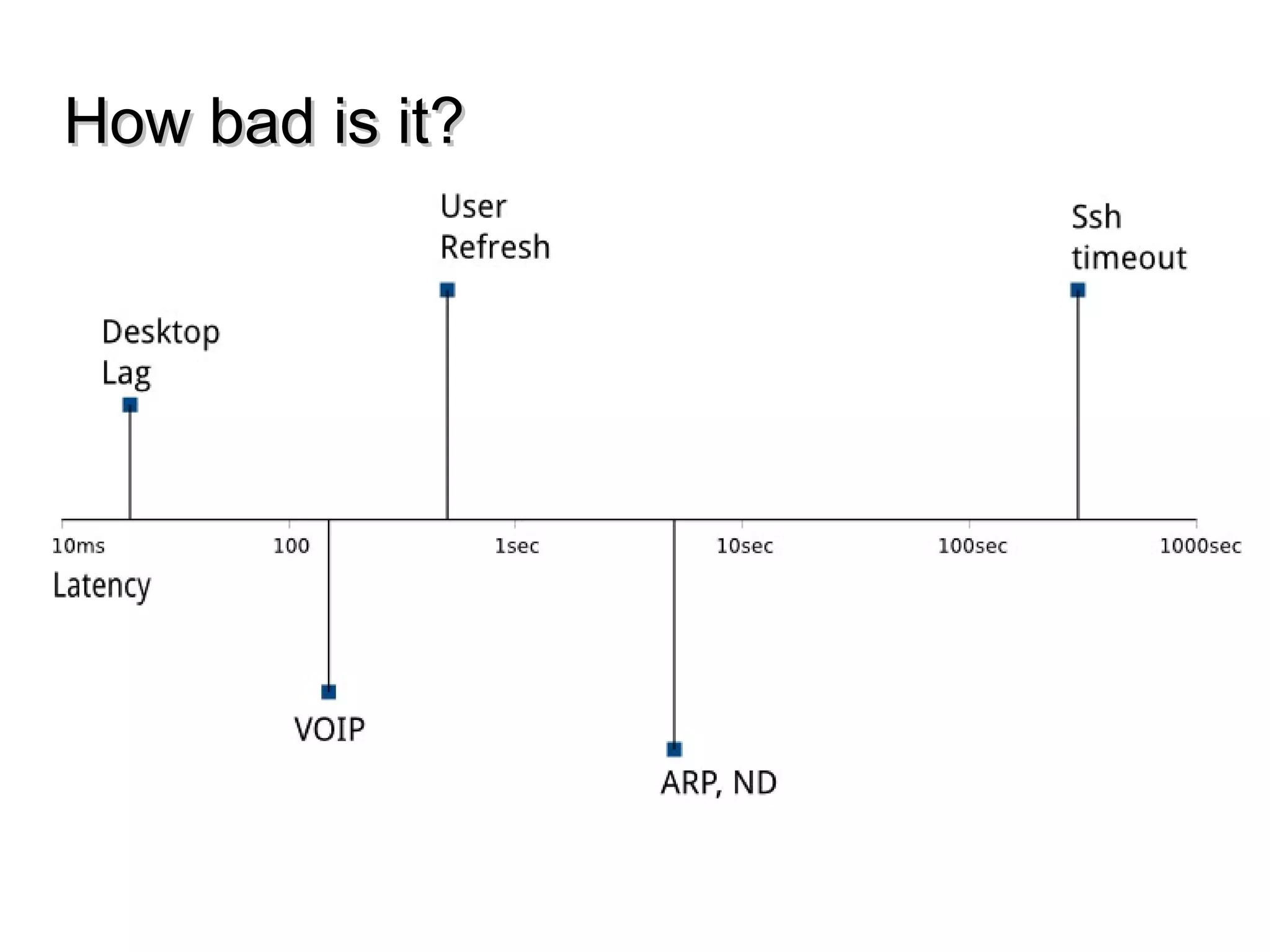
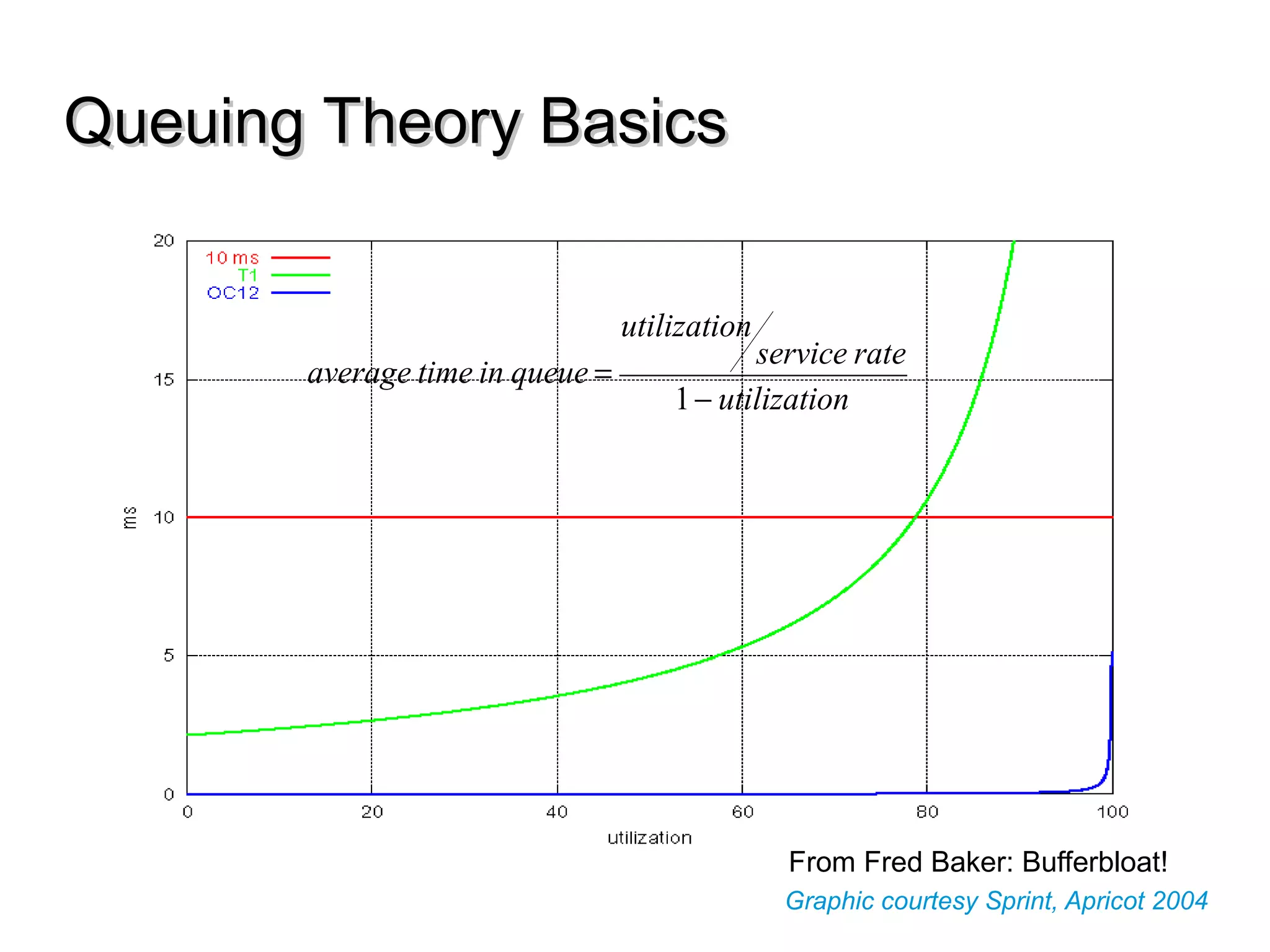
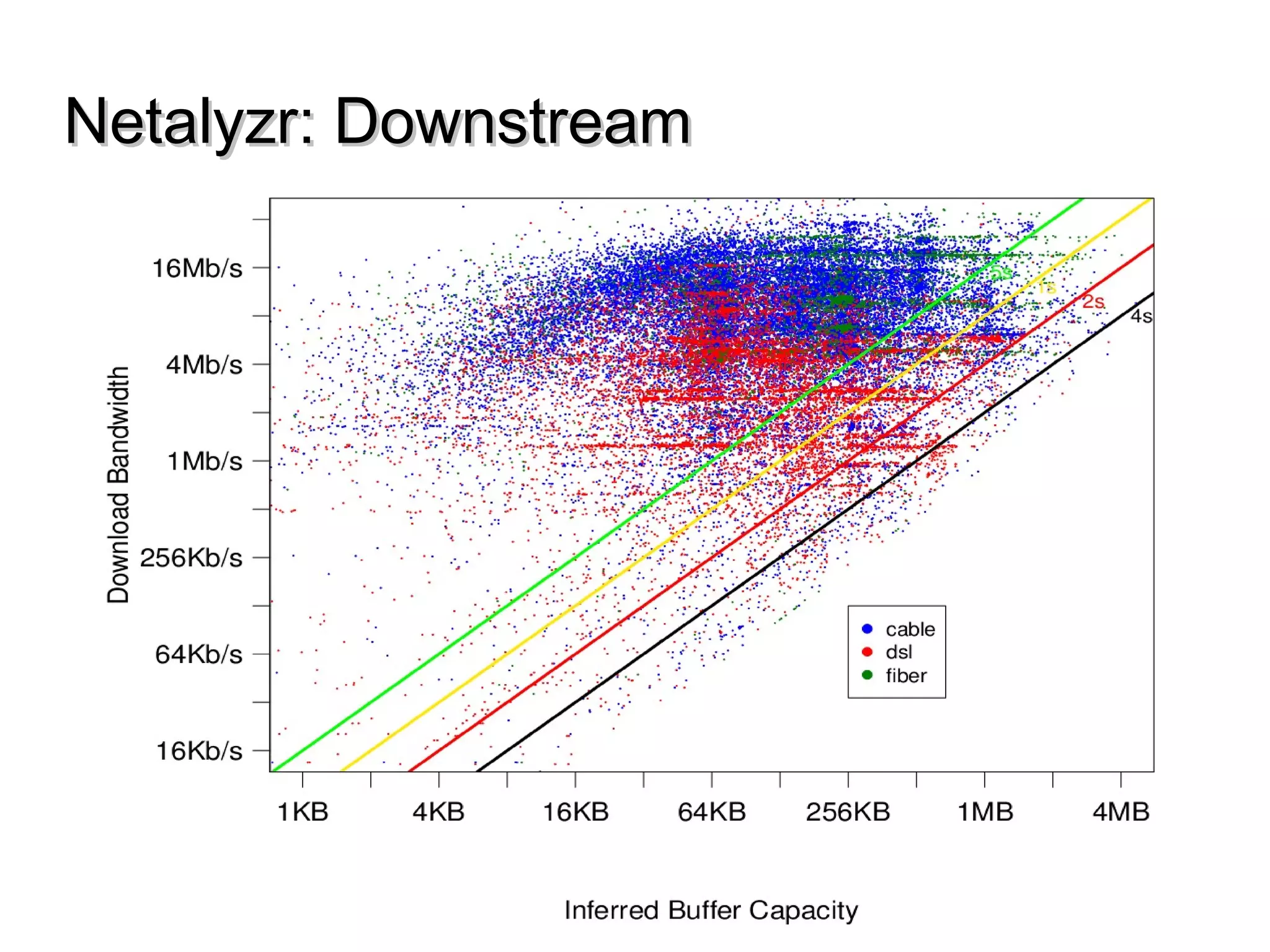
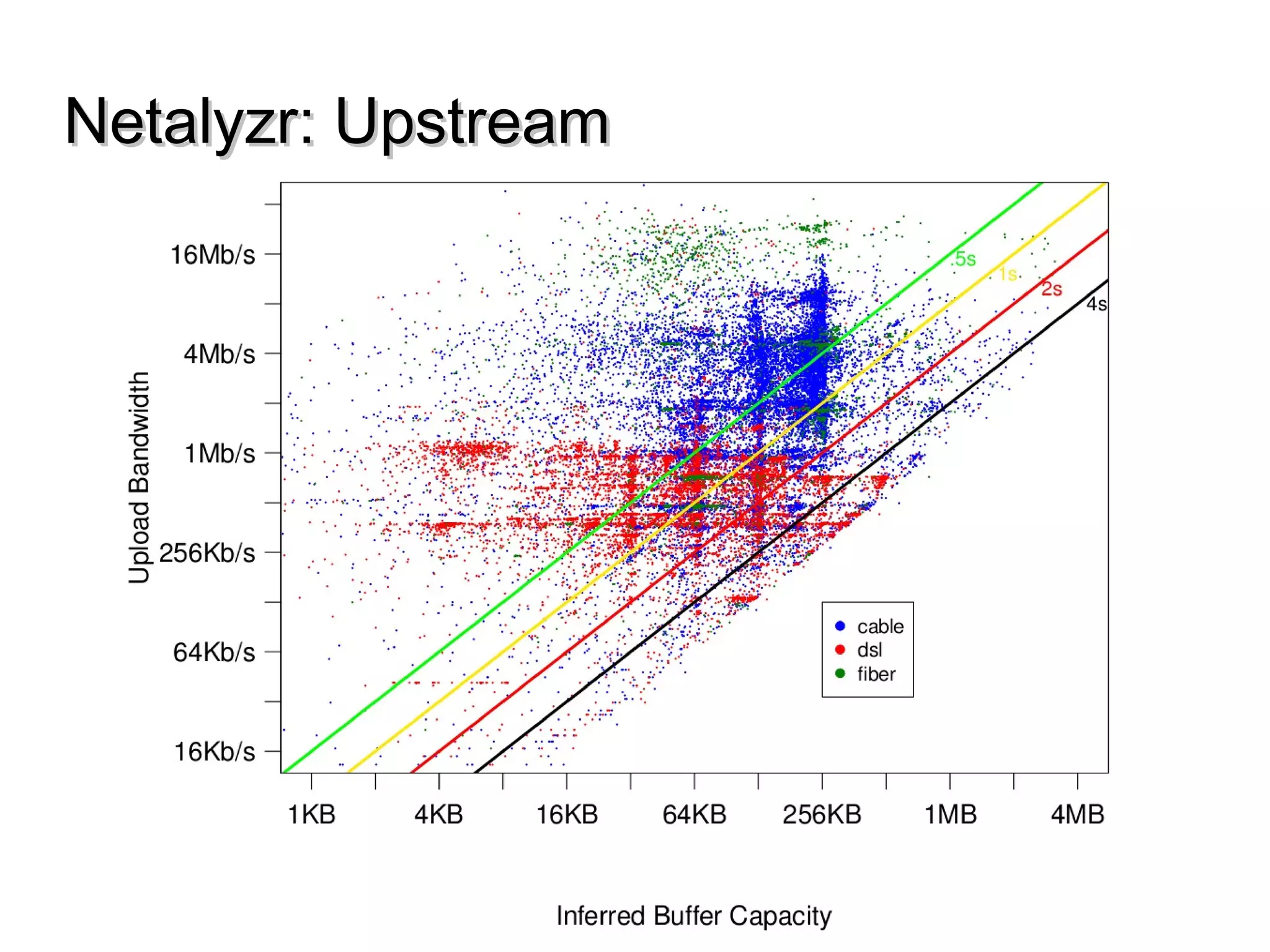
