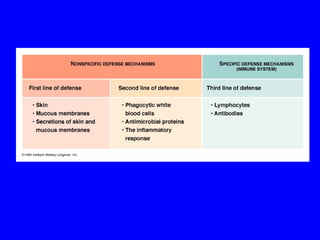
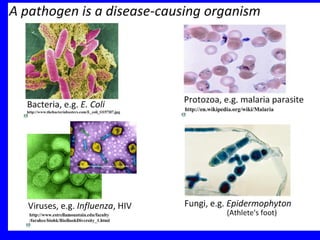
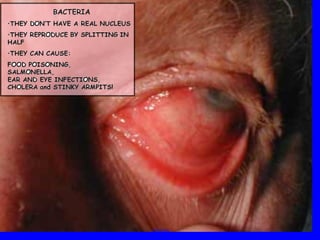
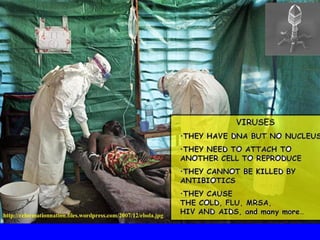
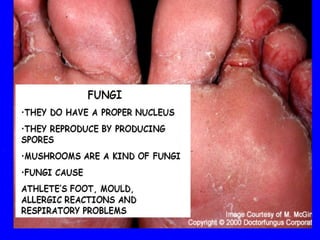
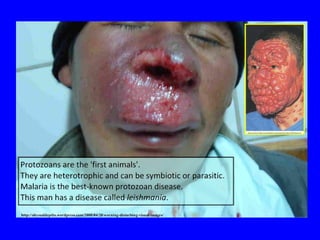
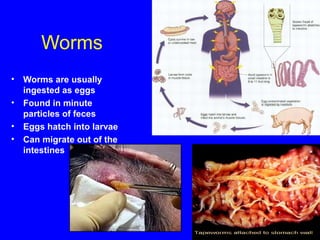
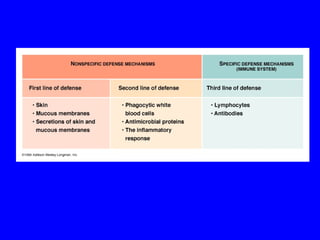
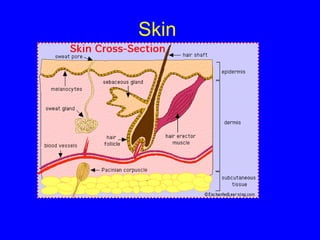
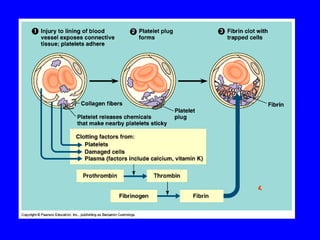
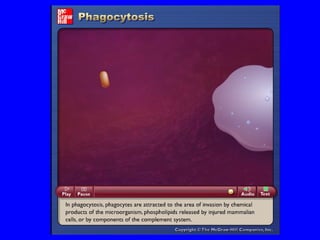
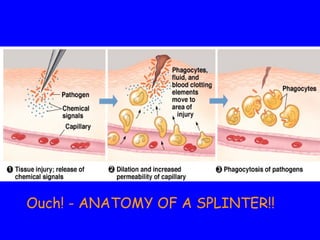
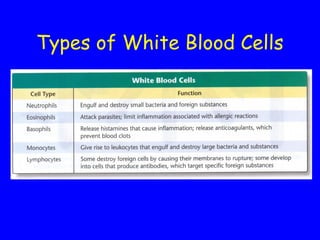
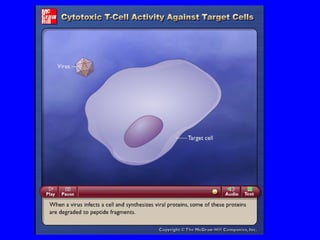
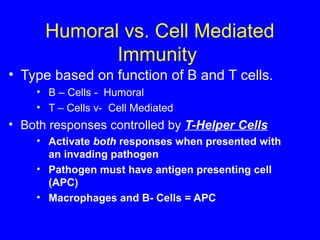
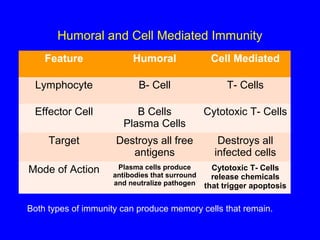
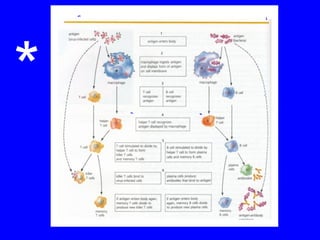
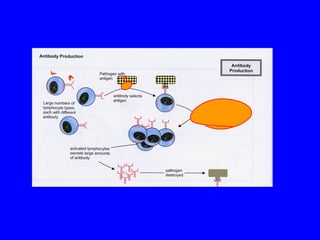
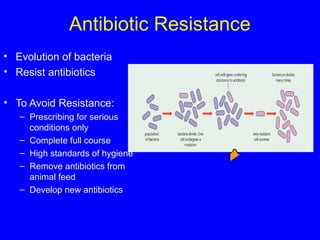
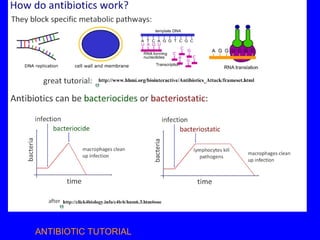
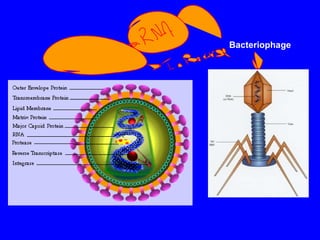
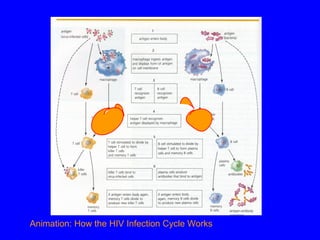
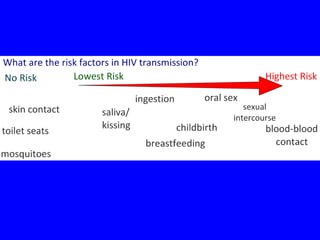
The human body has multiple lines of defense against pathogens. The skin and mucous membranes provide the first line of defense through physical and chemical barriers. The second line of defense involves white blood cells that attack and destroy invading pathogens. The third and most specific line of defense involves antibodies and lymphocytes (B and T cells) that provide long-lasting immunity. B cells produce antibodies to target free pathogens for destruction, while T cells target infected cells through cell-mediated immunity. Antibiotics can treat bacterial but not viral infections by targeting bacterial processes without harming human cells. HIV attacks and destroys helper T cells, weakening the immune system and leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections.