Embed presentation
Downloaded 179 times







A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the genetic outcomes of a breeding experiment, named after Reginald C. Punnett. It allows biologists to determine the probability of offspring having specific genotypes, examining single or multiple traits. The process involves determining alleles from each parent and mapping them in a square to visualize potential genetic combinations.










Introduction to the Punnett Square diagram, its purpose in predicting genetic outcomes, and its namesake, Reginald C. Punnett.
Usage of the Punnett Square by biologists for determining offspring genotype probabilities from both single and multiple trait crosses.
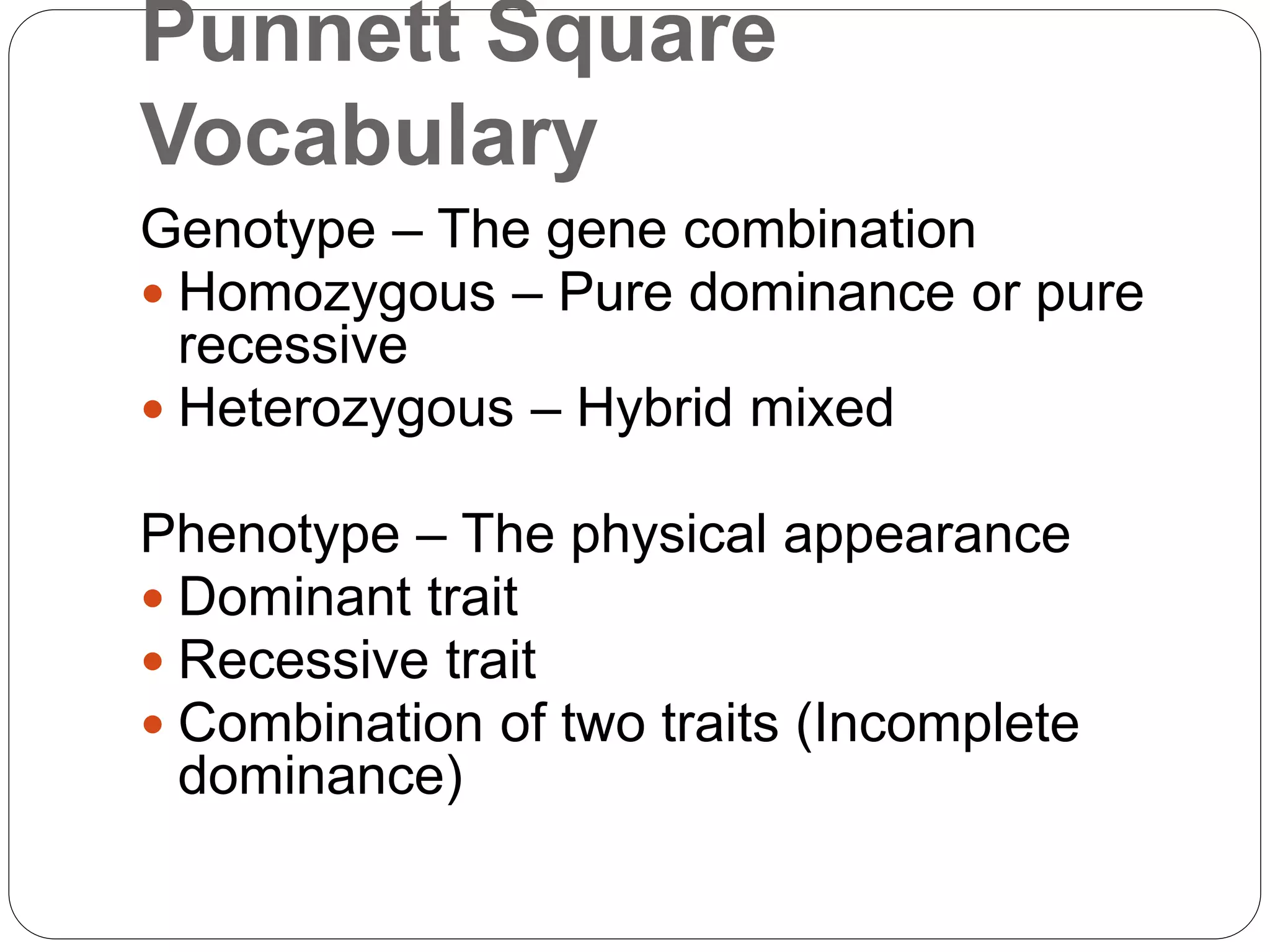
Key terms related to the Punnett Square such as dominant/recessive genes, genotypes, phenotypes, homozygous, and heterozygous.