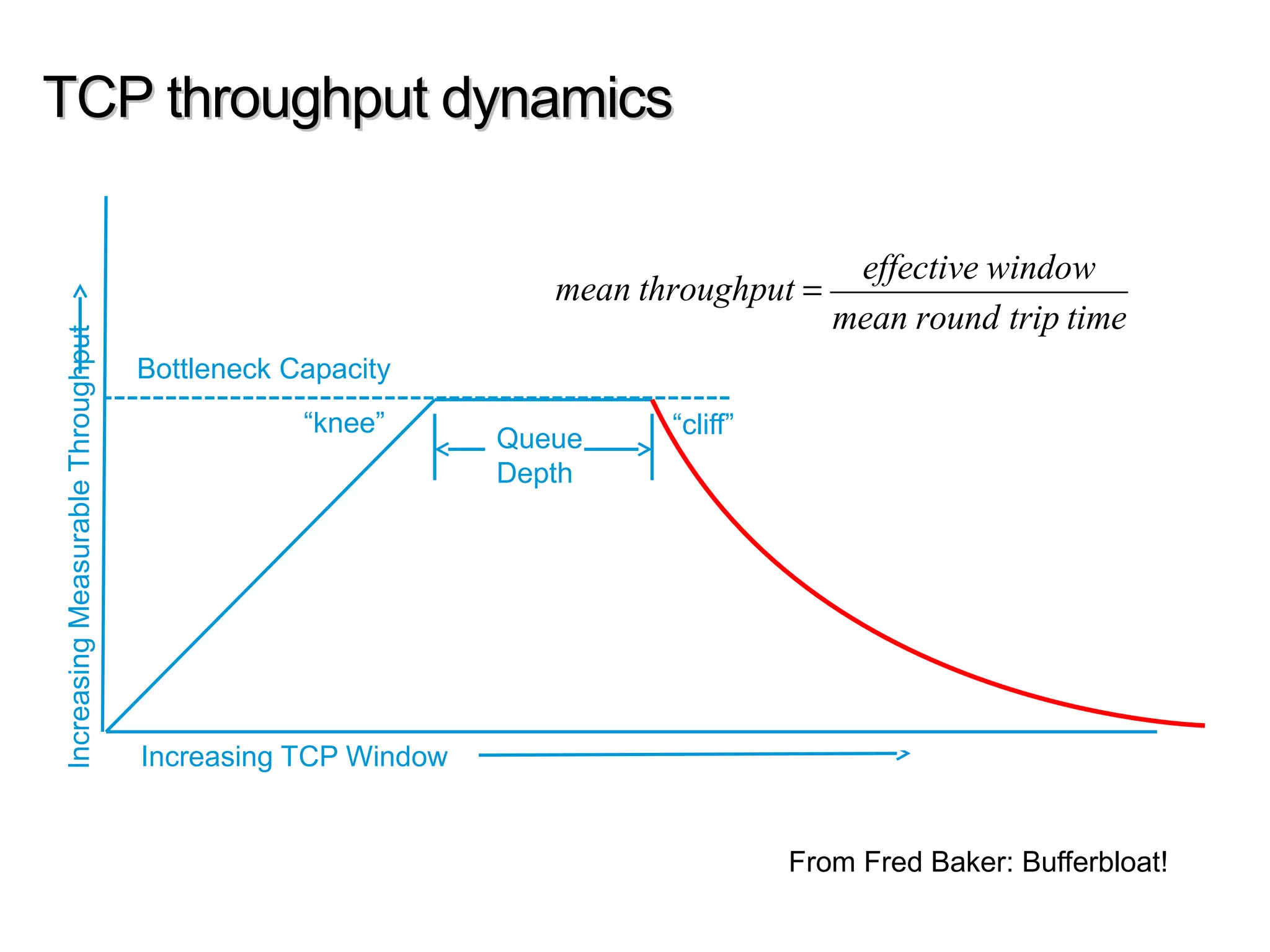
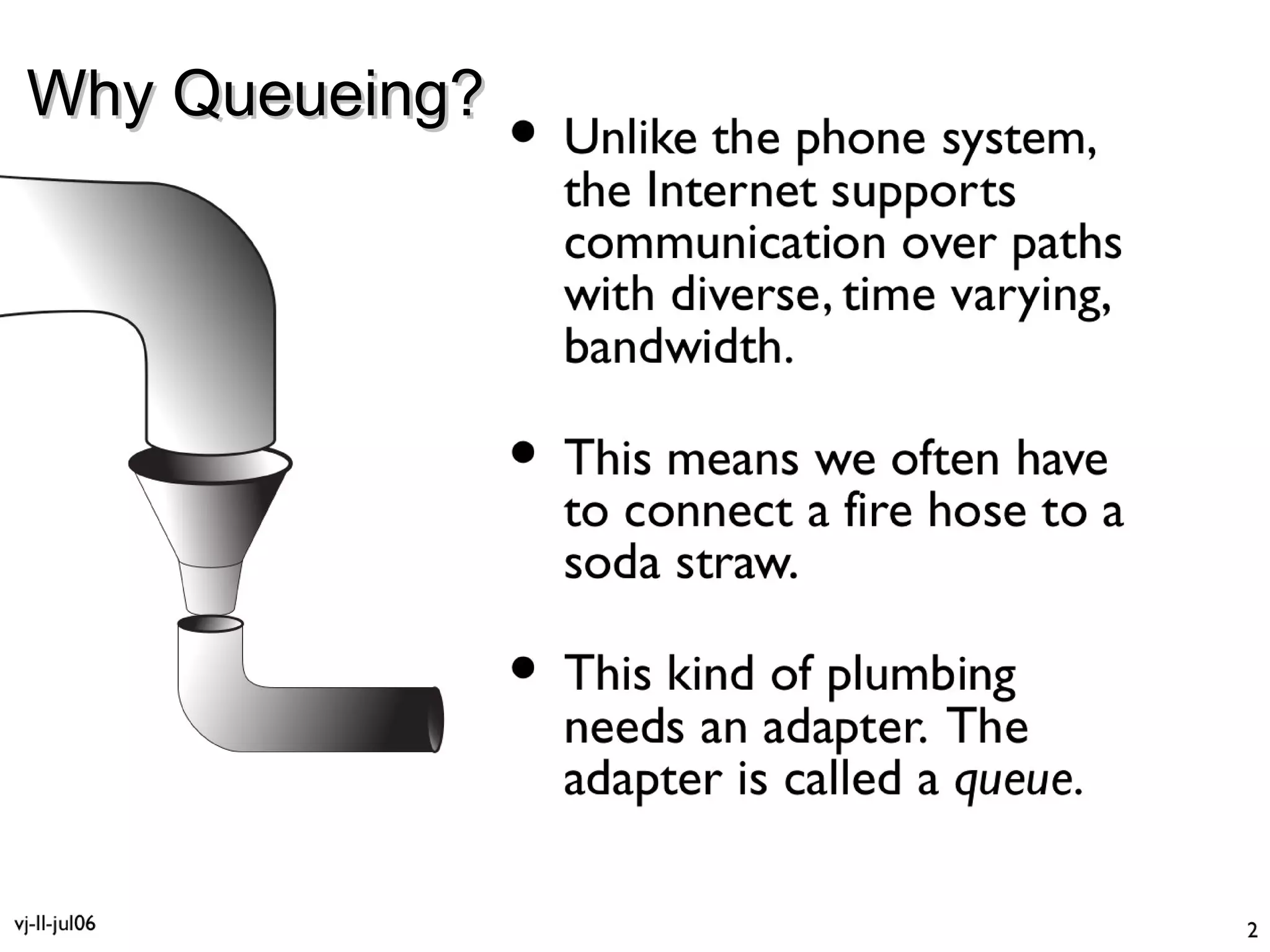
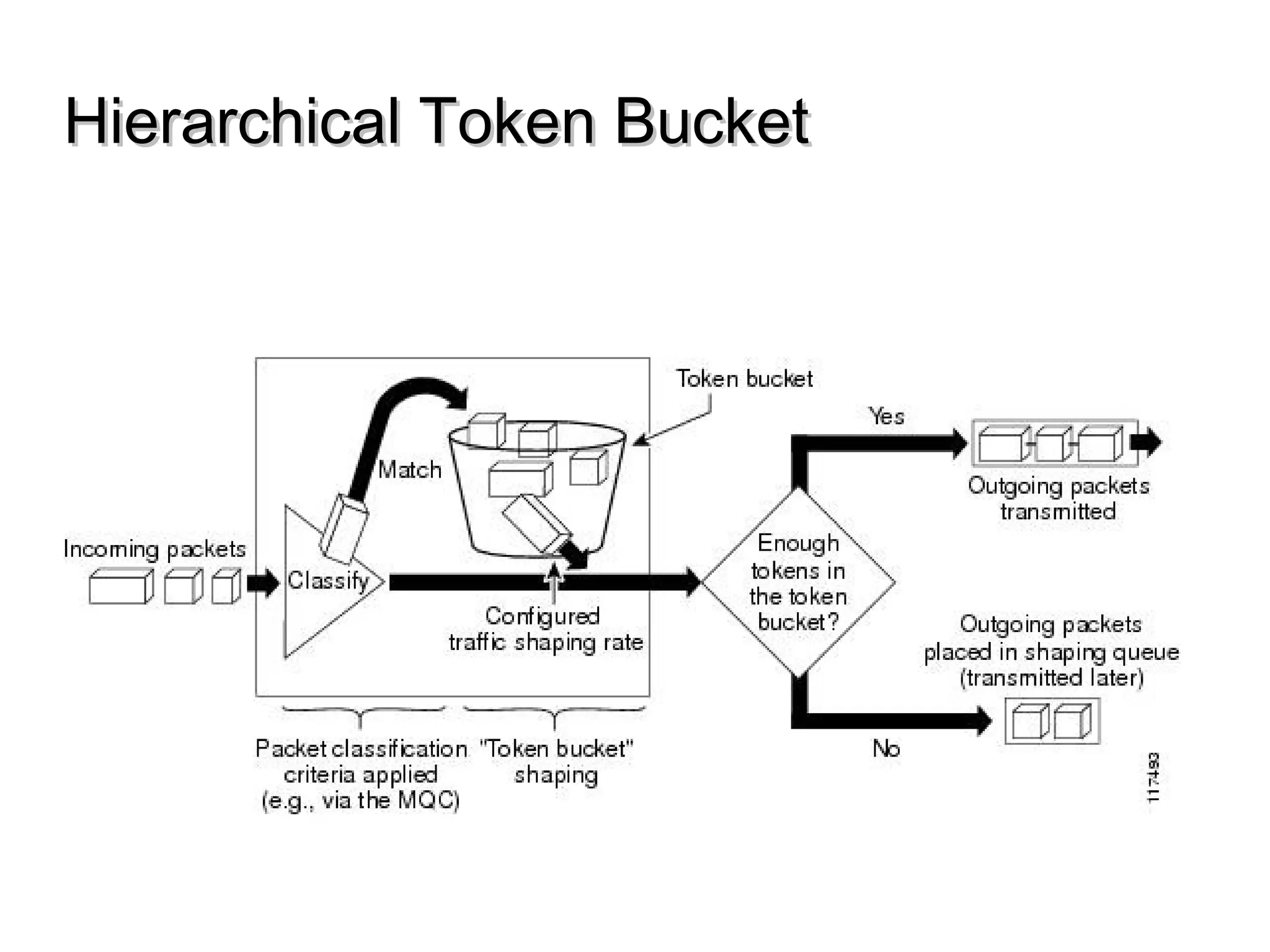
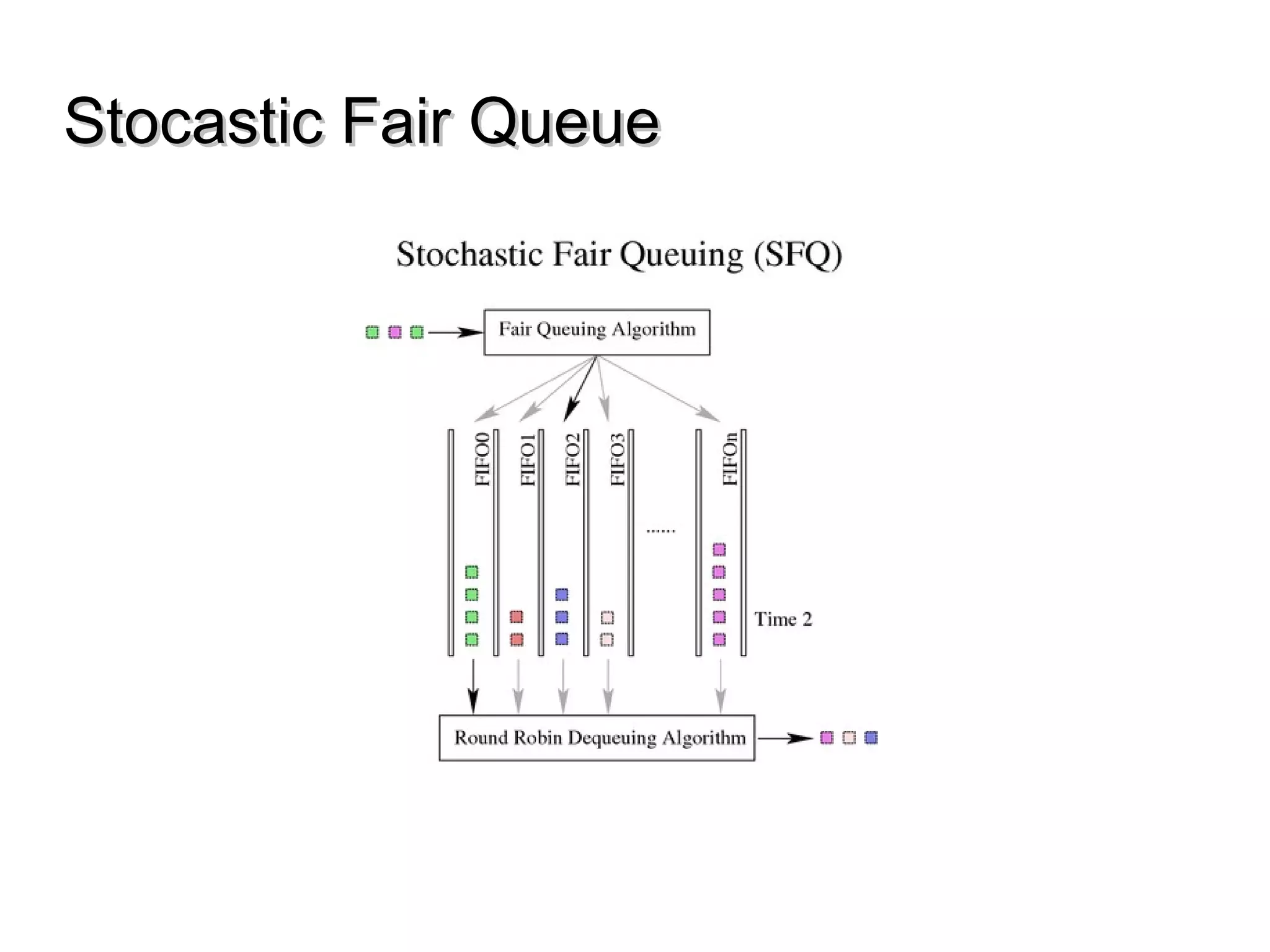
