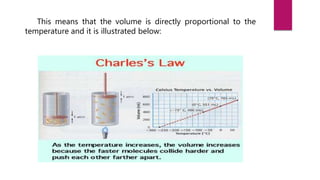
- Jacques Charles discovered Charles' law by observing that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant pressure while experimenting with hot air balloons.
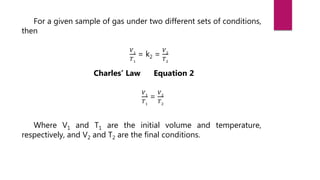
- Charles developed an equation to represent this relationship: V ∝ T, where V is volume and T is temperature. He found that as temperature increases, volume increases, and vice versa.
- Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use Charles' law equation to calculate the volume of a gas at a different temperature by keeping pressure constant.