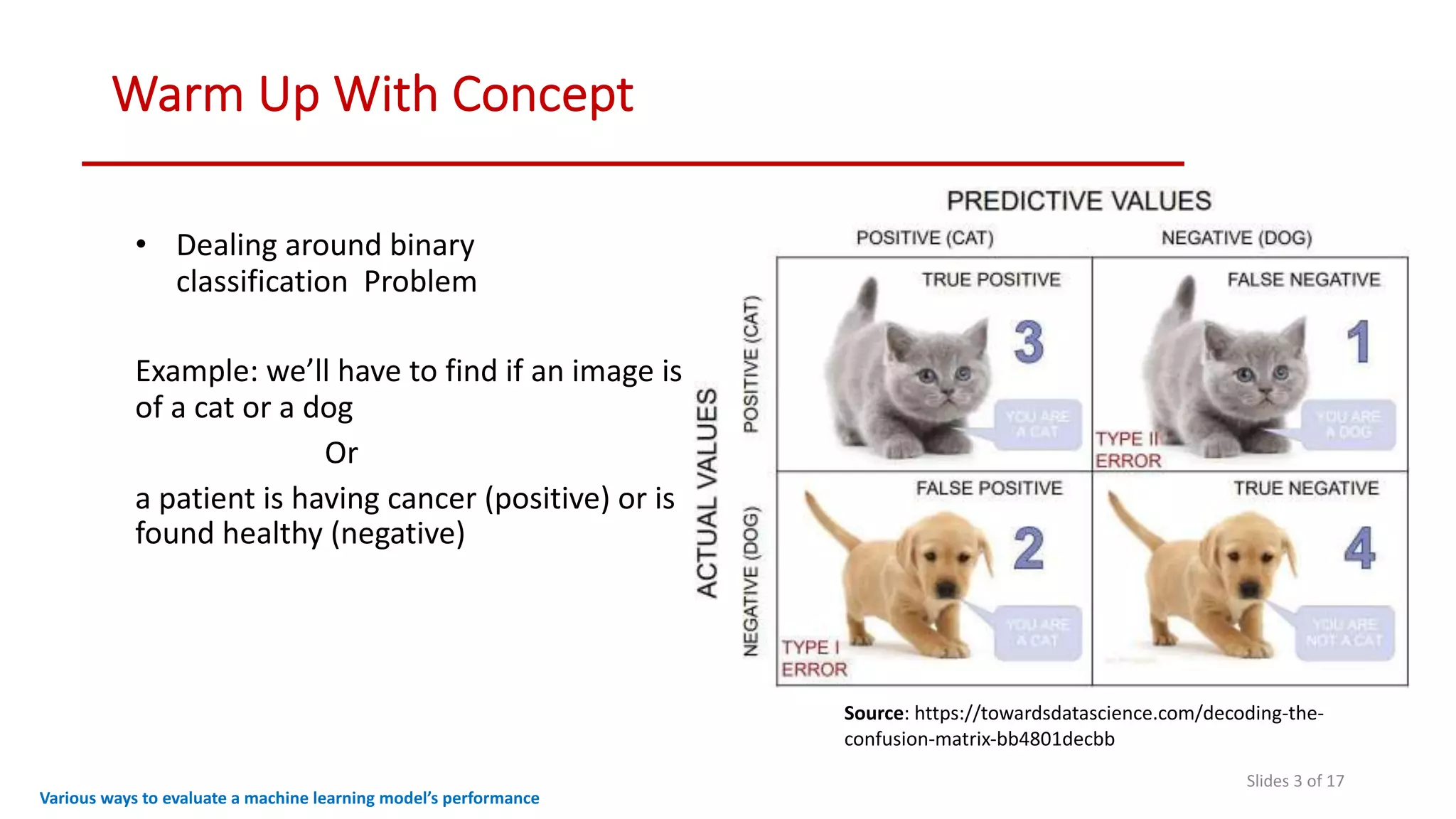
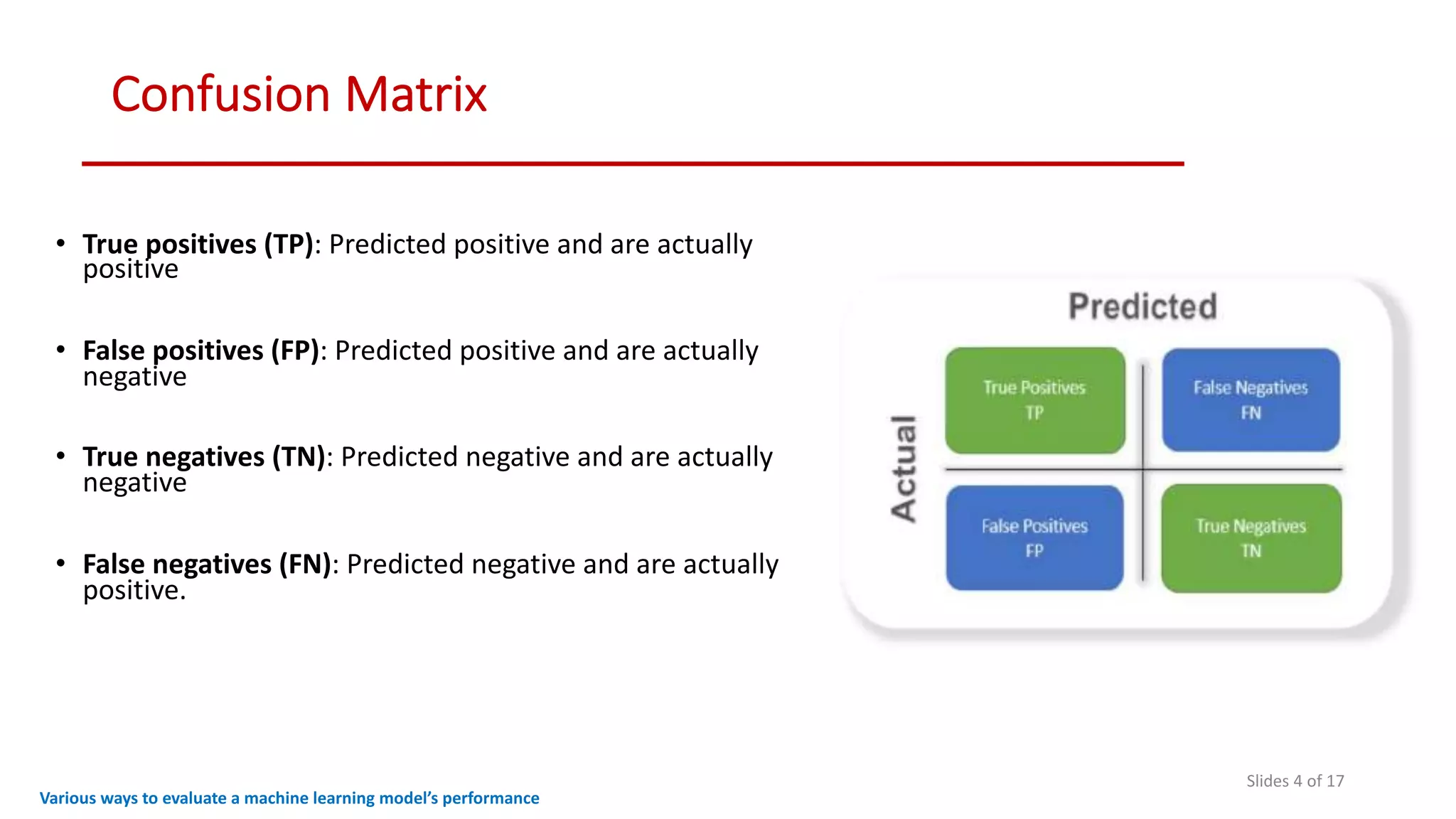
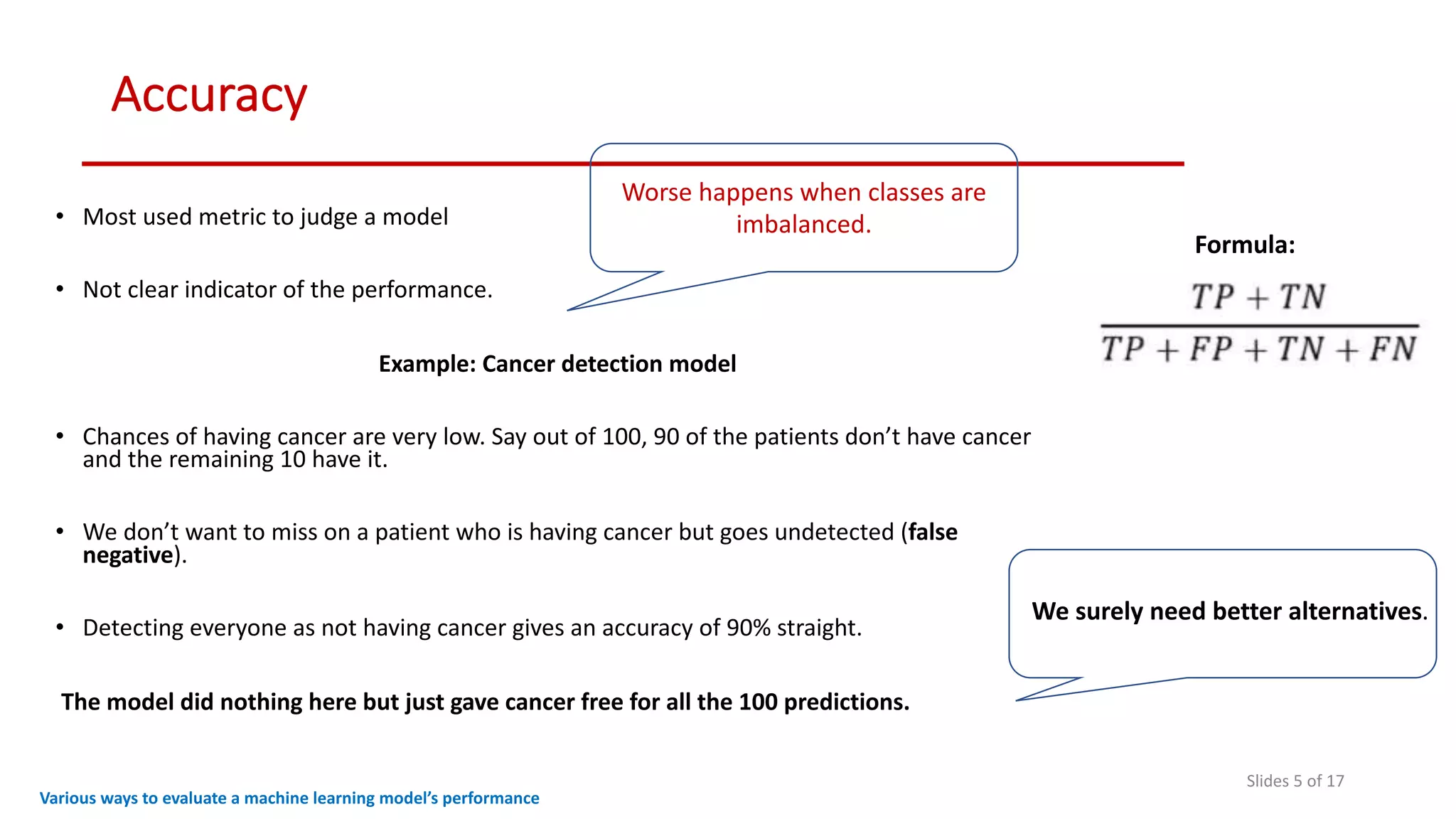
