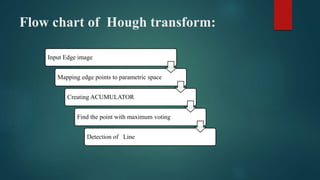
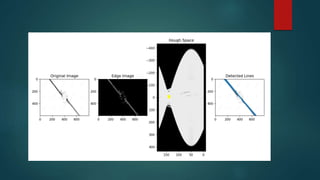
This document discusses line detection through the Hough transform. It begins with an introduction to the Hough transform and how it can be used to extract features like lines from an image. It then provides details on the process, which involves edge detection using the Canny edge detector followed by the Hough transform. The Canny edge detector uses Gaussian and Sobel operators for noise reduction and edge detection. The Hough transform maps edge points to a parameter space where lines are represented as peaks, allowing line detection. Examples and applications are provided, such as building edge extraction, lane detection, and extracting shapes.