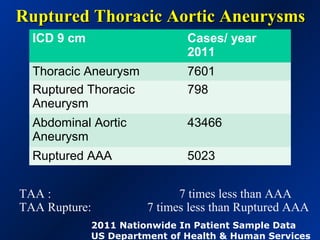
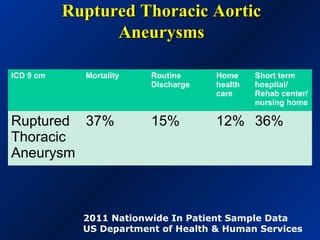
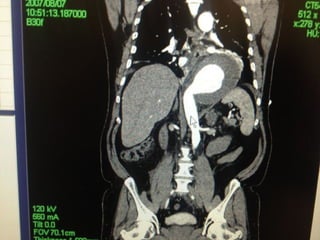
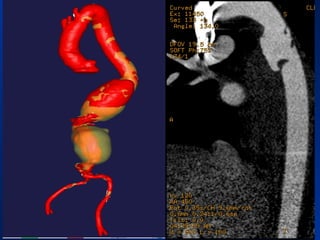
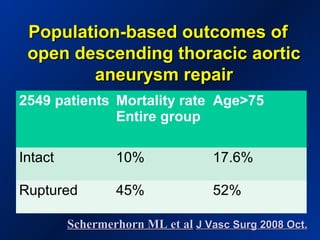
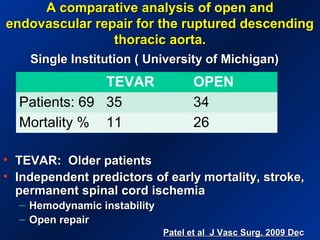
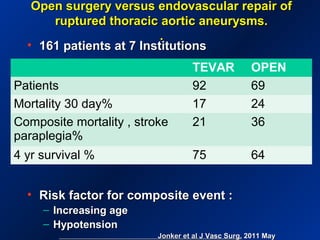
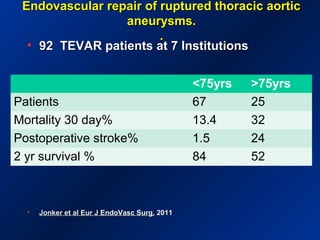
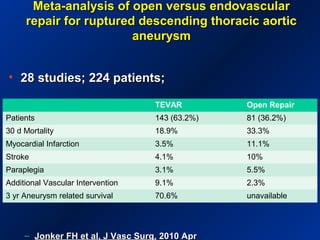
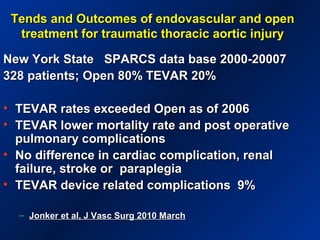
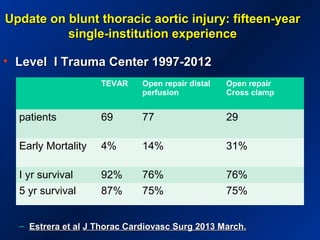
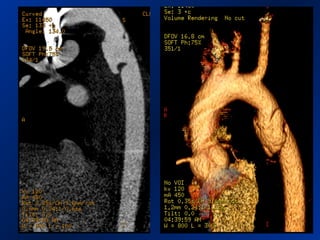
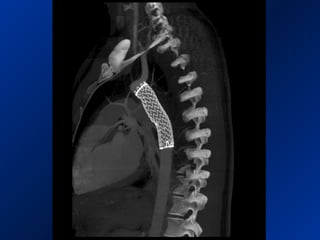
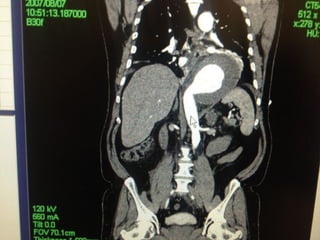
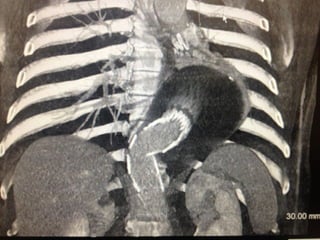
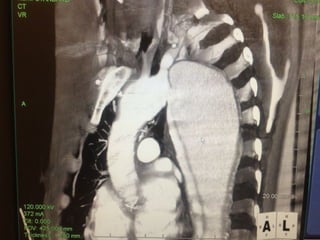
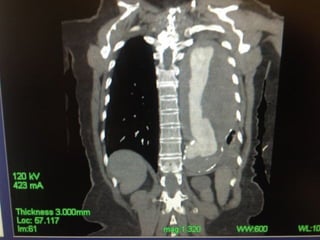
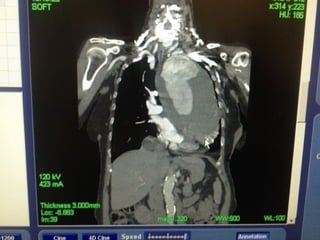
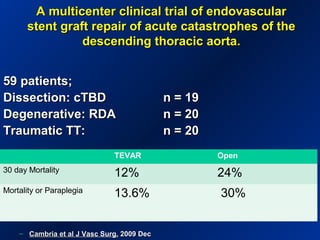
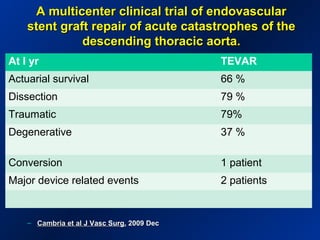
This document reviews endovascular repair (TEVAR) for ruptured thoracic aortic aneurysms. It provides data on the incidence, mortality rates, and management of ruptured thoracic aneurysms. Open surgical intervention has mortality rates of 18-27% while TEVAR has shown lower 30-day mortality rates of 11-17% in single-institution studies. However, TEVAR is associated with higher mortality risks in older patients (>75 years old) and those with hemodynamic instability. The document recommends TEVAR as a less invasive alternative to open surgery for ruptured thoracic aneurysms, particularly when performed at experienced centers.