Definition of a Monohybrid Cross involving crossing of two parents with contrasting traits for a single characteristic.
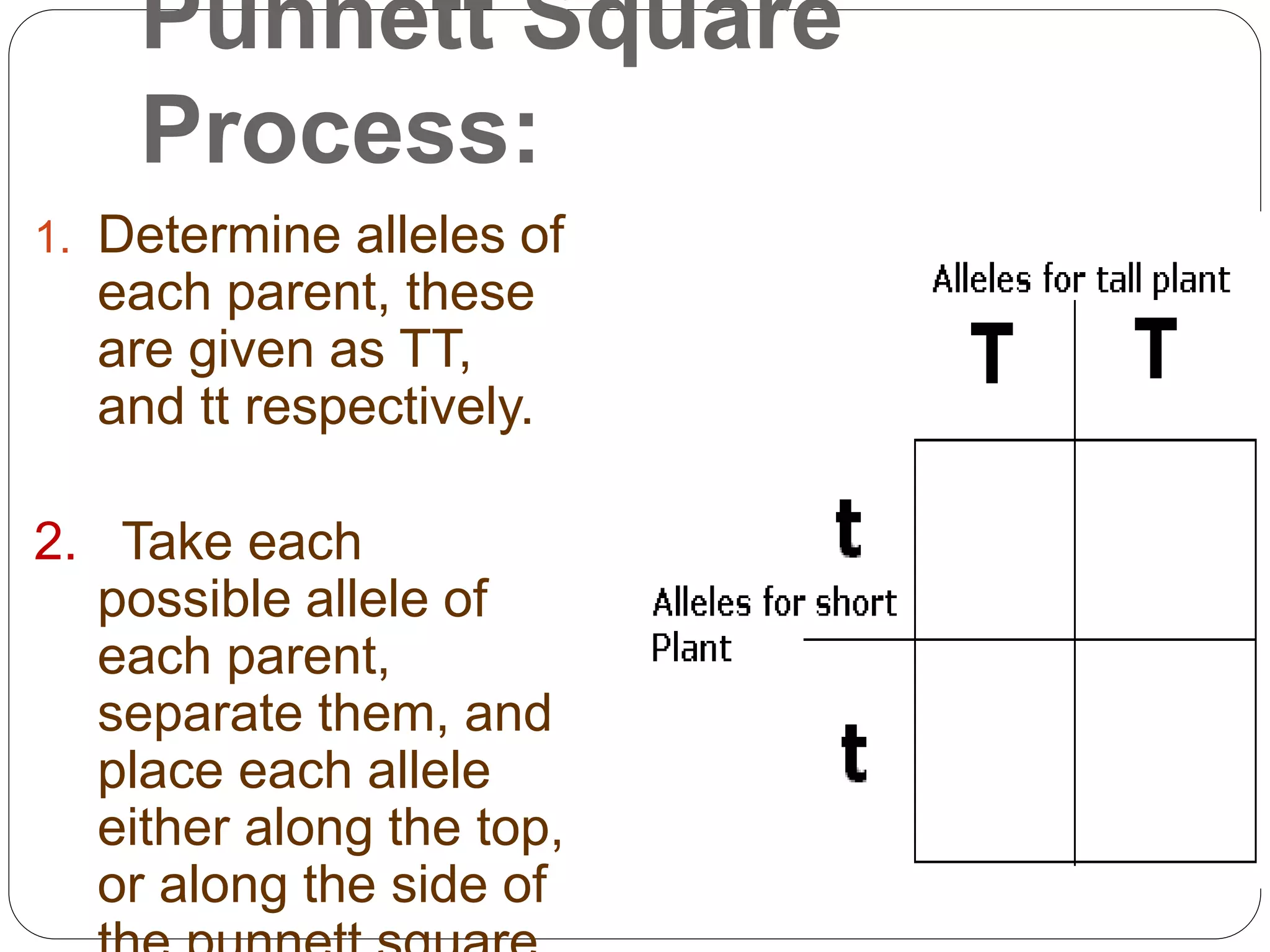
Steps in using a Punnett Square for a monohybrid cross; how to determine alleles and record genotypic outcomes.
Description of Dihybrid Cross involving two different independent alleles, with a process similar to that of a Monohybrid Cross.