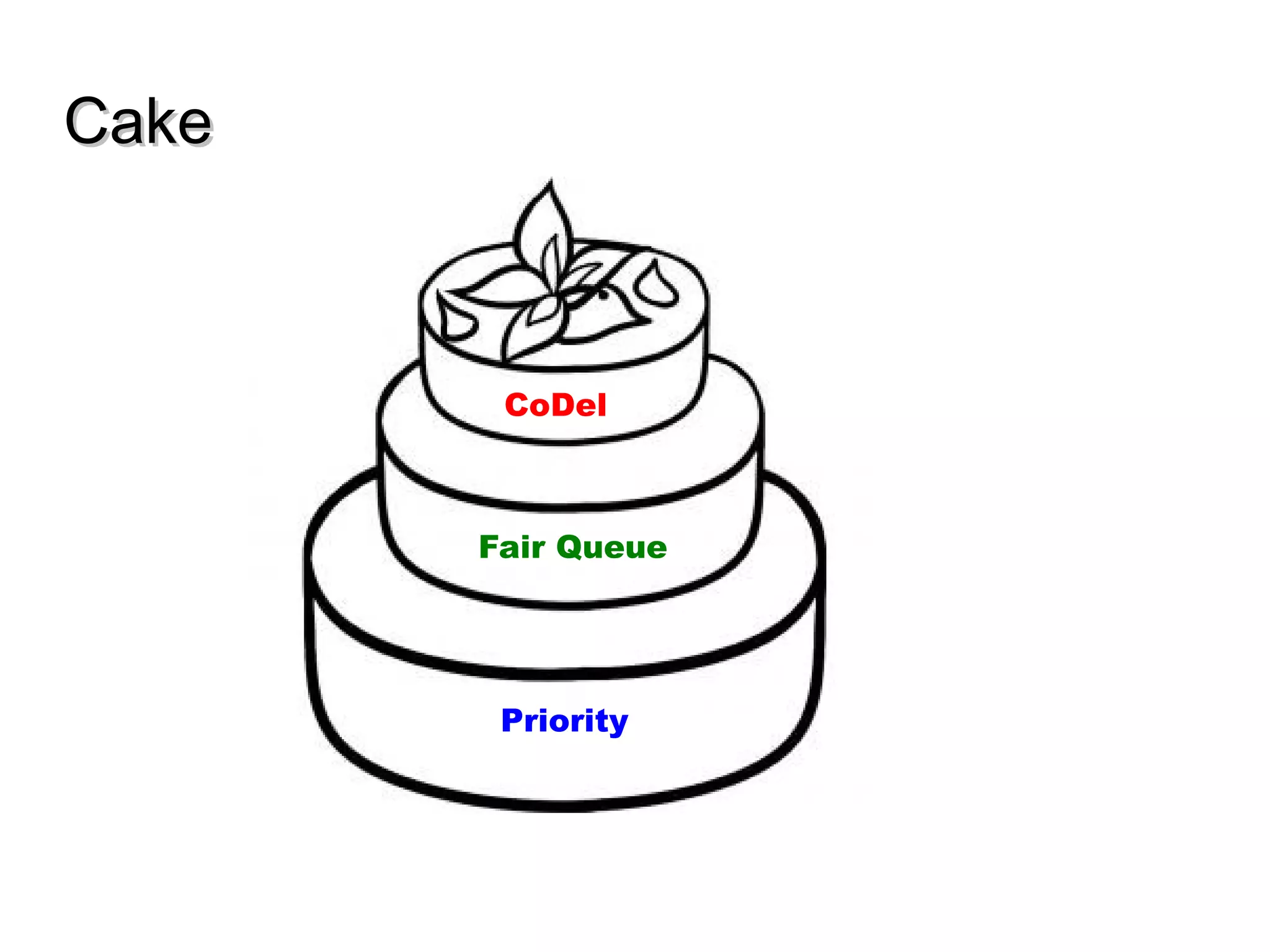
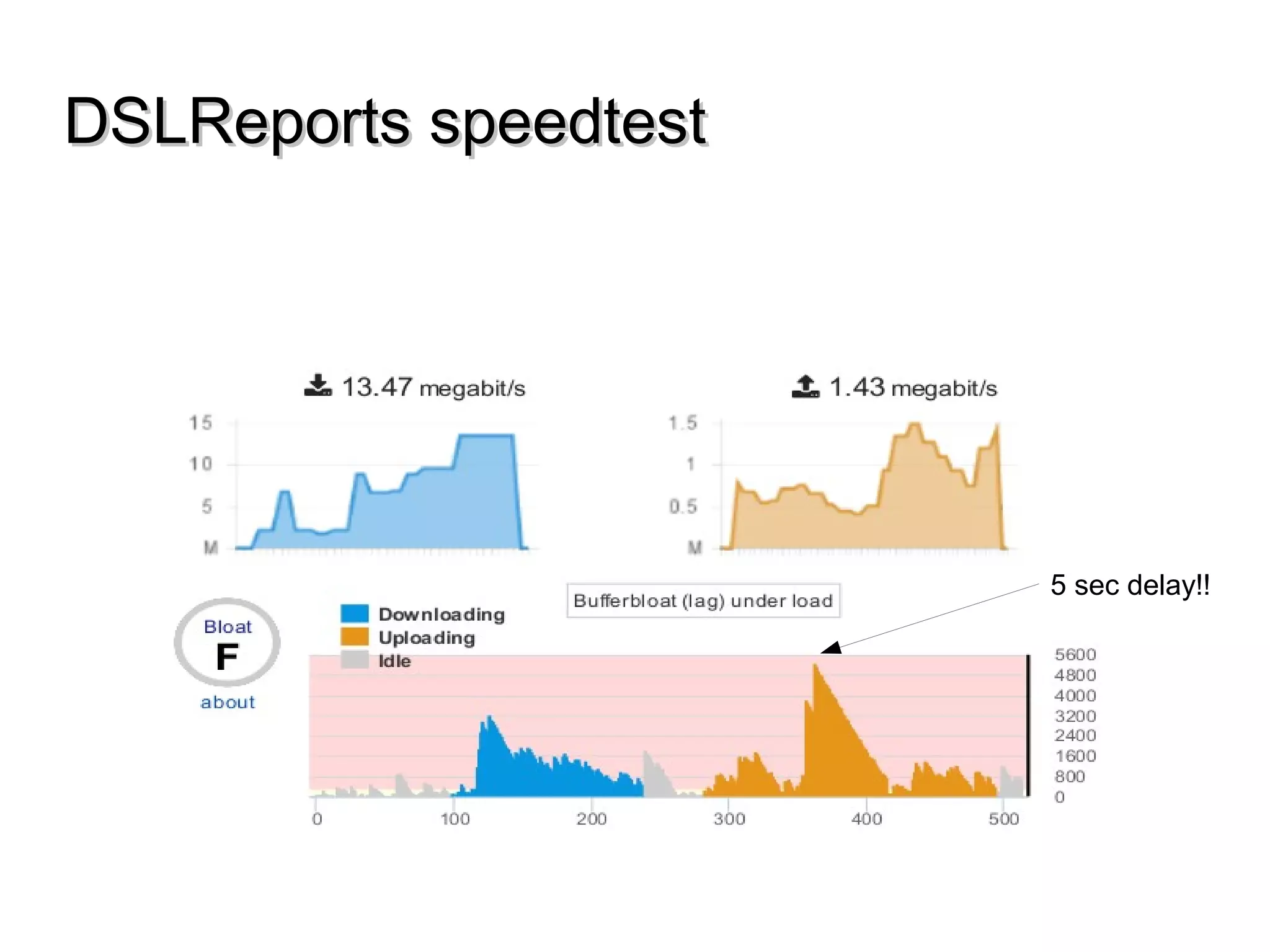
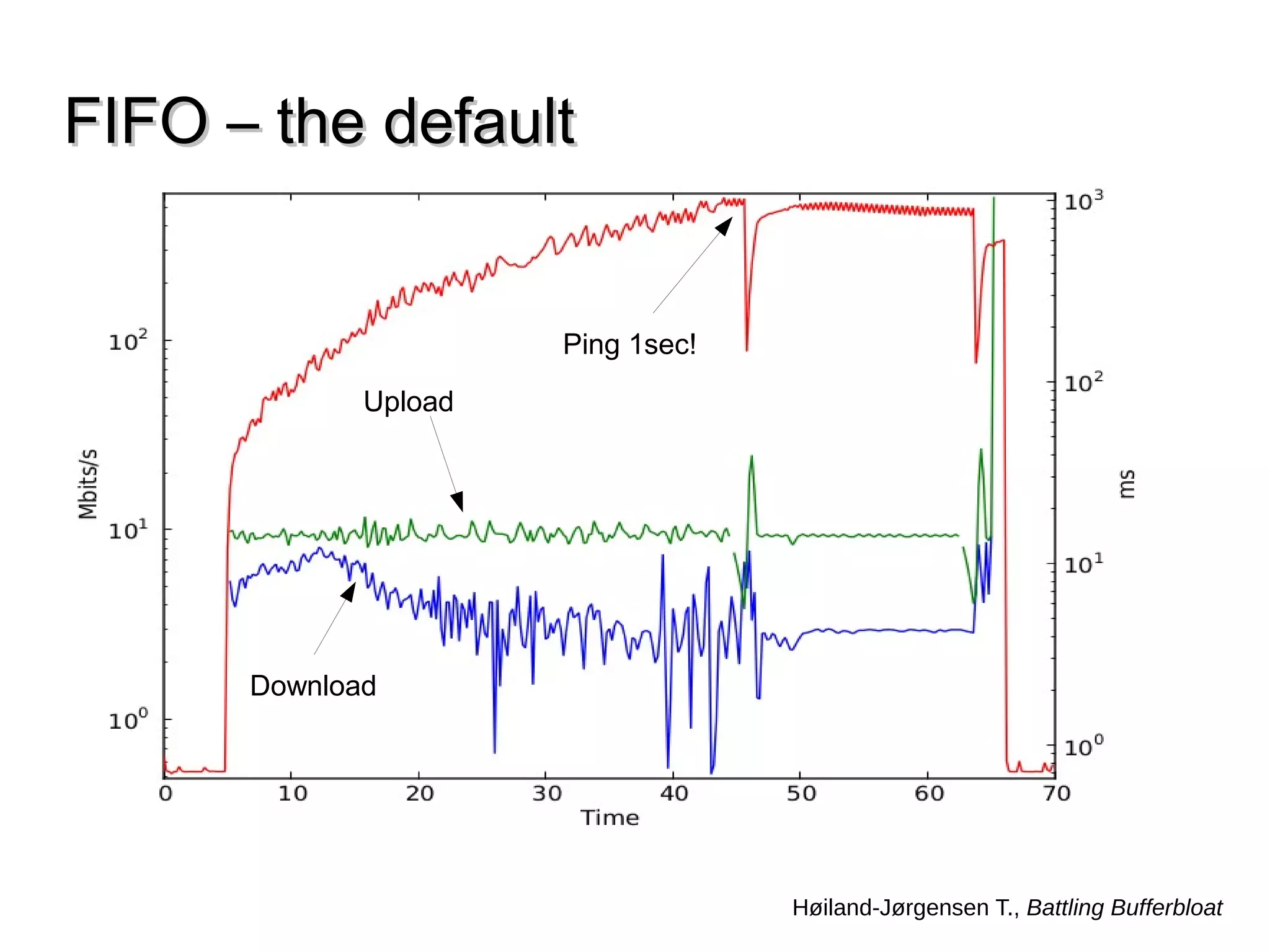