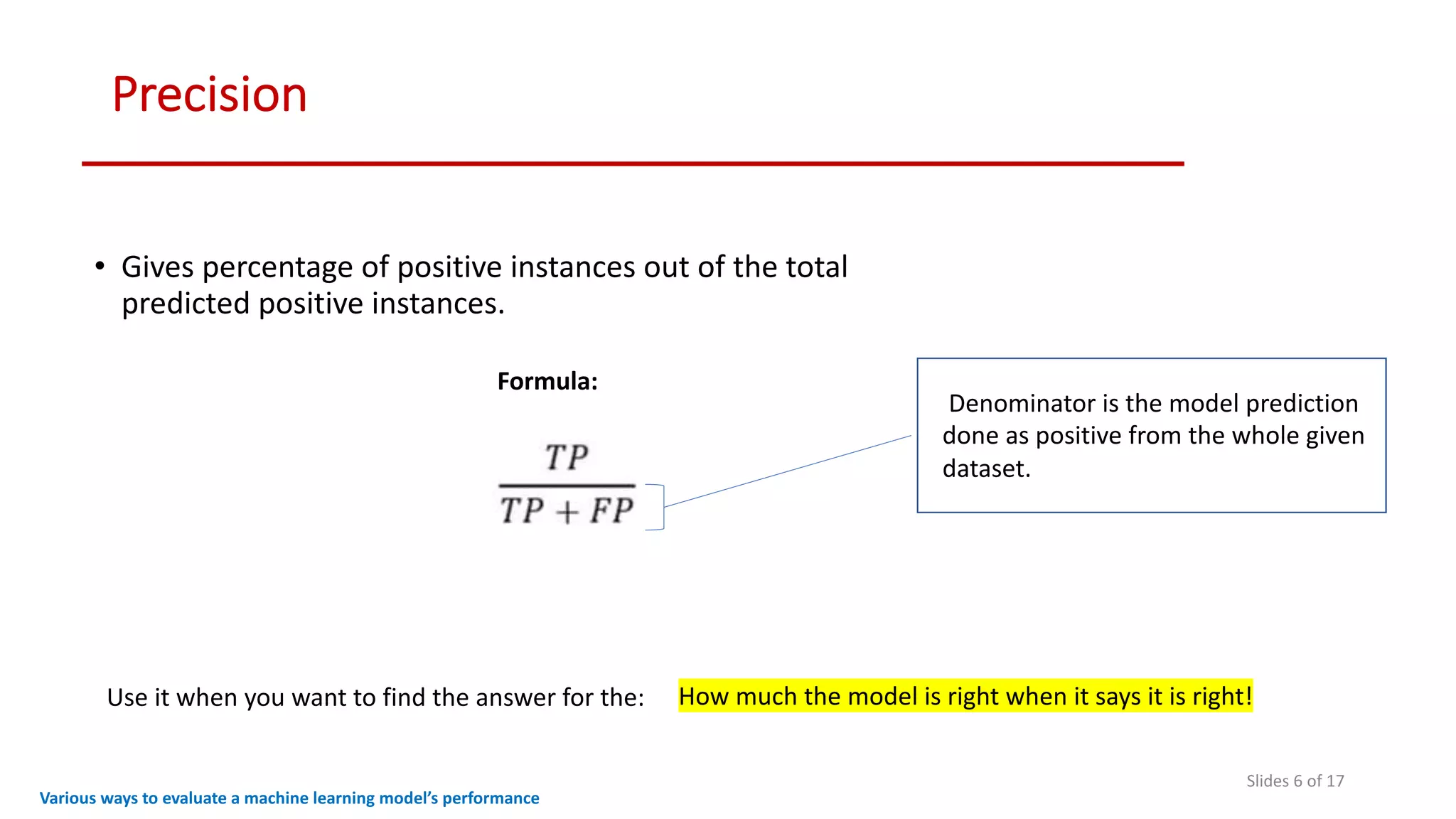
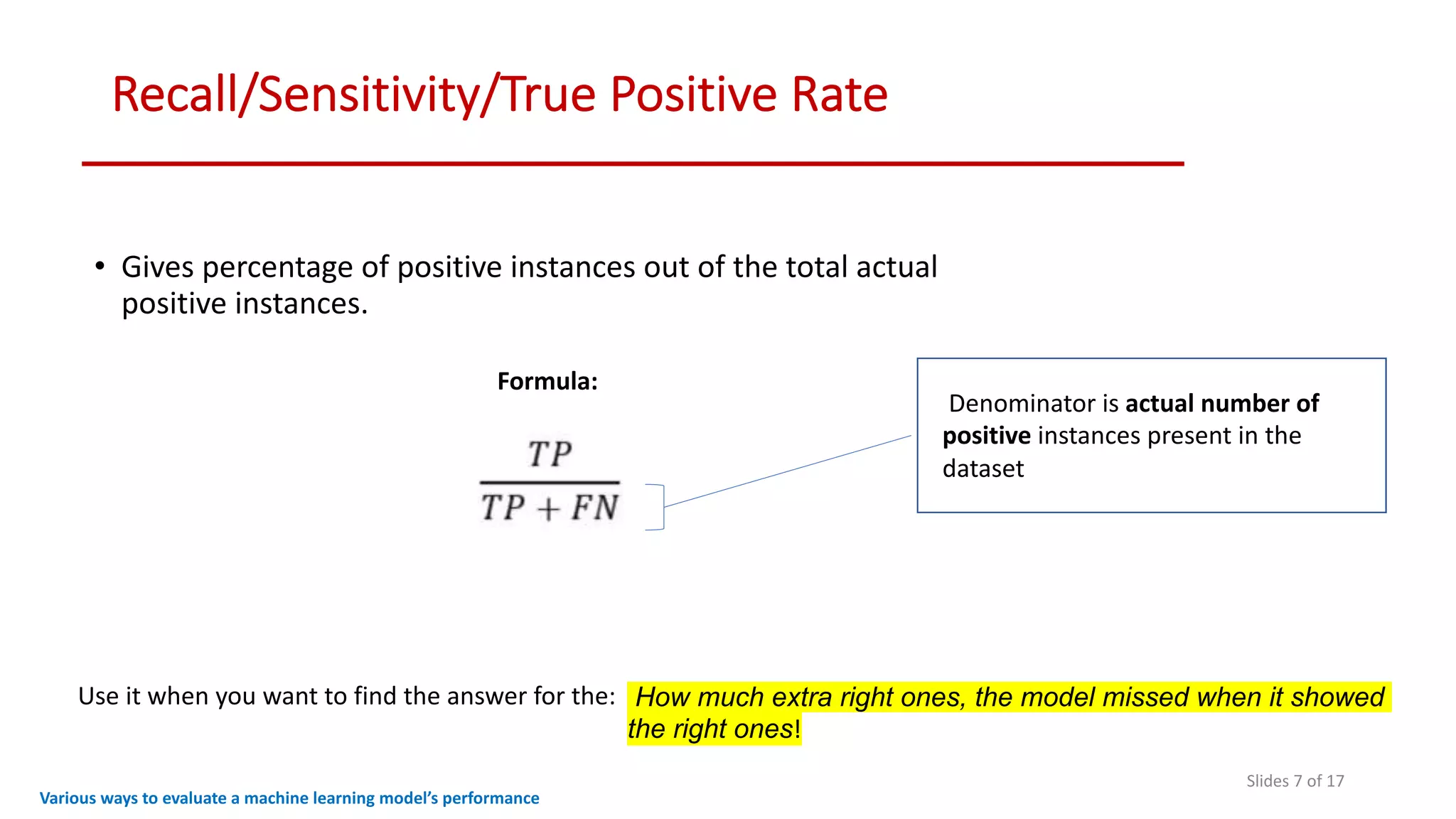
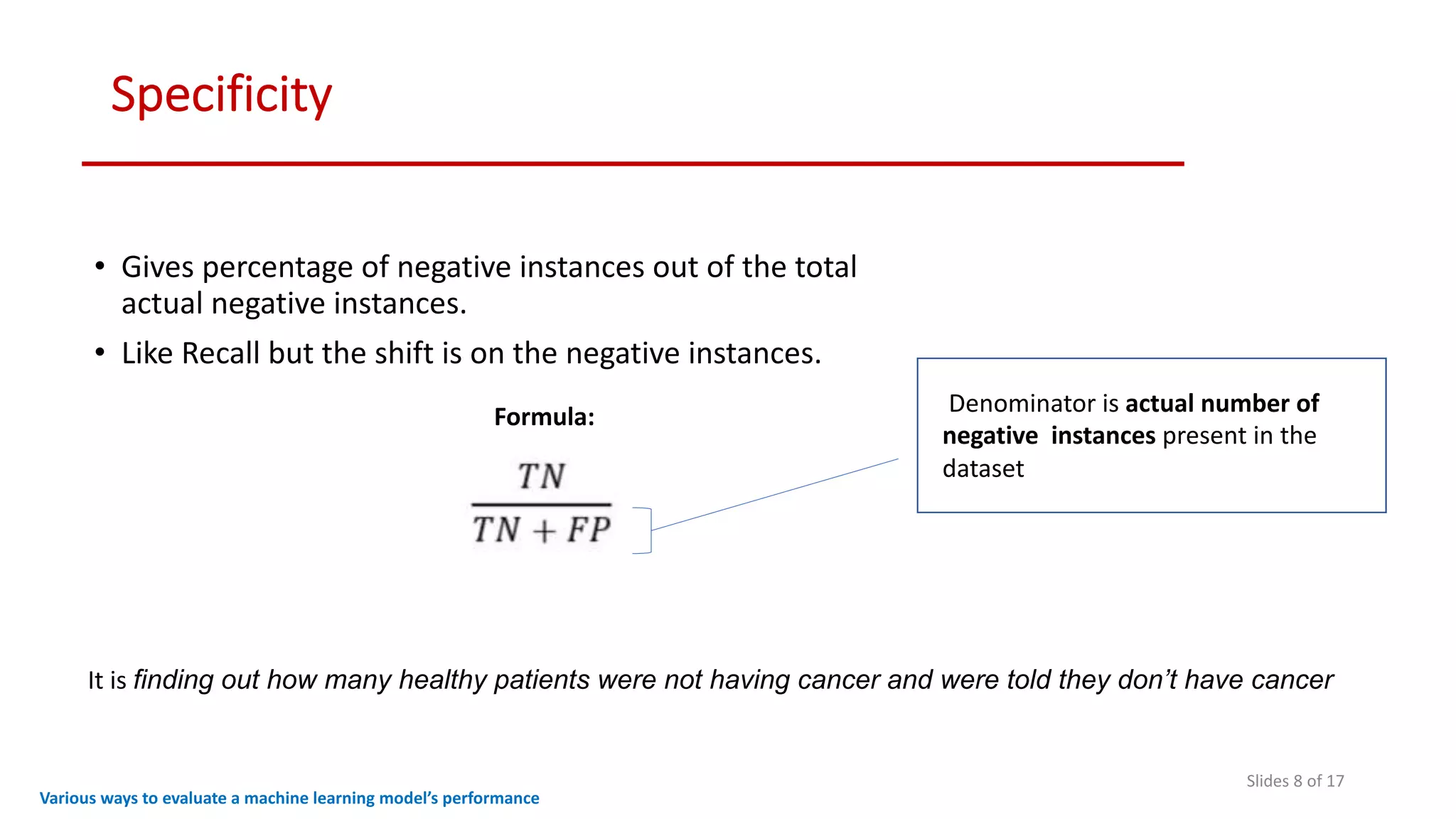
