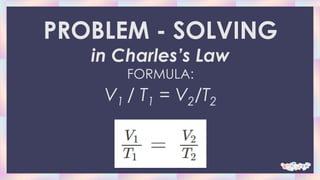
Charles's law describes how gases tend to expand when heated. It states that when the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and volume will be directly related. Specifically, if the temperature is increased, the volume will also increase in direct proportion. The document provides examples of problems applying Charles's law formula to calculate new volumes given changes in temperature. It also gives real-life examples of how Charles's law applies, such as how hot air balloons and deodorant bottles work based on gas expansion with temperature changes.