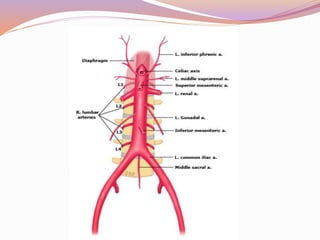
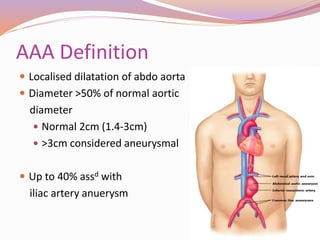
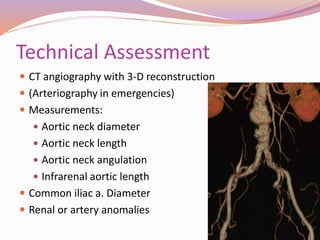
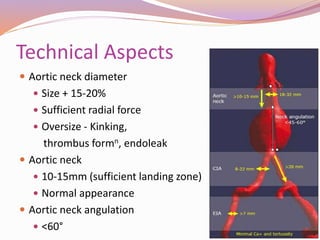
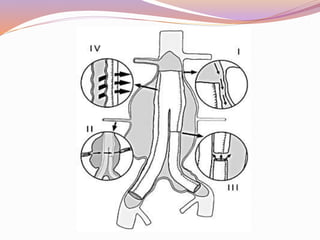
This document discusses abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) and their endovascular repair (EVAR). It defines AAAs as a dilatation of the abdominal aorta over 3cm in diameter. EVAR involves inserting a folded graft through the femoral artery which expands to exclude the aneurysm sac from blood flow and pressure. The benefits of EVAR over open repair include lower peri-operative mortality and complications. Proper patient assessment including vascular anatomy and medical comorbidities is important for determining candidacy for EVAR. The procedure involves deploying graft components in the aorta and iliac arteries under imaging guidance. Post-operative surveillance with imaging is needed to monitor for complications like endoleaks.