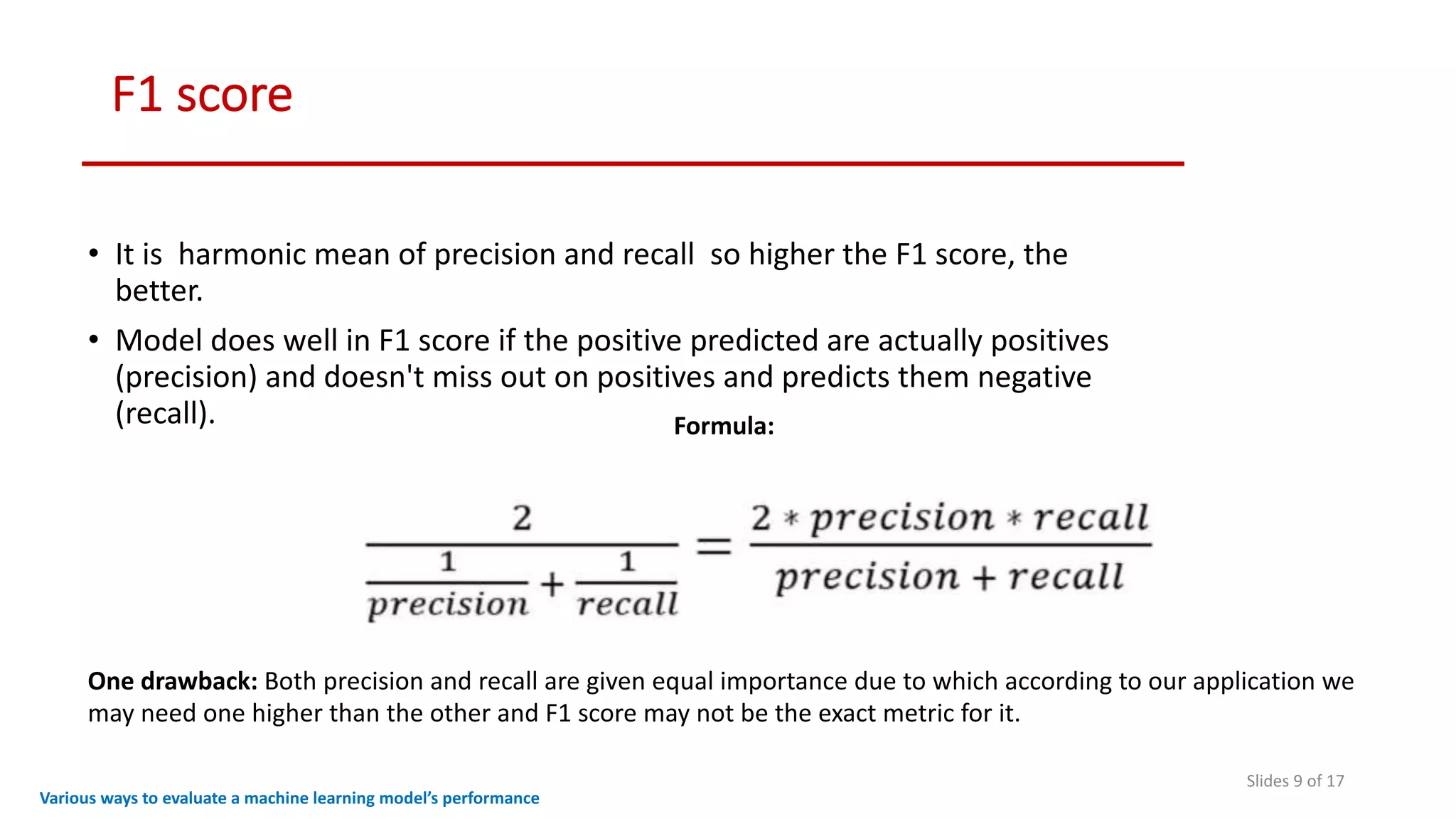
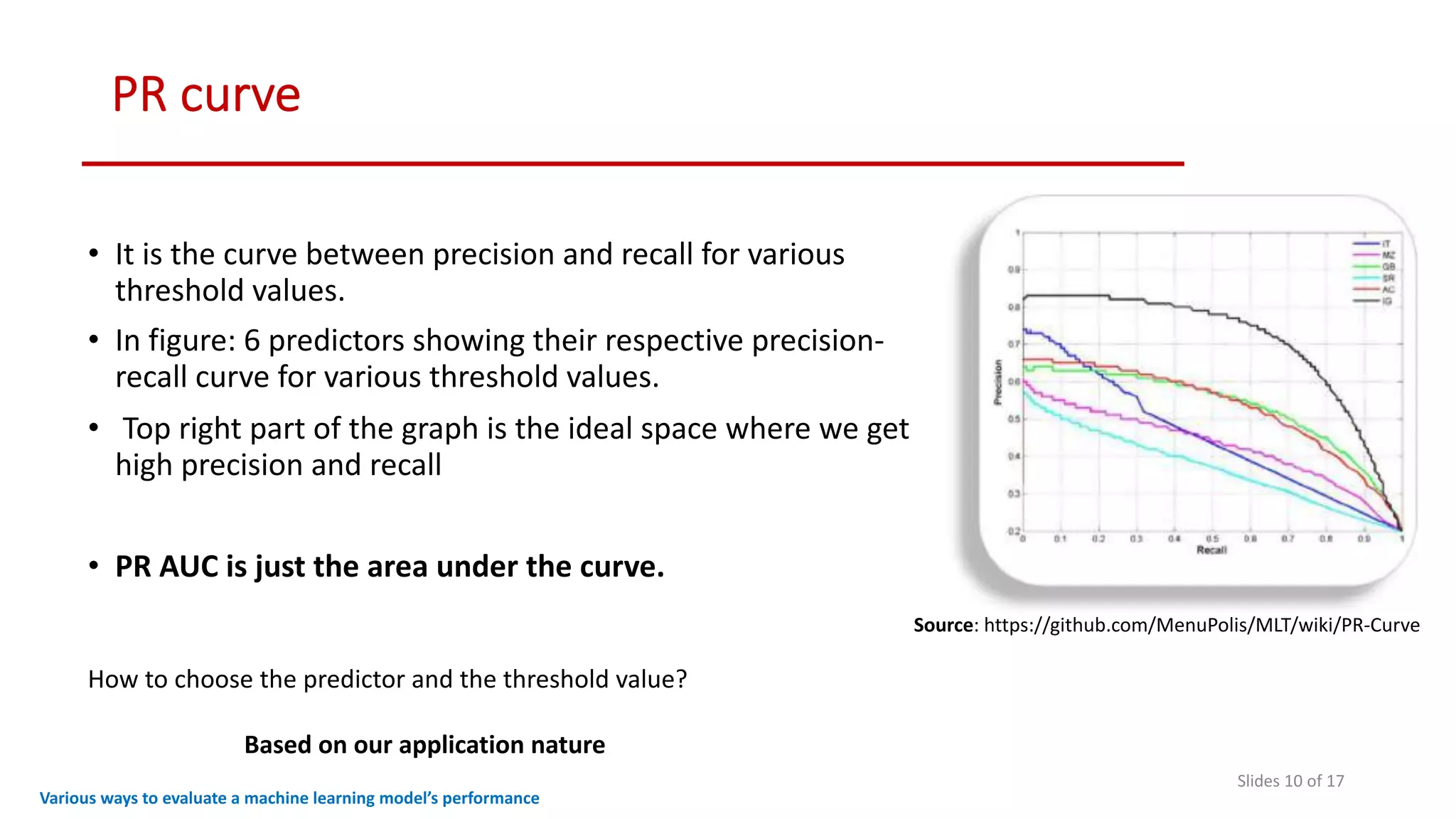
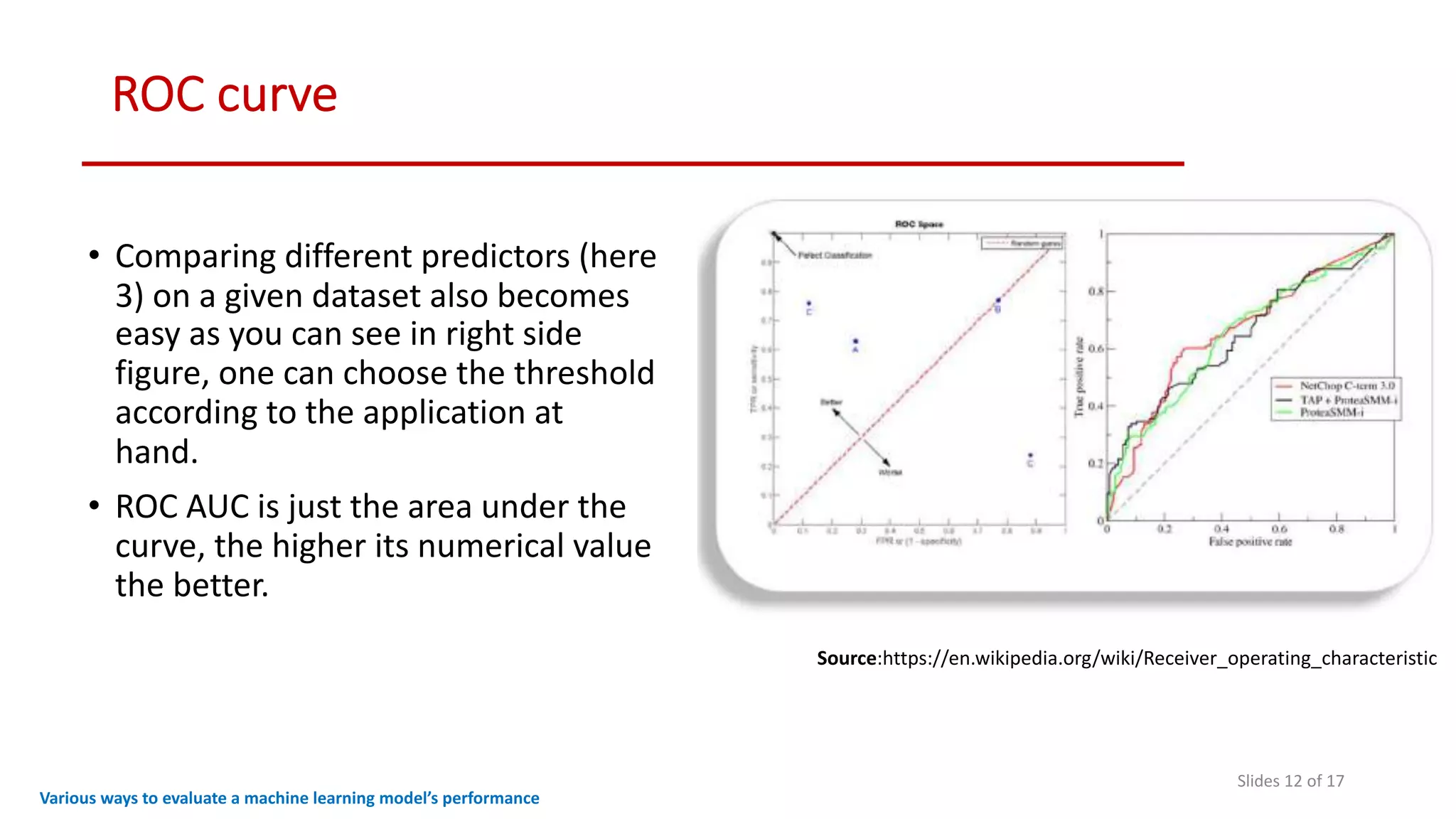
