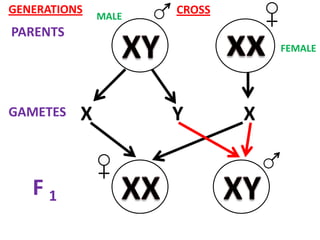
Chromosomal theory best explains human sex determination. Females are XX and produce X-bearing eggs, making them homogametic. Males are XY and produce both X- and Y-bearing sperm, making them heterogametic. The presence of a Y chromosome results in male development due to Y-linked genes, while its absence results in female development. Other factors like genetic balance and hormones can influence sex development but not determination.