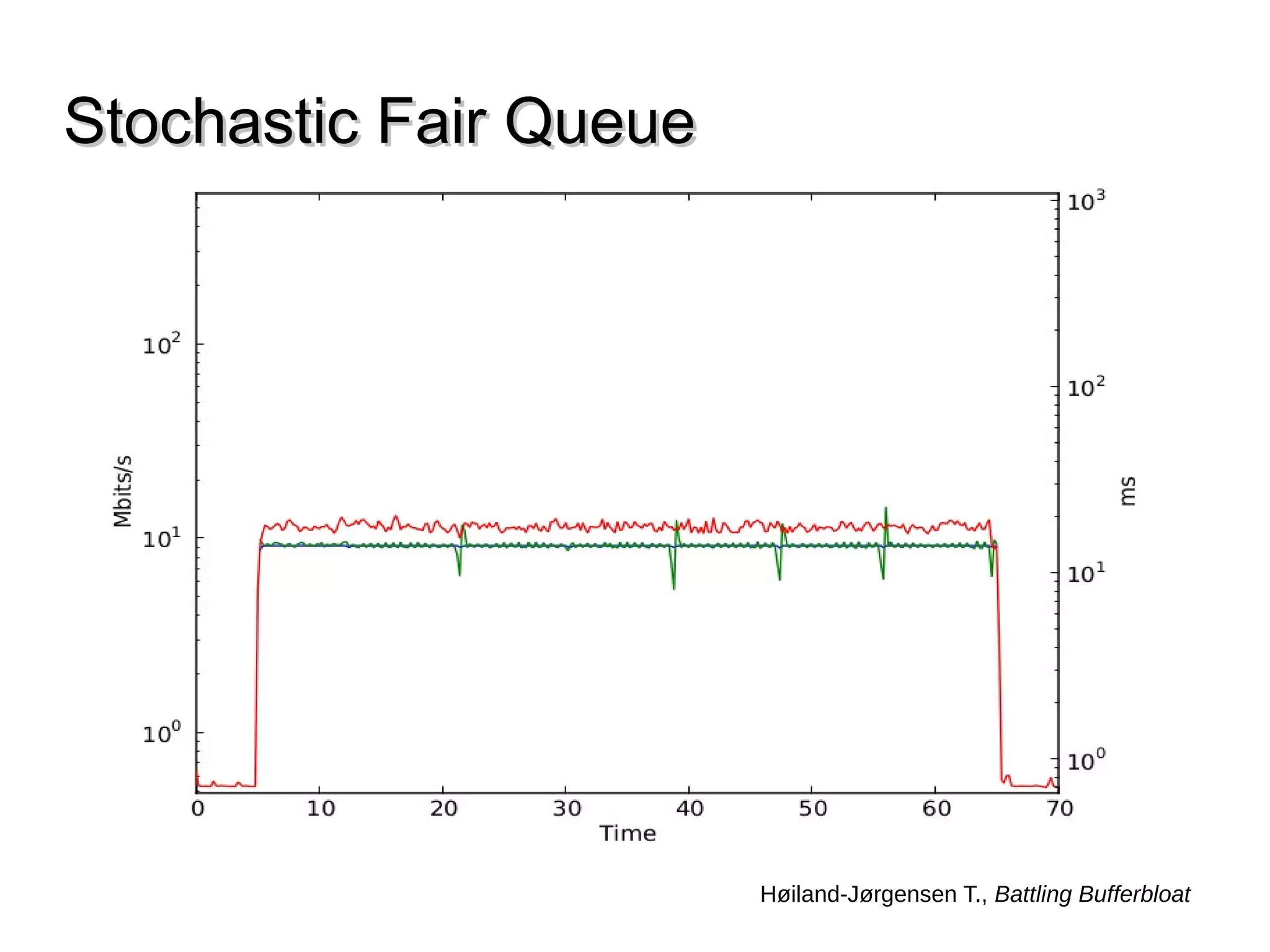
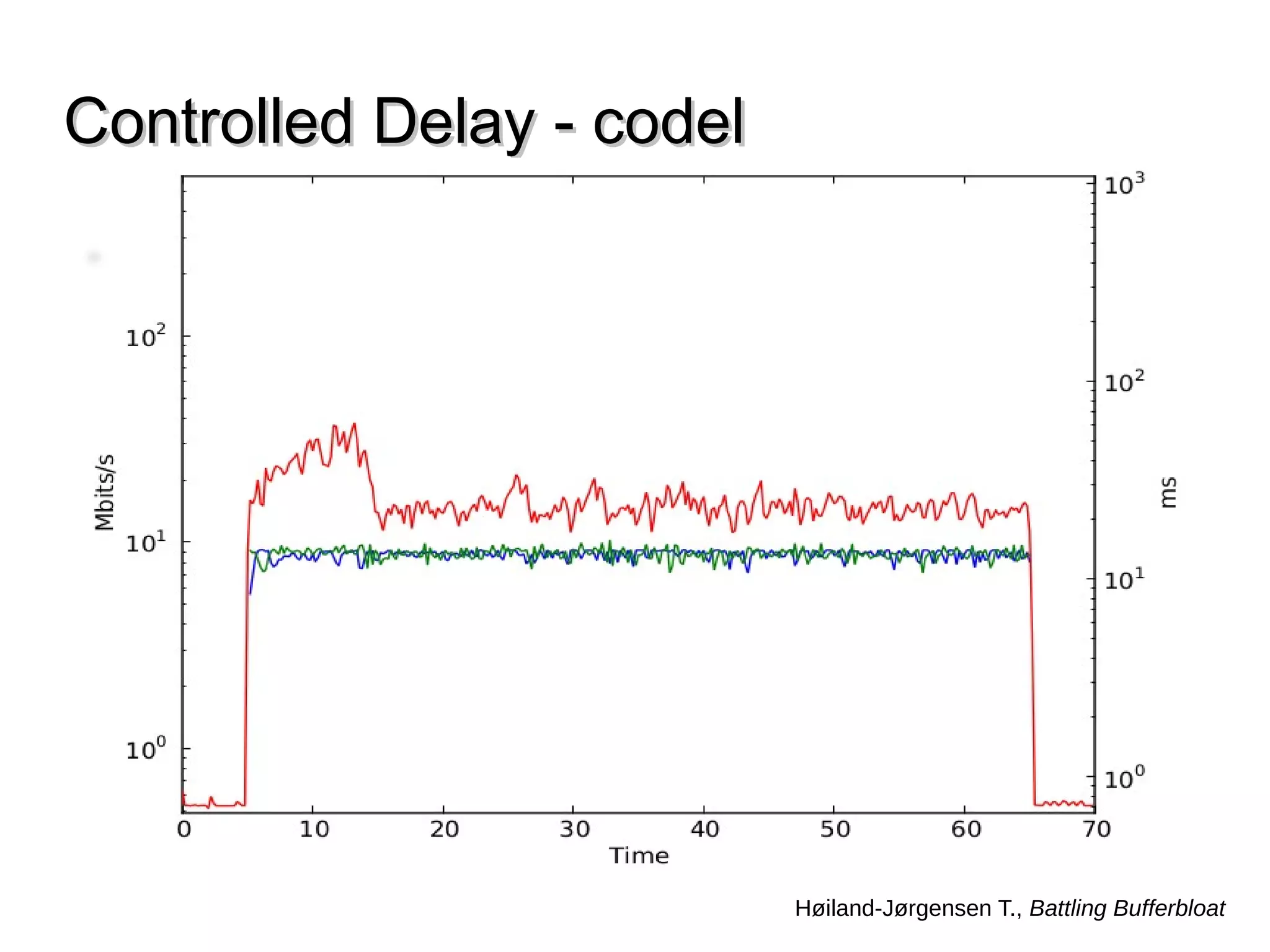
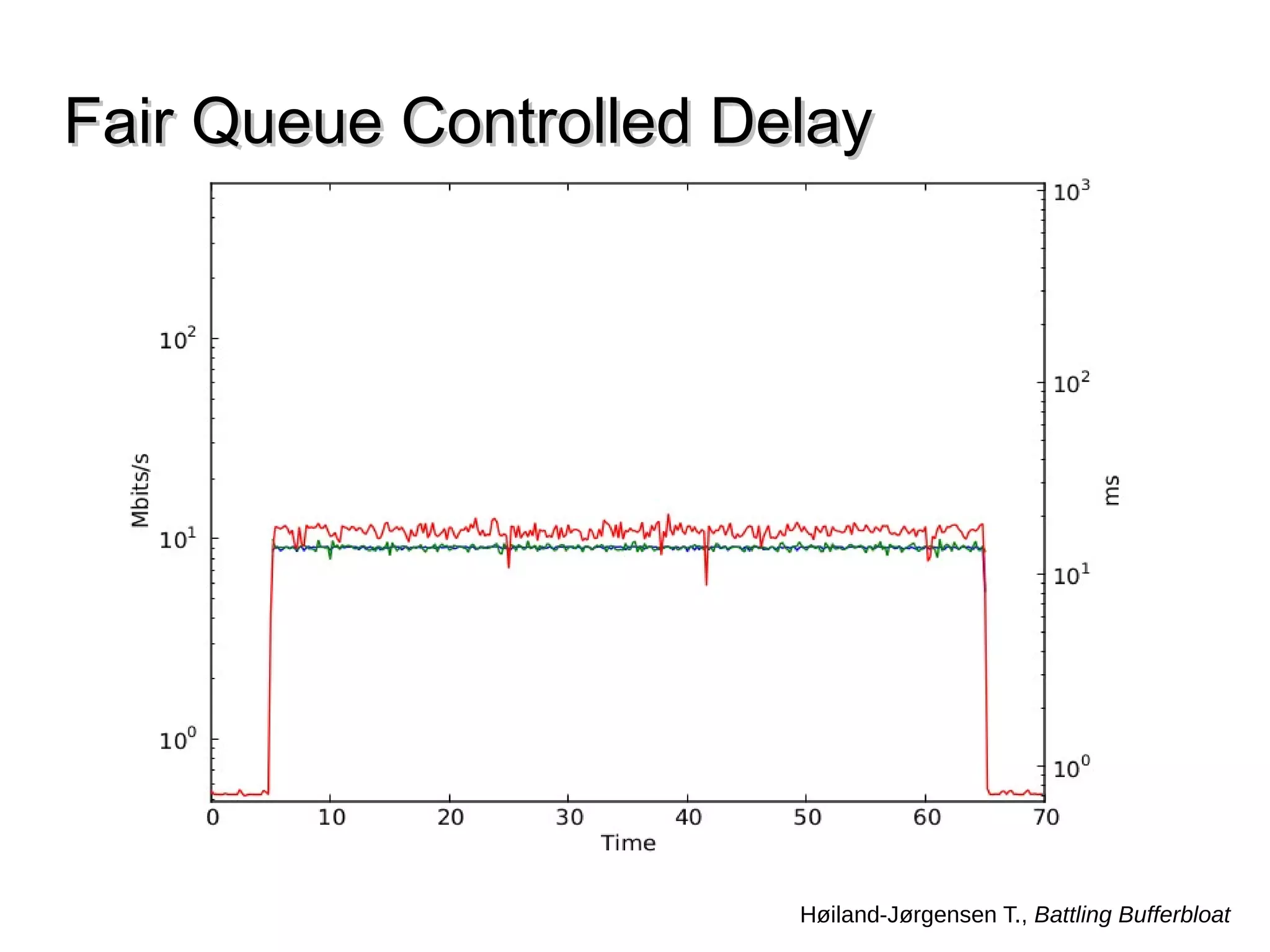
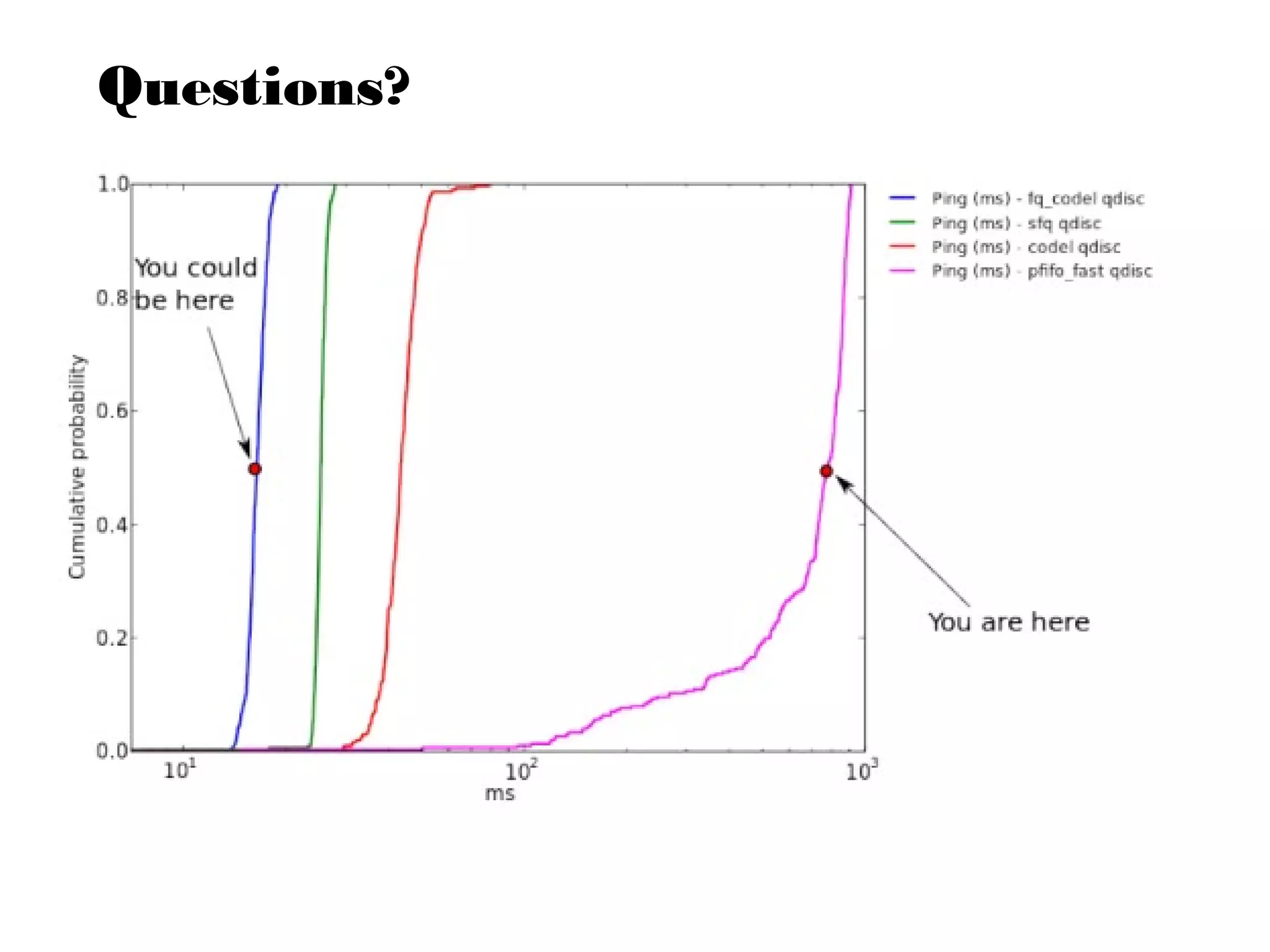
This document discusses the problem of bufferbloat on the internet. It explains that bufferbloat occurs when routers and switches have too much buffering capacity, which leads to increased latency. The causes of bufferbloat include increased bandwidth usage from applications, large TCP initial windows, and routers being configured to avoid dropping packets. Solutions presented are queue management techniques like CoDel and PIE that aim to control latency while maintaining high throughput. The document notes that while awareness of bufferbloat has increased, legacy equipment and congestion on backbones continue to cause issues.