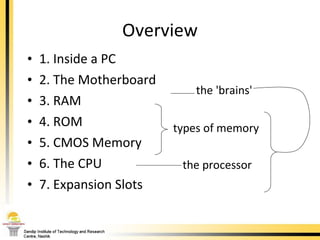
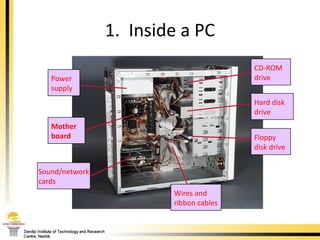
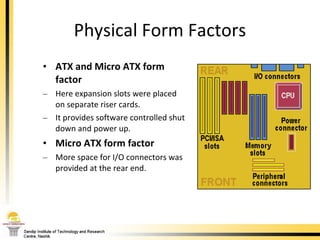
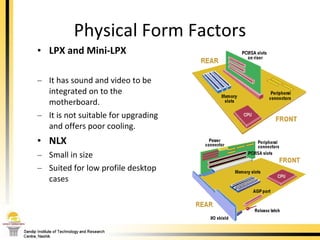
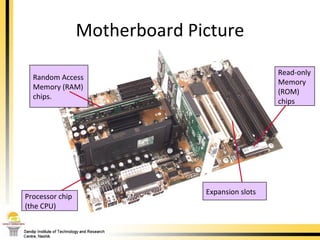
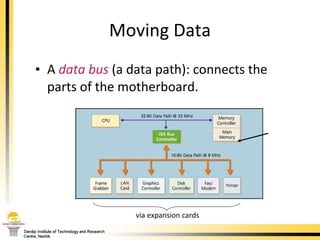
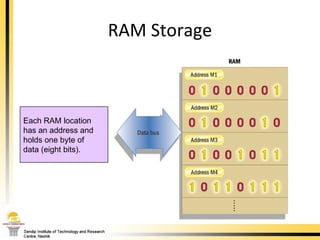
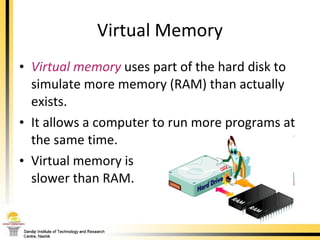
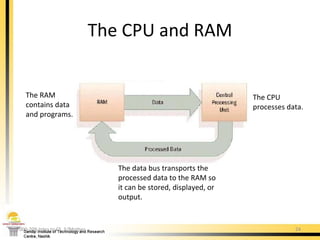
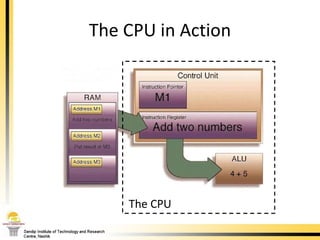
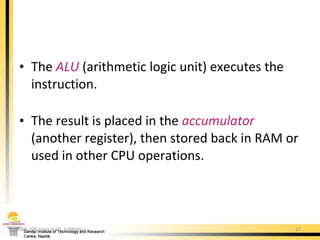
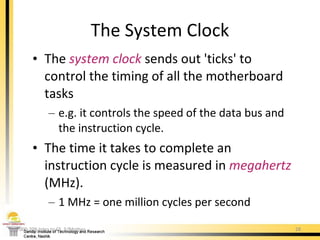
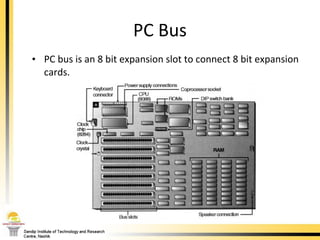
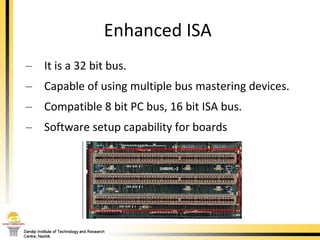
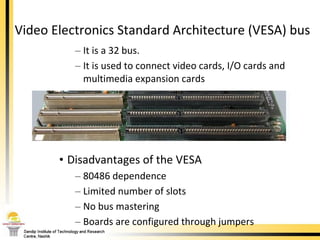
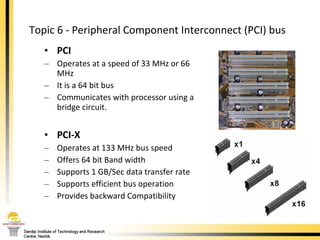
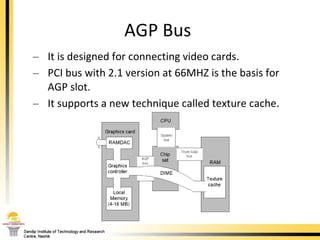
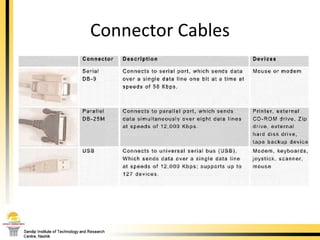
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the internal components of a PC, detailing the functions and characteristics of the motherboard, CPU, RAM, ROM, and CMOS memory. It explains memory types, data buses, expansion slots, and different form factors, along with their roles in connecting peripherals and handling data processing. Additionally, it outlines various expansion cards and bus technologies that enhance a PC's capabilities.