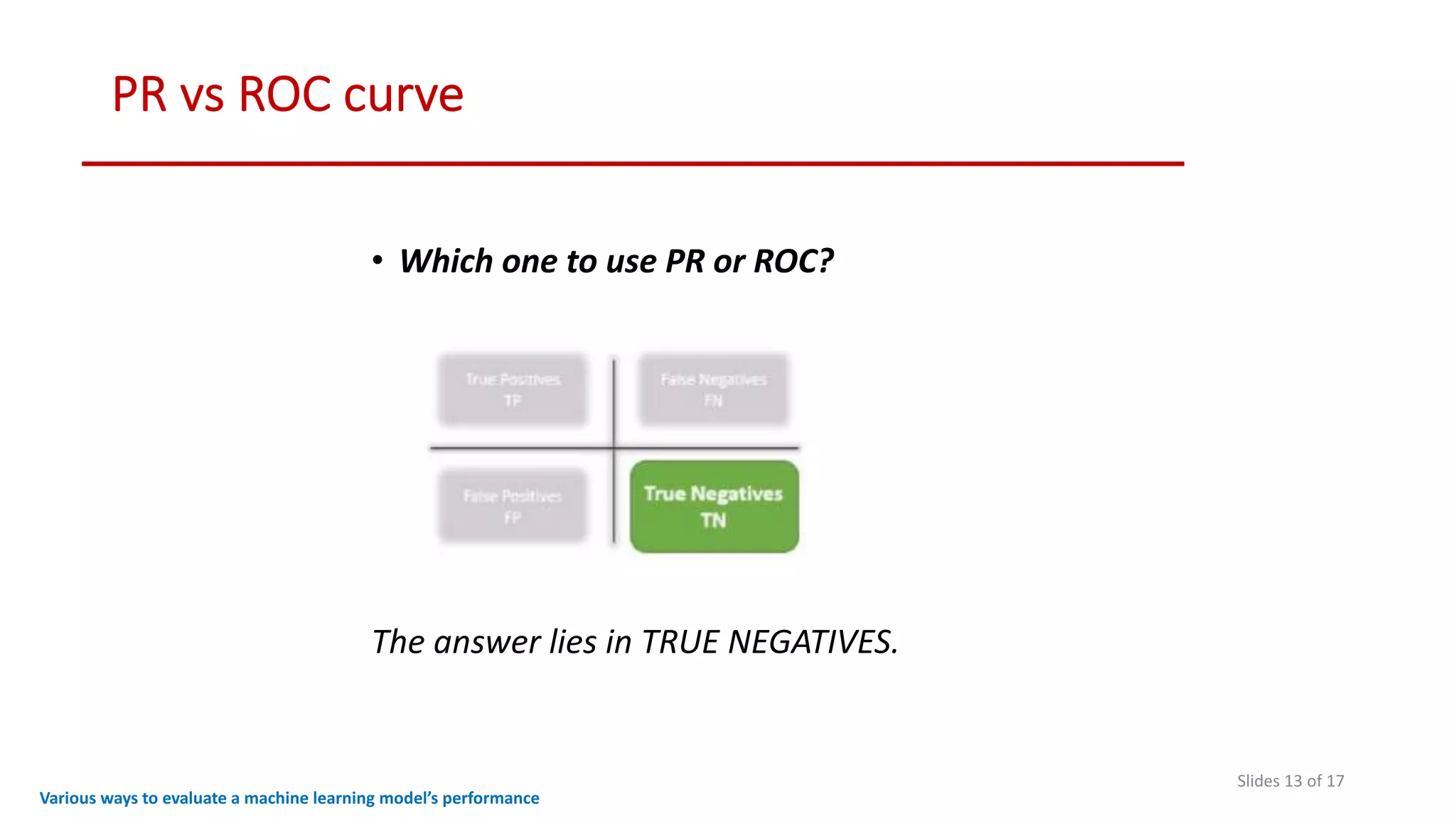
The document discusses various methods to evaluate the performance of machine learning models, particularly focusing on metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, specificity, F1 score, and the confusion matrix. It describes the importance of these metrics in the context of binary classification problems, such as cancer detection, and highlights the need for appropriate evaluation metrics depending on class balance and application requirements. Additionally, it compares precision-recall curves and ROC curves for assessing model performance in different scenarios.