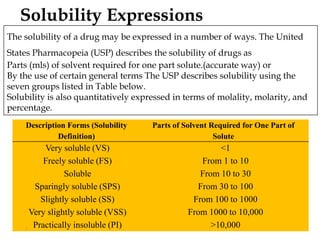
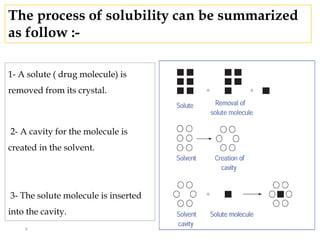
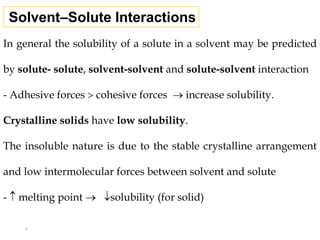
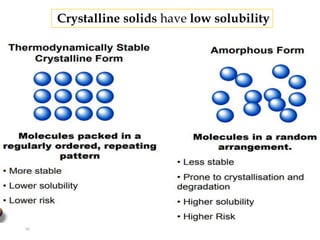
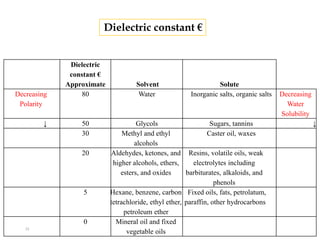
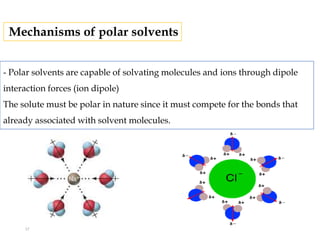
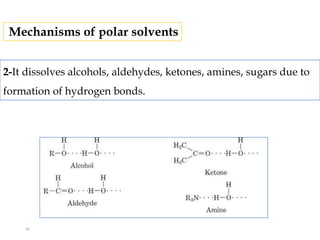
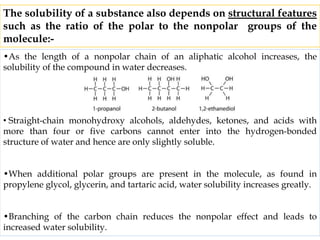
This document discusses solubility and distribution phenomena. It defines different types of solutions such as unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions. It also describes how solubility can be expressed both qualitatively using terms like very soluble or slightly soluble, and quantitatively using units like parts per million. The document explains how solvent properties like polarity affect solubility, with polar solvents being able to dissolve ionic compounds and form hydrogen bonds. Structural features of solutes like molecular size and branching also impact solubility.