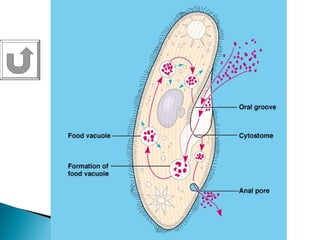
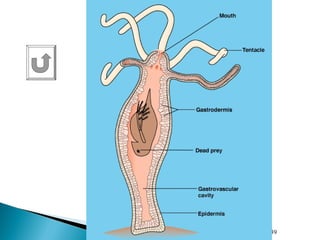
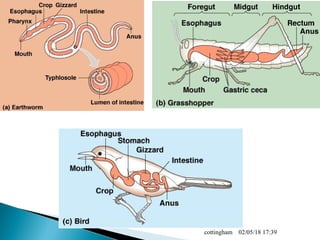
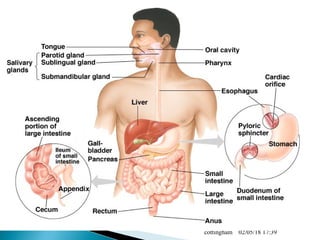
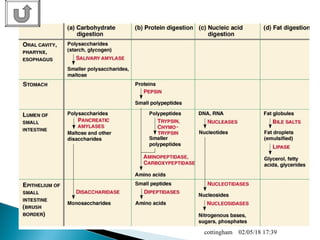
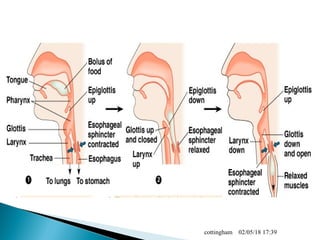
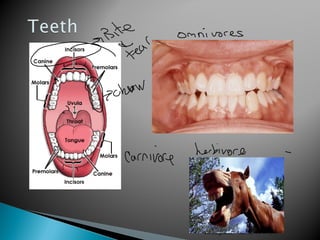
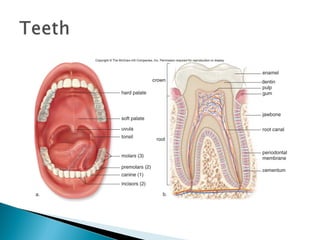
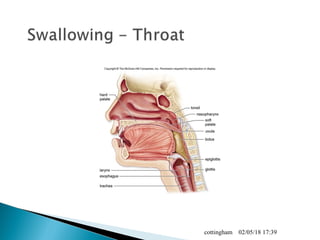
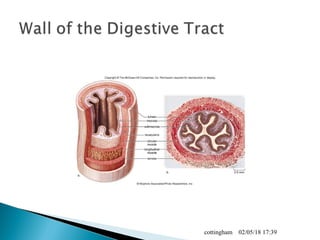
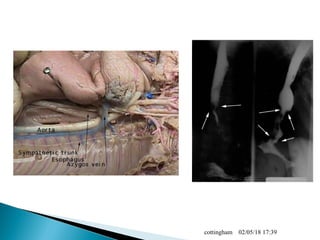
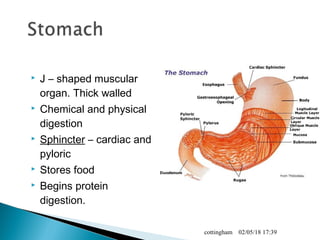
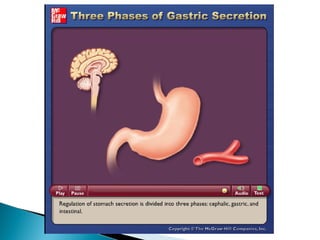
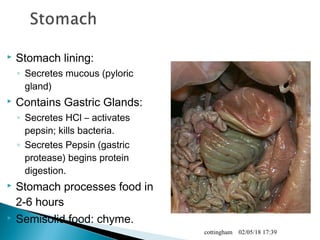
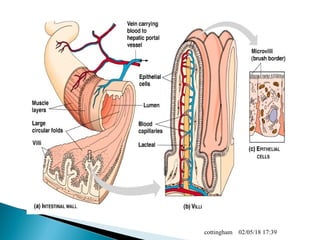
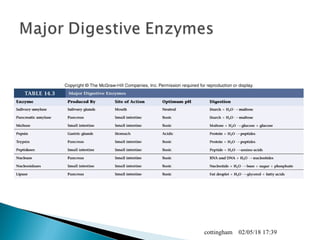
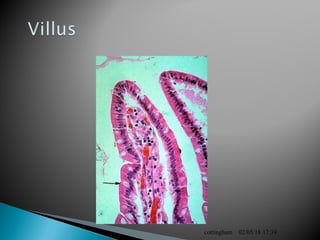
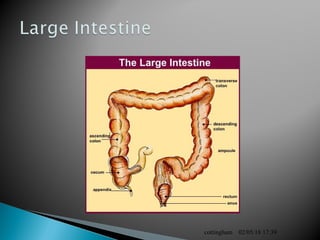
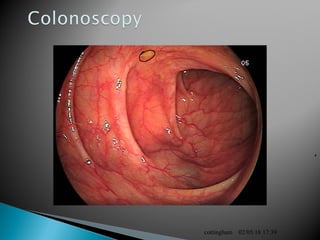
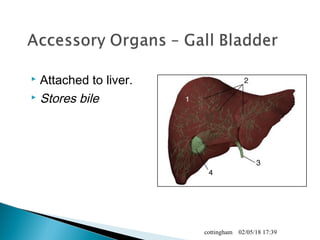
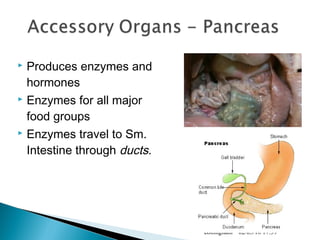
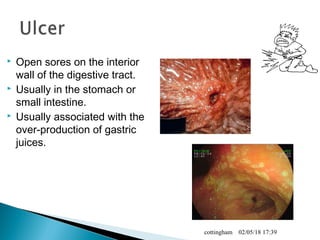
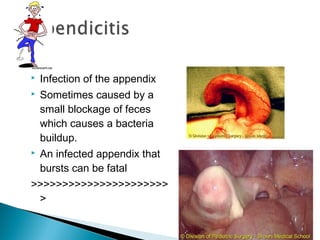
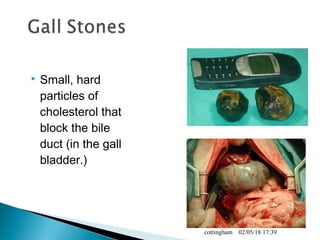
The document provides an overview of the human digestive system, including definitions of key terms like digestion, the organs of the digestive system and their functions, and examples of digestive disorders. It explains that digestion involves breaking down food into smaller molecules through mechanical and chemical processes. The major organs - mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine - work sequentially to ingest, break down, absorb and eliminate food and waste. Accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder and pancreas produce enzymes and substances that aid digestion.